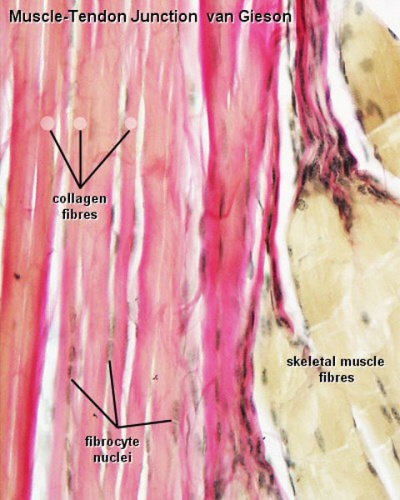
Types of Muscular Tissue
- Skeletal Muscle Tissue These muscles are attached to the skeleton and help in its movement. These muscles are also known as striated muscles because of the presence of alternate patterns of light and dark bands. ...
- Smooth Muscle Tissue These are non-striated, involuntary muscles controlled by the Autonomous Nervous System. ...
- Cardiac Muscle Tissue These are found only in the heart. ...
What are the 4 characteristics of muscle tissue?
- Excitability- can be stimulated by chemical signals, nerves and stretch.
- Conductivity- the signal for a muscle to contract is spread from the point of stimulation throughout the entire muscle.
- Contractility- ability of the muscle to shorten.
- Extensibility-
- Elasticity-
What are the three types of muscles and their functions?
What are the 3 types of skeletal muscle?
- Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscle, attached to bones, is responsible for skeletal movements.
- Smooth Muscle.
- Cardiac Muscle.
What are the three muscle types?
The Three Types of Muscles in Human Body
- The Common Factors. ...
- Get to Know Skeletal Muscle. ...
- Skeletal Muscular System and Movement. ...
- Skeletal Muscle Structure. ...
- Voluntary and Involuntary Muscle Movement. ...
- Brush Up on Cardiac Muscle. ...
- Sort Out Smooth Muscle. ...
- Examples of Muscle Types. ...
What are the three types of muscle cells?
What are the parts of muscular system and their functions?
- Skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles are the only muscles that can be consciously controlled. …
- Smooth muscle. Smooth muscle lines the inside of blood vessels and organs, such as the stomach, and is also known as visceral muscle. …
- Cardiac muscle.
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue and their functions?
The three main types of muscle include:Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. ... Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. ... Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
What are the 3 types of muscle tissues?
In the body, there are three types of muscle: skeletal (striated), smooth, and cardiac.Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscle, attached to bones, is responsible for skeletal movements. ... Smooth Muscle. ... Cardiac Muscle.
What are the 4 main types of muscles?
They are:Skeletal: As part of the musculoskeletal system, these muscles work with your bones, tendons and ligaments. Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones all over your body. ... Cardiac: These muscles line the heart walls. ... Smooth: These muscles line the insides of organs such as the bladder, stomach and intestines.
What are the different types of muscle tissue quizlet?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
What are the 6 major types of muscles?
6.3: Types of Muscle TissueWork Those Eye Muscles!What is Muscle Tissue?Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Skeletal Muscle Pairs. Skeletal Muscle Structure. Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Fibers.Smooth Muscle. Structure of Smooth Muscle. Functions of Smooth Muscle.Cardiac Muscle. Feature: Human Body in the News.
What are muscle tissues?
Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. The tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels.
What are the 4 main characteristics of muscle tissue?
All muscle tissues have 4 characteristics in common:excitability.contractility.extensibility - they can be stretched.elasticity - they return to normal length after stretching.
What are the 5 characteristics of muscle tissue?
All muscle cells share several properties: contractility, excitability, extensibility, and elasticity: Contractility is the ability of muscle cells to forcefully shorten.
What are the 3 components of a muscle?
In the muscular system, muscle tissue is categorized into three distinct types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role. Skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures.
How many basic types of muscle tissue are there?
3 typesThe 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striped (striated), and are under involuntary control.
What are the three types of muscle tissue and how do they differ?
Skeletal muscle tissue is found in the skeletal muscles of the human body. The control over them is completely voluntary. Smooth muscle cells are found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels, they are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Cardiac tissue is present in the heart muscle.
What are the three types of muscle tissue What are their functions quizlet?
Terms in this set (3)Skeletal Muscle. Under voluntary control, contracts to pull on bones. NEED TO KNOW THIS.... ... Cardiac Muscle. Under involuntary control, found only in heart, pumps blood. ... Smooth Muscle. Under Involuntary muscle, found in walls of hallow organs such as stomach, uterus, and blood vessels.
What is the most common type of muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle tissueSkeletal muscle tissue is the most common type of muscle tissue in the human body. By weight, an average adult male is about 42 percent skeletal muscles, and the average adult female is about 36 percent skeletal muscles.
What are the characteristics of the three muscle tissues?
Skeletal muscle is voluntary and striated, cardiac muscle is involuntary and straited and smooth muscle is involuntary and non-striated.
What are the 3 tissue types in the heart?
The wall of the heart separates into the following layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. These three layers of the heart are embryologically equivalent to the three layers of blood vessels: tunica adventitia, tunica media, and tunica intima, respectively.
What is the difference between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle?
Smooth muscles are not under conscious control while skeletal muscles are under conscious control. 4. Smooth muscles can be found within the walls of the internal organs like the stomach and the uterus while skeletal muscles are found in the biceps of the arm, the chest, and other muscles that can be moved.
What are some examples of smooth muscles?
Smooth muscle occurs in multiple locations throughout the body. It is found in the lining of the digestive organs, the walls of vessels, the walls...
What is cardiac muscle tissue?
Cardiac muscle tissue composes the muscular walls of the heart. It is striated and contains intercalated discs. The individual cells contain a sing...
Where are smooth muscles found in the body?
Smooth muscles are found in the digestive system, the reproductive system, the renal system, and throughout the vessels of the circulatory system....
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue and their functions?
Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and results in the beating of the heart. Smooth muscle is found in many organs throughout the body and control...
What are the different types of muscle fibres?
The muscle fibres vary in size, shape, and arrangement, from being small, broad, and parallel to being large, narrow, and oblique. 7
What are the two types of skeletal muscle?
There are two types of skeletal muscle found within the human body: type 1 ( slow-twitch fibres) and type 2 ( fast-twitch fibres ). 9. Slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibres differ in their colour, diameter, myoglobin content, speed of contraction, degree of force produced, degree of fatiguability, primary energy reserve, and primary storage fuel used.
How do muscle fibres get ATP?
These fibres receive ATP primarily through glycolysis with creatinine phosphate and glycogen being the primary energy source. This muscle fibre type is typically utilised for the shorter duration anaerobic activity. 9
What is the law of contraction of skeletal myocytes?
The contraction of skeletal myocytes follows the ‘ all or none law ‘ which states that for any given nerve impulse that reaches the threshold of activation of a muscle fibre, the response will always be the same irrespective of the strength of impulse that reaches the fibre.
Where are cardiac muscle cells located?
Cardiac muscle cells ( cardiomyocytes ) are specialised cells only found in the myocardium. Cardiac myocytes are rectangular cells with one to two central nuclei arranged in an extensive branching organisation among its fibres (Figure 4). 16.
What is the outermost layer of muscle?
The outermost part of the muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath termed epimysium. Around each bundle of muscle fibres lies the perimysium (a.k.a. fascia) and surrounding each muscle fibre lies the endomysium. 6.
What are the functional units of muscle?
The functional units of a muscle are termed myocytes, multi-nucleated cells that make up the muscle tissue. 4. There are three main categories of muscle tissue found within the human body: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Each type has unique histological features, enabling the muscle to carry out its specific functions. 5.
What is muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue consists of fibers of muscle cells connected together in sheets and fibers. Together these sheets and fibers and known as muscles, and control the movements of an organisms as well as many other contractile functions. There are three different types of muscle found in animals, depending on their use.
What is the function of muscle tissue?
Function of Muscle Tissue. Muscle tissue functions as a single unit, and is often connected to the same nerve bundles. A nerve impulse traveling from the brain or another outside signal tells the muscle to contract. The nerve impulse is transferred almost instantaneously to all the nerve cells in the muscle tissue, and the entire muscle contracts.
Why does muscle feel hard when flexed?
They are necessary for supporting the body and organs. Muscle only seems hard when flexed because the cells are being packed much closer together. The pressure on the cells and the tension in the fibers create the sense that the tissue is rigid, but it is not. 3. Dr.
What is a sarcomere?
This can be seen in image (a) below. These tiny light and dark bands are sarcomeres, highly organized bundles of actin, myosin, and associated proteins.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is found surrounding many organs, blood vessels, and other vessels used for transporting fluids. The smooth muscle can contract to apply a force on organ. This can be used to move blood or food throughout their respective systems.
Does smooth muscle have striations?
Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue has no striations. The fibers of myosin and actin in smooth muscle fiber is not nearly as organized as in the other types of muscle tissue. In smooth muscle, the contractions are not quick and rapid but rather smooth and continuous. Smooth muscle is found surrounding many organs, blood ...
Is skeletal muscle branching or parallel?
While the striations in skeletal muscle tissue are even and parallel, complex and branching striations are seen in cardiac muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle can be seen in image (c) below. While the striations are hard to see in this image, the branching nature of the cells is easy to pick out. The branching is caused by the connection ...
How many types of muscle tissue are there?
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body:
What is muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue is a specialized contractile tissue in the body. When stimulated by an action potential (or electrical stimulating signal), muscle fibers contract and shorten. All movements in the body are cause by muscular contraction; thus, life would not be possible without muscle tissue.
What is the most common muscle in the body?
Skeletal muscle is the most common muscle in the body. Skeletal muscle is voluntary muscle (controlled when an individual chooses to use them) via somatic neurons and is responsible for supporting the skeleton and movement of the body. This muscle tissue allows for walking, running, sitting, and raising the arm among many other movements. The cells in muscle tissue are long and large in diameter compared to the cells in cardiac and smooth muscle tissue. This is because the contractions in skeletal muscle are stronger, and the strength of a contraction is proportional to the cross section of a muscle fiber.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle characteristics are very different than skeletal and cardiac muscle types. Smooth muscle (also called visceral muscle) gets its name from the smooth appearance it has under a microscope. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue, the actin and myosin filaments of smooth muscle tissue are not as well organized and pronounced. Thus, it has no apparent striation. Smooth muscle also appears more "messy." The muscle cells are not organized in straight lines or branching patterns but instead appear wispy and spindled. Each smooth muscle cell contains a single nucleus. Examine the example of smooth muscle tissue below.
How do muscles contract?
Muscles contract when they are stimulated by an action potential. An electric signal travels down a neuron to an effector muscle that receives the signal. The electrical stimulation causes a change in membrane potential for a muscle fiber, and the fiber contracts as the gradient returns to its resting state. Troponin and calmodulin help these contractions in skeletal and cardiac muscle by binding to calcium. This allows actin heads to bind to myosin filaments. When theses fibers connect, they pull, and the muscle fiber shortens. This is a brief overview of muscle contractions. The processes by which muscles contract are very complex beyond the scope of this lesson.
Which muscle tissue is ideal for continuous contractions like those found in the digestive system?
Unitary smooth muscle tissue: Unitary smooth muscle tissue is ideal for continuous contractions like those found in the digestive system.
Where is the cardiac muscle found?
Cardiac muscle tissue is found in the heart, has a striated appearance, and contains intercalated discs which increase the spread of an electrical stimulation. Cardiac muscle tissue contracts continuously and does not fatigue. It is also involuntary tissue and thus is not controlled by conscious thought. The contraction speed of cardiac muscle is controlled by pacemaker and Purkinje cells.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue can be of three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is attached directly or indirectly to the bone and facilitates movement and/or gives support to the body. From an economic standpoint, skeletal muscle is the most important and it is the major component of the carcass. Cardiac, as the name implies, is the muscle ...
What is a muscle made of?
A single muscle is made up of many “bundles” (or fasciculi) of muscle cells or fibers held together by connect ive tissue (perimysium). The size of the bundles varies in different muscles in the same animal and in different species. When the fiber bundles are small, the meat has a fine grain.
What is the difference between skeletal muscle and connective tissue?
Skeletal muscles differ in length, in depth and in thickness. Each muscle is interspersed with connective tissue and fat and is surrounded by connective tissue (called the epimysium or muscle sheath) which may vary in thickness over different parts of the muscle.
How big are muscle fibers?
Muscle fibers vary greatly in length and have an average diameter of about 0.0002 inch. Muscles that are used for locomotion and power (e.g., in the legs and shoulders) have more connective tissue and yield less tender meat.
Which muscle is the heart?
Cardiac, as the name implies, is the muscle which forms the heart. Smooth muscles, also called visceral muscles, are found in the digestive and reproductive tracts as well as throughout the blood vessels, capillaries and arteries of the circulatory system. Skeletal muscles differ in length, in depth and in thickness.
How many types of muscular tissue are there?
The muscular tissue is of three types:
What are the properties of muscle tissue?
Properties of Muscular Tissue. Contractibility – It is the ability of muscle cells to shorten forcefully. Extensibility – A muscle has the ability to be stretched. Elasticity – The muscles have the ability to recoil back to its original length after being stretched. Excitability – The muscle tissue responds to a stimulus delivered ...
What is the specialized tissue in animals that applies forces to different parts of the body by contraction?
Muscular tissue is a specialized tissue in animals which applies forces to different parts of the body by contraction. It is made up of thin and elongated cells called muscle fibers. It controls the movement of an organism. The cytoplasm in the muscle fibers is called sarcoplasm. It contains a network of membrane called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What are the light and dark bands in the skeletal muscle?
These light and dark bands are sarcomeres which are highly organized structures of actin, myosin, and proteins. These add to the contractility and extensibility of the muscles. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles composed of muscle fibers. 40% of our body mass comprises skeletal muscles. Each skeletal tissue contains myofibrils.
What tissues help in the movement of bones, squeeze different organs, or compress chambers?
Muscular tissues help in the movement of bones, squeeze different organs, or compress chambers.
What is the function of muscular tissue?
Movement is the main function of muscular tissue. They have the ability to contract and this is what brings about the movement of body parts. They also help to maintain body posture and position.
What type of tissue is found only in the heart?
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. These are found only in the heart. These are involuntary muscles and the heart pumps the blood through cardiac contractions. The cells of the cardiac muscles known as the cardiomyocytes are striated. They are single-celled and uninucleated.
What are the three words that make up skeletal muscle?
You may want to write the following words onto your pillowcase: skeletal, striated, and voluntary. Perhaps doing so will permanently link these three words in your mind.
Where is smooth muscle found?
Smooth muscleis widely distributed throughout the body, being found in the walls of hollow organs such as our digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts, tubes such as blood vessels and airways, and in other locations, such as the inside of the eye.
Which muscle is striated like skeletal muscle?
Cardiac Muscle. Cardiac muscleis only found in the heart, and although it is striated like skeletal muscle, it functions involuntarily. Cardiac and most smooth muscles are autorhythmic-they are capable of contracting spontaneously without nervous or hormonal stimulation.
Why is skeletal muscle striated?
Skeletal muscle, along with cardiac muscle, is also referred to as striated ("striped") because it has a microscopically streaked or striped appearance. Skeletal muscle and its associated connective tissue comprise about 40% of our weight. You may want to write the following words onto your pillowcase: skeletal, striated, and voluntary. Perhaps doing so will permanently link these three words in your mind. More likely, however, is that your landlord will make you replace your pillowcase.