
Different types of classification have been studied – artificial classification, natural classification phylogenetic classification. Scientist follows several principles and criteria in natural classification like morphology, anatomy, geology, ontology, phylogeny etc of an organism to put into different categories.
What are some examples of binomial nomenclature?
Binomial Nomenclature Examples. Felis concolor: This animal is also known as the puma, mountain lion, cougar, painter, or catamount. This large cat has many different names not only in English but also in Spanish. It is a predatory single-colored cat that is known as poema, yaguá-pitá, león Colorado, guasura, and onça-vermelha.
What does nomenclature stand for?
binomial nomenclature (Noun) The scientific system of naming each species of organism with a Latinized name in two parts; the first is the genus, and is written with an initial capital letter; the second is some specific epithet that distinguishes the species within the genus.
What is the difference between nomenclature and terminology?
What is the difference between Nomenclature and Classification? • Nomenclature is a system in taxonomy where naming of objects, elements, compounds, organisms, and plants makes it easy for students to refer to them in an easy manner and also identify them in a crowd. • Classification is a system of grouping that allows a student to learn ...
What are the rules for nomenclature?
While the USDA and the FDA have outlined a regulatory framework for foods containing cultured meat and seafood cells, they have not yet nailed down the nomenclature. The labeling of meat and poultry from cultured cells is in the USDA’s remit, while the labeling of seafood (except catfish) from cultured cells is in the FDA’s remit.
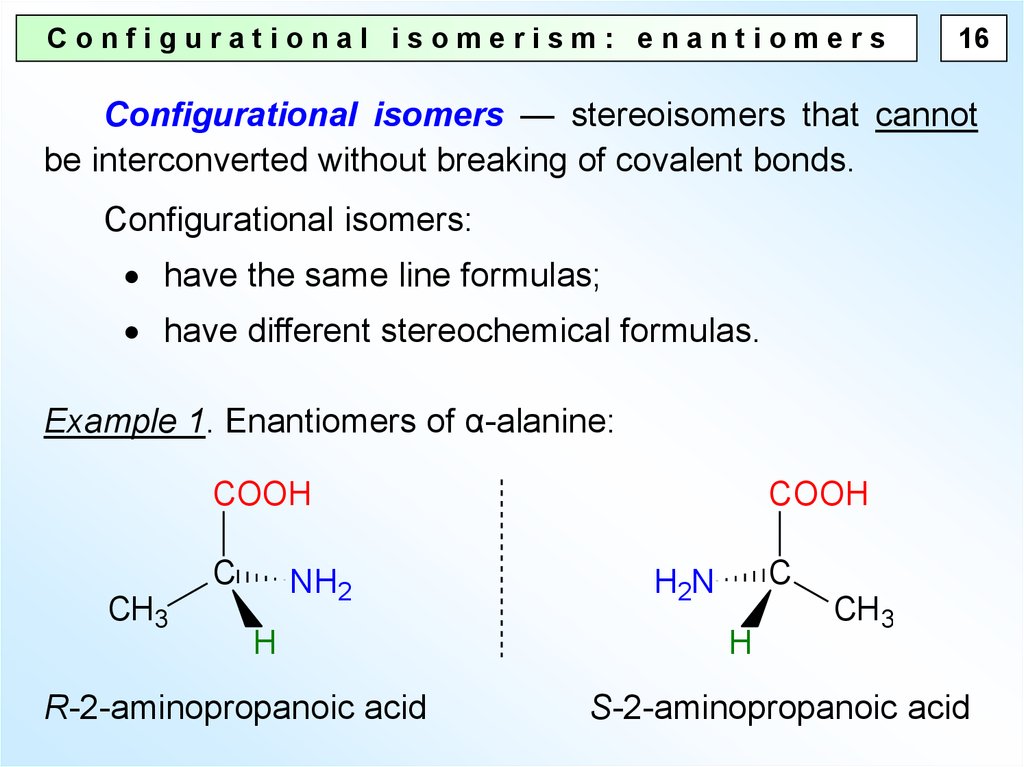
What are the type of nomenclature?
They are: International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) – Deals with the biological nomenclature for plants. International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) – Deals with the biological nomenclature of animals.
What is nomenclature and its types?
nomenclature, in biological classification, system of naming organisms. The species to which the organism belongs is indicated by two words, the genus and species names, which are Latinized words derived from various sources.
How many types of nomenclature are there in chemistry?
Then, prefixes are used to indicate the numbers of each atom present: these prefixes are mono- (one), di- (two), tri- (three), tetra- (four), penta- (five), hexa- (six), hepta- (seven), octa- (eight), nona- (nine), and deca- (ten).
How many types of nomenclature are there in biology?
Probably the best known of these nomenclatural systems are the five codes of biological nomenclature that govern the Latinized scientific names of organisms.
What are the seven classification of nomenclature?
The levels of classification he used are: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. You can see that genus and species are the two most specific categories, which is why they are used in binomial nomenclature to identify an organism.
What is nomenclature 11th?
The system of providing organisms with appropriate and distinct names is called nomenclature.
What are the two types of nomenclature in chemistry?
Generally, there are two types of inorganic compounds that can be formed: ionic compounds and molecular compounds.
What is nomenclature in chemistry class 10?
The rules for nomenclature are as follows: Identify the number of carbon atoms in carbon compound. Name the carbon compounds according to the number of carbon atoms....IUPAC.Functional groupPrefixSuffixAlkylAlkyln/aHalogenChloro− for chlorine, Bromo− for bromine Iodo− for iodinen/aAlcoholn/aolAldehyden/aal4 more rows
What is an example of nomenclature?
Nomenclature is a system for giving names to things within a particular profession or field. For instance, you may have heard of binomial nomenclature in biology class. It refers to the way of referring to living things by two names, like calling humans Homo sapiens.
What are the 3 codes of nomenclature?
Name the three codes of nomenclature.International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.International Code of Bacteriological Nomenclature.
What is nomenclature in biology class 9?
Nomenclature is the process of standardising the naming of living organisms such that a particular organism is known by the same name all over the world.
What is common nomenclature?
Common name: A nomenclature system useful for naming simple organic molecules. It often fails for more complex molecules, in which case systematic or (better yet) IUPAC nomenclature is preferable. The prefix "n-" (or normal) is used when all carbons form a continuous, unbranched (linear) chain.
What is nomenclature in science?
Nomenclature ( UK: / nəˈmɛŋkləˌtʃər /, US: / ˈnoʊmənˌkleɪtʃər /) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agreed principles, rules and recommendations that govern the formation and use of the specialist terms used in scientific and any other disciplines.
Where does the word nomenclature come from?
The word nomenclature is derived from the Latin nomen (' name '), and calare ('to call'). The Latin term nomenclatura refers to a list of names, as does the word nomenclator, which can also indicate a provider or announcer of names.
What is the IUPAC nomenclature?
The IUPAC nomenclature is a system of naming chemical compounds and for describing the science of chemistry in general. It is maintained by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry . the Blue Book and the Red Book: the two publications containing the rules for naming organic and inorganic compounds.
What is the use of names in linguistics?
The use of names, as the many different kinds of nouns embedded in different languages, connects nomenclature to theoretical linguistics, while the way humans mentally structure the world in relation to word meanings and experience relates to the philosophy of language . Onomastics, the study of proper names and their origins, ...
What are some examples of binomials?
When made up of two words (a binomial) the name usually consists of a noun (like salt, dog or star) and an adjectival second word that helps describe the first, and therefore makes the name, as a whole, more "specific," for example, lap dog, sea salt, or film star . The meaning of the noun used for a common name may have been lost or forgotten ( whelk, elm, lion, shark, pig) but when the common name is extended to two or more words much more is conveyed about the organism's use, appearance or other special properties ( sting ray, poison apple, giant stinking hogweed, hammerhead shark ). These noun-adjective binomials are just like our own names with a family or surname like Simpson and another adjectival Christian or forename name that specifies which Simpson, say Homer Simpson. It seems reasonable to assume that the form of scientific names we call binomial nomenclature is derived from this simple and practical way of constructing common names—but with the use of Latin as a universal language.
What is modern scientific taxonomy?
Modern scientific taxonomy has been described as "basically a Renaissance codification of folk taxonomic principles. " Formal systems of scientific nomenclature and classification are exemplified by biological classification. All classification systems are established for a purpose.
What is the branch of taxonomy concerned with the application of scientific names to taxa?
Doing taxonomy entails identifying, describing, and naming taxa, therefore nomenclature, in the scientific sense, is the branch of taxonomy concerned with the application of scientific names to taxa, based on a particular classification scheme, in accordance with agreed international rules and conventions.
What are the rules of nomenclature?
The following points highlight the eight main rules of nomenclature. The rules are: 1. Nomenclatural Type 2. Rule of Priority 3. Names of Taxa 4. Effective and Valid Publication 5. Retention of Specific and Infra-specific Epithets 6. Rejection of Names 7. Splitting of a Genus 8. Synonym and Basionym.
What is the nomenclature of a taxon?
Nomenclature: Rule # 1. Nomenclatural Type: The nomenclatural type is that constituent element (a specimen, or a description or a figure) of a taxon to which the name is permanently attached. This need not be the most typical or representative element but is the original material on which the description of the taxon is based.
What is the valid publication of a name of a new taxon?
Valid publication of a name of new taxon is necessary to have it effectively published, to have a correct form and to be accompanied by a description or diagnosis or a reference to a previously published description. For the name of a new taxon to be valid it is necessary that the description or the diagnosis should be in Latin.
How is the name of a family derived?
This is not followed at present. The name of a family is derived from the name of the genus which is the type for the family. The name of a subfamily, a tribe or a sub-tribe is derived from the name of the type-genus belonging to that subfamily, tribe or sub-tribe.
What is the name of a species?
The specific epithet is an adjective and is of the same gender as the generic name, or is a noun in apposition to the generic name. The specific epithet must not exactly repeat the generic name.
When the name of a species or of an infra-specific taxon is changed, what is the?
When the name of a species or of an infra-specific taxon is changed the synonym of which the epithet is to be taken for the valid name, is Basionym for that taxon. Botany, Biology, Angiosperm, Nomenclature, Rules.
When a species is transferred to another genus without change of rank, the specific epithet must be retained?
When a species is transferred to another genus without change of rank the specific epithet must be retained. If the name of a genus is changed being illegitimate, the binary combinations for all the species under that genus should be changed also and in doing so the new generic name should be used retaining the older specific epithets.
Why is nomenclature important in chemistry?
Nomenclature, the naming of chemical compounds is of critical importance to the practice of chemistry, as a chemical can not only have many different names, but different chemicals can have the same name! S o how can you do science if you do not know what you are talking about??? In this section we will look at nomenclature of simple chemical compounds. The rules we use depends on the type of compound we are attempting to name.
How many types of monatomic cations are there?
There are two types of monatomic cations, those of metals that form only one charge state, and those that can form multiple charged states, but there is only one type of monatomic anion as none of them form multiple charged states ( review section 2.6.4.1) For simplicity, we are going to label the metal cations as Type 1 (invariant charge) and type 2 (variable charge)
What is the name of the ions that are attached to a nonmetal?
Naming Oxyanions: Oxyanions are polyatomic ions where oxygen is attached to a nonmetal and as was discussed in section 2.6.4.2.1, nonmetals of the same periodic group from homologous oxyanions. Lets look at the 4 oxyanions of bromine
Which element forms acids of the same formula as other alkali metals?
Figure 2.7. 5: Hydrogen forms acids of the same "formula" as other alkali metals. On the left is the acid with chloride, HCl and on the right the salt of chloride NaCl.
Which video goes over the nomenclature of the salts of carbonate?
Video 2.7. 5 goes over the nomenclature of the salts of carbonate and Video 2.7. 6 goes over the nomenclature of the salts of phosphate.
Which ions are polyatomic?
C) Ammonium nitrate. both are polyatomic ions, so you simply state the name of cation followed by the name of the anion.
What is the difference between classification and nomenclature?
Classification is the grouping of organisms into progressively more inclusive groups based on phylogeny and phenotype, while nomenclature is the application of formal rules for naming organisms. ...
What is the nomenclature of a taxa?
Nomenclature is the set of rules and conventions which govern the names of taxa. It is the application of formal rules for naming organisms. Classification is the grouping of organisms into progressively more inclusive groups based on phylogeny and phenotype. Despite there being no official and complete classification of prokaryotes, ...
What is the name of the system of naming living things?
nomenclature : binomial nomenclature (also called binominal nomenclature or binary nomenclature) is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just “binomial”), a binomen or a scientific name; more informally it is also called a Latin name.
What is the set of rules and conventions that govern the names of taxa?
Nomenclature is the set of rules and conventions that govern the names of taxa. Recognize the factors involved with general classification and nomenclature used for microorganism classification.
How is a new species' name formed?
If a new or amended species is placed in new ranks, according to Rule 9 of the Bacteriological Code the name is formed by the addition of an appropriate suffix to the stem of the name of the type genus.
How are species named?
Borrelia burgdorferi). Their names are created by forming an adjective by joining the locality’s name with the ending -ensis (m. or f.) or ense (n.) in agreement with the gender of the genus name, unless a classical Latin adjective exists for the place. However, names of places should not be used as nouns in the genitive case.
Can tautonyms be used in zoology?
Despite it being common in zoology, tautonyms (e.g. Bison bison) are not acceptable and names of taxa used in zoology, botany or mycology cannot be reused for bacteria (Botany and Zoology do share names).
What are the two categories of nomenclature?
Nomenclaturists recognize two general classes of nomenclature, systematic and trivial. Perhaps the use of the word trivial is unfortunate, because its usual meaning in every-day English according to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED) is “of small account, little esteemed, paltry, poor, trifling, inconsiderable, unimportant, slight.” However, the OED lists several other meanings, some derived from a Latin word implying “three.” A more general common meaning listed in the OED is “such as met with anywhere, common, commonplace, ordinary, trite.” The word trivial was adopted when nomenclature was in its infancy and when its use in the latter sense was more usual, and that is why it is still used in that sense today. It is not intended to be dismissive.
When was nomenclature first used?
The first widely accepted systematic nomenclature proposals arose in France amongst Lavoisier and his colleagues in the 1780s, and they were dealing with what today we recognise as inorganic compounds.
What is substitution nomenclature?
Substitutive nomenclature is a principal IUPAC nomenclature system and the preferred method for naming organic compounds. This relies on selecting a suitable unsubstituted parent compound from which the compound at issue can be considered as ultimately derived, and then modifying the parent name in a series of formal operations. For example, a compound such as C 2 H 5 Cl would be considered to be derived from the parent compound, ethane, C 2 H 6, which is then substituted by removing a hydrogen atom to produce C 2 H 5 •, an ethyl radical, and then adding a chlorine atom to yield C 2 H 5 Cl, called chloroethane.
How to name an inorganic compound?
To name inorganic compounds, again the class of compound must be determined. A compound may span more than one class (e.g., it may be a salt and also contain a coordination entity) so that more than one system of nomenclature may need to be employed. To decipher the name of a coordination entity, the following steps are necessary: identify the central atom (s), identify the ligands (which may be organic compounds and be named using organic methods), and identify the coordination geometry and stereochemistry. The names of organometallic compounds reveal some specific aspects that need to be appreciated, and boron compounds often bear names that are derived using a different set of conventions.
Why do we use IUPAC names?
Trivial names for compounds are used by chemists everywhere, and such names are clearly useful for much exchange of information, especially within a given lab. However, IUPAC attempts to devise a fully systematic approach to the names of substances, which imply unequivocally their chemical constitutions. Such names should be used when an unambiguous identification of compounds is required, as in scientific documents, international treaties, patents, and legal definitions. This is why IUPAC nomenclature can sometimes appear to be so complicated.
What is IUPAC nomenclature?
In the first “Nomenclature Notes” (March-April 2012 CI) [above], it was stated that IUPAC nomenclature is composed of a set of different nomenclatures, which do not necessarily use the same conventions and methods. IUPAC bodies such as the Interdivisional Committee on Terminology, Nomenclature and Symbols (ICTNS) are trying to remove these inconsistencies, but nevertheless, if you are trying to decipher an IUPAC name, or to construct one, it is necessary to realize which type of nomenclature is being used, which means recognizing the type of compound that is being treated. An ideal IUPAC name should be unique, but should also convey the structure of a given compound.
What is the principle of chemical nomenclature?
Principles of Chemical Nomenclature is an attempt to show people how to find the name they require, but it also explains the misunderstandings that may arise before such a process is complete. In the first place, there is no monolithic construction called IUPAC Nomenclature.
What are the different types of classification?
Different types of classification have been studied –. artificial classification, natural classification. phylogenetic classification. Scientist follows several principles and criteria in natural classification like morphology, anatomy, geology, ontology, phylogeny etc of an organism to put into different categories.
What is the term for the method of naming organisms?
Binomial Nomenclature. It is the method of naming the organisms. The term Binomial Nomenclature means two-word names. Carolus Linnaeus devised this method. He explained the system in his book ‘ Systema Naturae’. Some of the universal rules of nomenclature are as follows:
What is the scientific name of a species?
Some of the universal rules of nomenclature are as follows: The scientific name of any organism will consist of 2 words the first one is the name of the genus and the second name the name of the species. For example, the scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica. In this Mangifera signifies the name of the genus whereas ...
What is the scientific study that attempts to recognize describe name and arrange the diverse organisms according to an organized system on unique?
Systematics. It is the scientific study that attempts to recognize describe name and arrange the diverse organisms according to an organized system on unique features of species and Groups. Systematics include: identification, classification, nomenclature and. taxonomy.
How is an organism identified?
The organism is identified according to morphological and anatomical features. It is then given a proper name and placed in a particular group.
Why do plants and animals have different names?
It could create a confusion in identifying the plant or animal. Hence there is a need to standardize the name of the living organism in such a way that a particular organism is known by the same name all over the world. This process is called nomenclature.
Why is classification important in biology?
Classification enables us to group the animals into convenient categories based on easily observable characters . Classification enables us to study phylogenetic relationships between the organisms.
What is drug nomenclature?
Drug nomenclature is a systematic approach to naming the active component of a drug product for the purposes of identification, standardization, and unequivocal differential characterization. However, over the last century, pharmaceutical and medical knowledge have changed remarkably due to innovative scientific discoveries and sophisticated technological advancements. Numerous new drug targets have been identified and many receptors have been cloned using sophisticated radioligand binding assays, providing better characterization of drug molecules. These innovation-driven advancements provided deeper understanding of the mechanisms of drug action; development of state-of-the-art medical equipment as well as rapid evolution of prescription and nonprescription drugs (Seifert, 2018; Vass et al., 2018; Kabbani, 2018 ).
What are the three main categories of organic chemicals?
Organic chemicals used as drugs can be classified into three main categories based on chemical, pharmacological, and therapeutic classifications. For example, consider the drug metoprolol. It can be classified as an aryloxypropanolamine (chemical), beta-2 (β 2) adrenergic receptor antagonist (pharmacological), and antihypertensive agent (therapeutic) depending on context.
What is the classification of antipsychotics?
The name “antipsychotic” is based on the Anatomical-Therapeutic-Chemical classification system of the World Health Organization . This system was established in the 1960s and classified psychotropic medications by indication ( Worley, 2017). As the variety of medications, knowledge on their pharmacodynamics, and clinical indications have diversified, this approach to psychotropic drug nomenclature has become obsolete. For example, antipsychotics are first-line treatment options for schizophrenia, but also for bipolar disorder, treatment-resistant depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder, among other forms of psychopathology. There are ongoing vigorous efforts from academic communities to migrate toward a neuroscience-based nomenclature for psychotropic medications (e.g., dopamine antagonists rather than antipsychotics) (Worley, 2017 ). One difficulty in establishing such nomenclature is that some dopamine antagonists may have “psychotropic” effects but are not used to treat psychopathology or induce AMEs (e.g., metoclopramide). Likewise, other dopamine antagonists may predominantly have peripheral action (e.g., domperidone). The proposed nomenclature is a work in progress and does not include a comprehensive term that contemplates the AMEs shared among these drugs. For this reason, we will continue to use the term antipsychotic throughout this chapter.
When was the FDA first examining drug names?
In an attempt to address these issues the FDA held the first public discussion, in June 2003, with the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America and ISMP, on how to evaluate proprietary and nonproprietary names of drugs. Although a gold standard for quantitative assessment of drug nomenclature could not be established at that meeting, subsequent meetings involved many stakeholders including consumers and frontline practitioners in the evaluation process. Eventually, a quantitative tool, “Socio-Technical Probabilistic Risk Assessment,” was suggested in June 2008 under the expanded Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA IV) 2007 [ Food Drug and Administration (FDA), 2007 ]. In essence, the FDA has developed internal procedures to assess the proposed product name as part of the new drug application (NDA), biologics license application, abbreviated new drug application (ANDA) or marketing authorization application.
Binomial Nomenclature
Types of Naming The Organisms
- The types of naming the organisms include the following: 1. Tautonym – It is a binomial naming system consisting of the same word twice. Example: Bison bison. 2. Synonym – Synonym is the alternative name used to the same organism after a certain period of time by a second scientist who works on the same species. Example: The synonym of Albugo candida is Cystopus candidu…
Rules Or Principles of Nomenclature
- Rules or principles for Binomial Nomenclature was given by the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) and the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) which aims at providing stable methods for naming organisms and avoiding the use of names that cause error or confusion. The rules or principles of nomenclature are as follows: 1. The scientific nam…
Advantages of Binomial Nomenclature
- Advantages of Binomial Nomenclature are as follows: 1. The scientific names are universally applied all over the world. 2. Every species has a single and precise name. 3. The scientific name gives important clues about the characteristics of the organisms. 4. The scientific names are derived from Greek and Latin languages. Hence, there is no chance of a change in the meaning …
Summary
- Every organism is placed under different kingdoms according to its characteristics. Similarly, the organisms are classified and named with a scientific naming system called nomenclature to represent their origin. The nomenclature system has made it easy to understand and identify every specific organism with its unique names. Through this article, we got to know how namin…
FAQs
- Q.1. What is an example of nomenclature? Ans: Scientific name of the man is Homo sapiens. Here, Homo is the genus name of the man and sapiens is the speciesname. Q.2. What is called nomenclature? Ans: The system of giving unique or distinct names to an organism is termed Nomenclature. Q.3. What is the purpose of nomenclature? Ans:The purpose of nomenclature is t…
Overview
Nomenclature is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agreed principles, rules and recommendations that govern the formation and use of the specialist terms used in scientific and any other disciplines.
Naming "things" is a part of general human communication using words and language: it is an asp…
Etymology
The word nomenclature is derived from the Latin nomen ('name'), and calare ('to call'). The Latin term nomenclatura refers to a list of names, as does the word nomenclator, which can also indicate a provider or announcer of names.
Onomastics and nomenclature
The study of proper names is known as onomastics, which has a wide-ranging scope that encompasses all names, languages, and geographical regions, as well as cultural areas.
The distinction between onomastics and nomenclature is not readily clear: onomastics is an unfamiliar discipline to most people, and the use of nomenclature in an academic sense is also not commonly known. Although the two fields integrate, nomenclature concerns itself more wit…
Influence of social, political, religious factors
Due to social, political, religious, and cultural motivations, things that are the same may be given different names, while different things may be given the same name; closely related similar things may be considered separate, while on the other hand significantly different things might be considered the same.
For example, Hindi and Urdu are both closely related, mutually intelligible Hindustani languages (on…
Cultural nomenclature
Names provide us with a way of structuring and mapping the world in our minds so, in some way, they mirror or represent the objects of our experience.
Elucidating the connections between language (especially names and nouns), meaning, and the way we perceive the world has provided a rich field of study for philosophers and linguists. Relevant areas of study include: the distinction between proper names and proper nouns; as wel…
Names and nouns
A name is a label for any noun: names can identify a class or category of things; or a single thing, either uniquely or within a given context. Names are given, for example, to humans or any other organisms, places, products—as in brand names—and even to ideas or concepts. It is names as nouns that are the building blocks of nomenclature.
The word name is possibly derived from the Proto-Indo-European language hypothesised word n…
Scientific nomenclature
In a strictly scientific sense, nomenclature is regarded as a part of taxonomy (though distinct from it). Moreover, the precision demanded by science in the accurate naming of objects in the natural world has resulted in a variety of codes of nomenclature (worldwide-accepted sets of rules on biological classification).
Taxonomy can be defined as the study of classification including its principles, procedures and r…
See also
• International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
• British Approved Name
• Controlled vocabulary
• Metadata