- Quadriplegia: Under this kind of CP, a person’s limbs are affected and weakened, rendering them unable to move. ...
- Diplegia: Diplegia is the kind of CP, where a person left immobile as his/her legs are weakened and unable to support them. ...
- Hemiplegia:
What are the early signs of cerebral palsy?
Early signs of cerebral palsy in a child include developmental delays, abnormal appearance, floppy or stiff muscle tone, abnormal posture, and convulsions.
What is it like to live with cerebral palsy?
Most children with Cerebral Palsy can live long, happy, quality lives. Admittedly, their care may involve more visits to the doctor, require therapy or medications, and perhaps surgery. They may be evaluated for early intervention, special education services and assistive technology. The severity level, as well as improper management of his or her conditions, may put the child at risk for diminished life span.
What does palsy mean in the Bible?
Palsy is a general term which can refer to various types of paralysis. In the Bible it seems to be used for various types of conditions having to do with motor control or lack of feeling. This could be a permanent or temporary paralysis. It could also be related to seizures. Some translations of the Bible use the word paralytic.
What are the symptoms of cerebral palsy?
Symptoms - Cerebral palsy
- Movement and development problems. The main symptoms of cerebral palsy are problems with movement, co-ordination and development. ...
- Other symptoms
- Types of cerebral palsy. Your doctors may refer to your or your child's condition as a particular type of cerebral palsy, based on the symptoms you or your child has.

What are the 4 main types of cerebral palsy?
There are four main types of CP:Spastic Cerebral Palsy. ... Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy (also includes athetoid, choreoathetoid, and dystonic cerebral palsies) ... Ataxic Cerebral Palsy. ... Mixed Cerebral Palsy. ... In a Baby Younger Than 6 Months of Age. ... In a Baby Older Than 6 Months of Age. ... In a Baby Older Than 10 Months of Age.More items...
What are the three major types of cerebral palsy?
Types of cerebral palsyQuadriplegia (a form of bilateral cerebral palsy) Both arms and legs are affected. ... Diplegia (a form of bilateral cerebral palsy) Both legs are affected. ... Hemiplegia (a form of unilateral cerebral palsy) One side of the body (one arm and one leg) is affected.
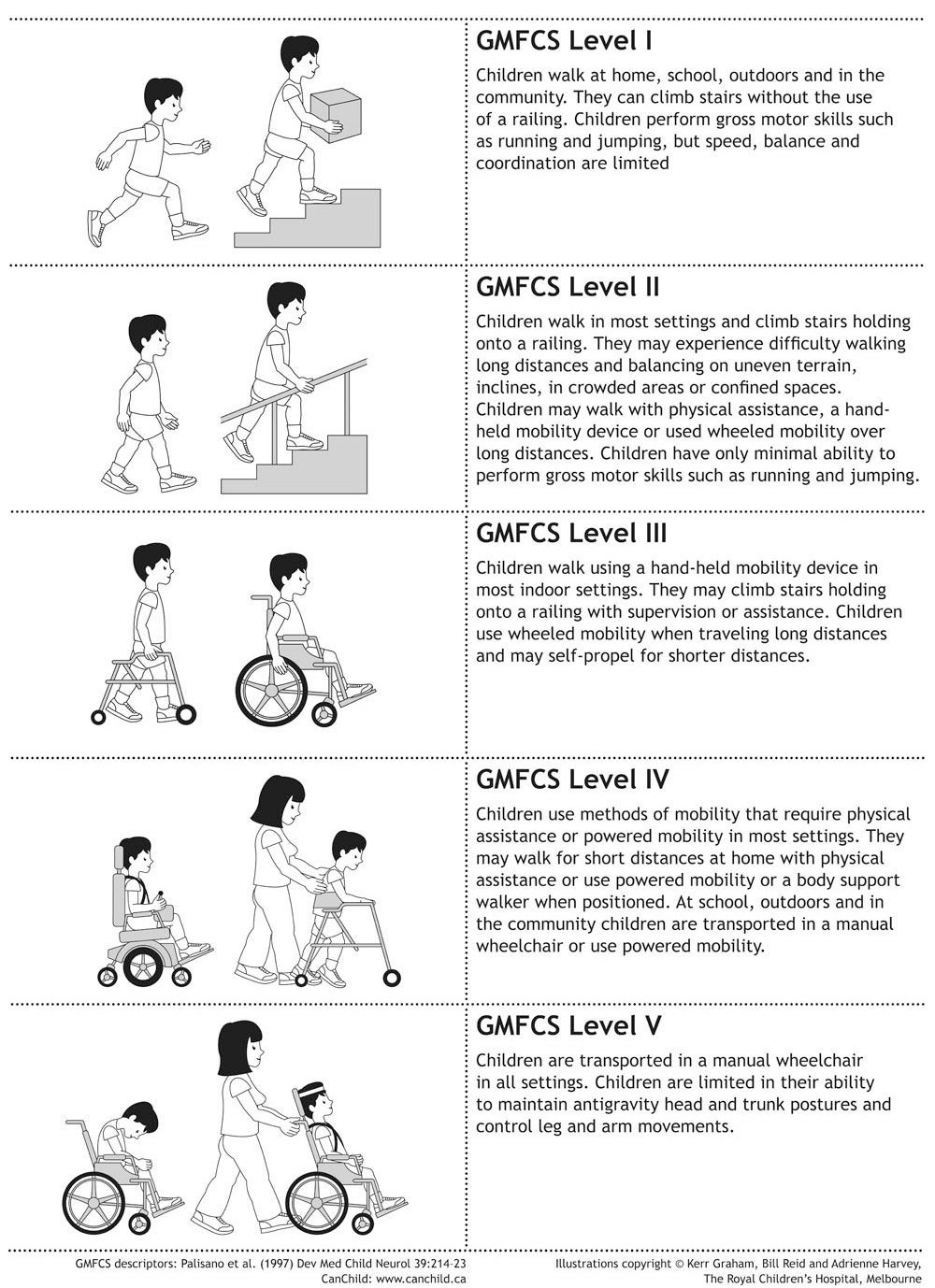
What is Level 5 cerebral palsy?
Background: The Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) of cerebral palsy categorizes patients by mobility. Patients at GMFCS level 5 are considered the most disabled and at high risk of hip and spine problems, yet they represent a wide spectrum of function.
Are there different stages of cerebral palsy?
Cerebral Palsy is often classified by severity level as Mild, Moderate, Severe. These are broad generalizations that lack a specific set of criteria. Even when doctors agree on the level of severity, the classification provides little specific information, especially when compared to other means of Classification.
What is palsy called today?
More modern editions simply refer to a man who is paralysed. Although the term has historically been associated with paralysis generally, "is now almost always used in connection to the word 'cerebral'—meaning the brain".
What is the most mild form of cerebral palsy?
Individuals with mild cerebral palsy are often classified as GMFCS level 1. These individuals are generally able to walk and perform everyday activities without assistance. Because they're able to maintain their independence, mild CP can go unnoticed and consequently untreated for years.
Does CP get worse with age?
The brain disorder causing cerebral palsy doesn't change with time, so the symptoms usually don't worsen with age. However, as the child gets older, some symptoms might become more or less apparent. And muscle shortening and muscle rigidity can worsen if not treated aggressively.
Can a person with cerebral palsy walk?
Over half (about 50%-60%) of children with CP can walk independently. About 1 in 10 children identified with CP walk using a hand-held mobility device. Many children with CP have one or more additional conditions or diseases along with their CP, known as co-occurring conditions.
Can a child with cerebral palsy talk?
Some people with cerebral palsy may not be able to produce any sounds, others may be able to produce sounds but have difficulty controlling their movement enough to produce speech that is clear and understood by others. 1 in 4 people with cerebral palsy cannot talk.
What is the average lifespan of someone with cerebral palsy?
Generally, children born with cerebral palsy can expect to live between 30 and 70 years on average. Those with the longest life expectancies usually have more mobility, better medical care and adaptive equipment and greater autonomy and independence. There is no cure for cerebral palsy and the condition lasts for life.
What is the main cause of cerebral palsy?
Cerebral palsy is usually caused by a problem that affects the development of a baby's brain while it's growing in the womb. These include: damage to part of the brain called white matter, possibly as a result of a reduced blood or oxygen supply – this is known as periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)
What's cerebral palsy caused from?
Cerebral palsy (CP) is caused by abnormal development of the brain or damage to the developing brain that affects a child's ability to control his or her muscles.
What is the most common type of cerebral palsy?
Spastic cerebral palsy is the most common type and accounts for 77% of all cases. Also referred to as hypertonic cerebral palsy, most individuals with this type experience high muscle tone and exaggerated, jerky movements (spasticity).
What is the most severe form of cerebral palsy?
Based on these three methods of classification, spastic pentaplegia is the most severe form of cerebral palsy. The effects of spastic cerebral palsy are greater than those of non-spastic cerebral palsy, and pentaplegia involves paralysis of the neck and face in addition to all four limbs.
What is Level 4 cerebral palsy?
A person with level 4 cerebral palsy can walk with the use of assistive devices. They're able to move independently in a wheelchair, and they need some support when sitting.
Is there a mild form of cerebral palsy?
Mild – Mild Cerebral Palsy means a child can move without assistance; his or her daily activities are not limited. Moderate – Moderate Cerebral Palsy means a child will need braces, medications, and adaptive technology to accomplish daily activities.
What are the 4 Different Types of Cerebral Palsy?
Generally, cerebral palsy can be classified into 4 main types: spastic, dyskinetic, ataxic, and mixed.
What are the two types of movement patterns that people with cerebral palsy may experience?
There are two main types of disordered movement patterns people with dyskinetic cerebral palsy may experience: choreoathetosis and dystonia. Choreoathetosis is characterized by uncontrollable fluctuations in muscle tone and rapid, jerky movements.
What is spastic cerebral palsy?
The different subcategories of spastic cerebral palsy include: Spastic diplegia describes motor impairments that predominantly affect the legs. While individuals with this type of CP may experience mild motor impairments in the arms, they should be more severe in the legs.
How does physical therapy help with cerebral palsy?
There, they will work on strengthening underused muscles, lengthening spastic muscles, fixing abnormal walking patterns, and improving overall movement and posture.
Why is spasticity so common in cerebral palsy?
Because constantly tight muscles make it difficult to move, individuals with spasticity typically exhibit stiff or exaggerated movements. Another unique characteristic of this type of cerebral palsy is that it can affect specific areas of the body. All other types of CP generally affect the entire body.
What is spastic CP?
Spastic CP is caused by damage to the motor cortex, the part of the brain responsible for controlling and planning voluntary movements. This type of cerebral palsy is primarily characterized by high muscle tone, otherwise referred to as spasticity.
How is cerebral palsy differentiated?
They are primarily differentiated by which regions of the brain have been damaged. Depending on the severity and location of that damage, individuals can experience a wide range of secondary effects. As a result, everyone experiences cerebral palsy differently and will require personalized treatment.
What is the term for a person who is paralyzed by weakness?
Palsy is a medical term which refers to various types of paralysis, often accompanied by weakness and the loss of feeling and uncontrolled body movements such as shaking.
What is the name of the degenerative disease that is caused by squatting?
Spinal muscular atrophy, also known as wasting palsy. Progressive supranuclear palsy, a degenerative disease. Squatter's palsy, a common name for bilateral peroneal nerve palsy that may be triggered by sustained squatting. Third nerve palsy, involving cranial nerve III.
What is the name of the disorder that affects the ability to move the eyes?
Cerebral palsy, a neural disorder caused by intracranial lesions. Conjugate gaze palsy, a disorder affecting the ability to move the eyes. Erb's palsy, also known as brachial palsy, involving paralysis of an arm.
What does Luke 5:18 mean?
In some editions, the Bible passage of Luke 5:18 is translated to refer to "a man which was taken with a palsy". More modern editions simply refer to a man who is paralysed. Although the term has historically been associated with paralysis generally, "is now almost always used in connection to the word 'cerebral'—meaning the brain".
What are the different types of cerebral palsy?
Spastic cerebral palsy is broken down into three different subtypes, which include: 1 Spastic diplegia – involves muscle stiffness, generally in the leg area but the arms may be mildly affected too and can cause difficulty walking 2 Spastic hemiplegia – when primarily one side of the body is involved, with movement difficulties mainly in the arm on the affected side 3 Spastic quadriplegia – characterized by motor dysfunction all over the body, is the most severe type of spastic cerebral palsy, and usually comes with other associated disorders
What are the risks of spastic quads?
Children with spastic quad have a heightened risk of developing spinal deformities, language and feeding disorders, seizures, muscle contractions, and cognitive issues. Dyskinetic cerebral palsy is the second most common type of cerebral palsy after spastic forms.
How many types of cerebral palsy are there?
There are four main types of cerebral palsy reflecting abnormalities in different parts of the brain, and resulting in various kinds of symptoms. The National Institutes of Health states that spastic cerebral palsy is the most common form of the disorder, affecting around 80% of all diagnosed cases of cerebral palsy.
Why is it difficult to walk with cerebral palsy?
There can be difficulties in walking and writing due to instability, effects on speech, and swallowing, as well as eye movements. Mixed Cerebral Palsy. Sometimes children develop a mix of the types CP. A combination of dyskinetic and spastic cerebral palsy is the most common, but children can create a blend of any CP.
What is it called when your legs cross at the knees?
Get Help Now. Spastic Diplegia. Children with diplegic cerebral palsy, also known as spastic diplegia, may display several different symptoms and traits, with the most common including: Hip and leg muscles are very tight causing the legs to cross at the knees and to pull inward, creating a “scissoring” effect.
What is cerebral palsy?
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a neurological disorder [1] that affects a person’s movements, muscle tone, and coordination. These effects can differ from one child with cerebral palsy to the next, and it’s generally due to the type and extent of the disorder each person has. There are four main types of cerebral palsy reflecting abnormalities in different ...
What is the movement disorder of cerebral palsy?
There are several types of movement disorders seen in dyskinetic cerebral palsy: Dystonia – where movements are twisting and repetitive, this can be present in one part of the body, or the entire body and the movements are unplanned and involuntary, usually stimulated by initiating a voluntary movement.
What types of Cerebral Palsy are there?
Below are the most commonly used classification systems understood and used by qualified practitioners.
How can I obtain a copy of the expanded and revised GMFCS Classification System?
More information about the GMFCS Classification System is available at:
What does severe cerebral palsy mean?
Severe – Severe Cerebral Palsy means a child will require a wheelchair and will have significant challenges in accomplishing daily activities.
How does cerebral palsy affect muscle tone?
Muscle tone. Many motor function terms describe Cerebral Palsy’s effect on muscle tone and how muscles work together. Proper muscle tone when bending an arm requires the bicep to contract and the triceps to relax. When muscle tone is impaired, muscles do not work together and can even work in opposition to one another.
What does it mean when a child has mild cerebral palsy?
Mild – Mild Cerebral Palsy means a child can move without assistance; his or her daily activities are not limited.
What is the specialty of a surgeon for cerebral palsy?
Professionals who specialize in the treatment of Cerebral Palsy approach the condition from a number of different vantage points. An orthopedic surgeon requires a definition of the limbs affected and the extent of impairment in order to prescribe treatment.
Why use GMFCS?
Using GMFCS helps determine the surgeries, treatments, therapies, and assistive technology likely to result in the best outcome for a child . Additionally, the GMFCS is a powerful system for researchers; it improves data collection and analysis and hence result in better understanding and treatment of Cerebral Palsy.
What causes ataxia and balance issues?
Ataxic Cerebral Palsy. Ataxic cerebral palsy makes up about 2.4% of all cerebral palsy cases. This type of cerebral palsy causes ataxia and issues with balance, coordination, and voluntary movement. Ataxic cerebral palsy is caused by damage to the cerebellum, which is responsible for coordinating physical movement.
What is the name of the condition where the muscles are loosened?
Athetoid cerebral palsy is characterized by a combination of hypotonia (loosened muscles) and hypertonia (stiffened muscles) which causes muscle tone to fluctuate.
How many children have athetoid cerebral palsy?
2.6% of all cases. About 2.6% of children with the condition are diagnosed with athetoid cerebral palsy (also known as non-spastic or dyskinetic cerebral palsy). This type causes issues with involuntary movement in the face, torso, and limbs.
Why do children miss milestones?
Instability and floppiness in muscles caused by hypotonic cerebral palsy can cause a child to miss developmental milestones such as crawling, standing, or walking.
What are the symptoms of spastic cerebral palsy?
Common symptoms of spastic cerebral palsy include: Abnormal walking. Awkward reflexes.
How does GMFCS work?
The GMFCS is a five-level ranking system that determines the type of cerebral palsy a child has by examining overall motor function. Early medical intervention before the age of 5 can help improve your child’s GMFCS level and overall mobility.
How many cases of cerebral palsy are caused by birth injury?
About 70% of cases of cerebral palsy results from a birth injury. Was your child one of them?
What is a spastic CP?
Spastic CP usually is described by what parts of the body are affected: Spastic diplegia/diparesis―In this type of CP, muscle stiffness is mainly in the legs, with the arms less affected or not affected at all.
What is dyskinetic cerebral palsy?
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy (also includes athetoid, choreoathetoid, and dystonic cerebral palsies) People with dyskinetic CP have problems controlling the movement of their hands, arms, feet, and legs, making it difficult to sit and walk. The movements are uncontrollable and can be slow and writhing or rapid and jerky.
What is the most common type of CP?
Spastic Cerebral Palsy. The most common type of CP is spastic CP. Spastic CP affects about 80% of people with CP. People with spastic CP have increased muscle tone. This means their muscles are stiff and, as a result, their movements can be awkward.
What does CP mean in a person?
Palsy means weakness or problems with using the muscles. CP is caused by abnormal brain development or damage to the developing brain that affects a person’s ability to control his or her muscles. The symptoms of CP vary from person to person.
What is cerebral palsy?
If You’re Concerned. Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that affect a person’s ability to move and maintain balance and posture. CP is the most common motor disability in childhood. Cerebral means having to do with the brain. Palsy means weakness or problems with using the muscles. CP is caused by abnormal brain development ...
Which type of CP affects only one side of the body?
Spastic hemiplegia/hemiparesis ―This type of CP affects only one side of a person’s body; usually the arm is more affected than the leg. Spastic quadriplegia/quadriparesis―Spastic quadriplegia is the most severe form of spastic CP and affects all four limbs, the trunk, and the face.
How does the sailor crawl?
He crawls in a lopsided manner, pushing off with one hand and leg while dragging the opposite hand and leg
What is dyskinetic motor pattern?
Dyskinetic motor patterns (also includes athetoid, choreoathetoid, and dystonia) are characterized by slow and uncontrollable writhing or jerky movements of the hands, feet, arms, or legs.
What is the most severe form of CP?
stiffness that is predominantly in the legs. The arms may. be affected to a lesser extent. Spastic quadriplegia/quadriparesis (Fig. 2) is the most. severe form of CP. It is caused by widespread damage to. the brain or significant brain malformations.
What is mixed CP?
Mixed types of CP refer to symptoms that don’t correspond to#N#any single type of CP but are a mix of types. For example, a#N#child with mixed CP may have some muscles that are too tight#N#and others that are too relaxed.
How are motor types determined in CP?
The specific motor types present in CP are determined by the extent, type, and location of a child’s abnormalities. (Fig. 1)
What is the term for the loss of movement?
PALSY. REFERS TO THE LOSS OR IMPAIRMENT OF MOTOR FUNCTION. Cerebral Palsy (CP) describes a group of permanent disorders of the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitations, attributed to non progressive disturbances that occurred in the developing fetal or infant brain.
Which part of the body is affected by spastic hemiplegia?
Different parts of the body can be affected: Spastic hemiplegia/hemiparesis (Fig. 2) typically affects. the arm, hand, and leg on one side of the body. Spastic diplegia/diparesis (Fig. 2) involves muscle. stiffness that is predominantly in the legs. The arms may. be affected to a lesser extent.
What is the best treatment for cerebral palsy?
Common types of treatment for cerebral palsy include 1, 2: Physical therapy and rehabilitation . A child with cerebral palsy usually starts these therapies in the first few years of life or soon after being diagnosed. Physical therapy is one of the most important parts of treatment. It involves exercises and activities that can maintain ...
What is the first FDA approved screening platform for lysosomal storage disorder?
SEEKER® – The First FDA-Authorized Newborn Screening Platform for Lysosomal Storage Disorders
What are some devices that help with posture?
Other devices that can help with movement and posture include wheelchairs, rolling walkers, and powered scooters. Assistive devices and technologies. These include special computer-based communication machines, Velcro-fastened shoes, or crutches, which can help make daily life easier. Medication.
What can a speech therapist do for a child?
A speech therapist can help a child learn to speak more clearly, help with swallowing problems, and teach new ways to communicate, such as by using sign language or a special communication device. Orthotic devices. Braces, splints, and casts can be placed on the affected limbs and can improve movement and balance.
What type of therapy helps a child learn to do everyday activities such as dressing and going to school?
Occupational therapy. This type of therapy helps a child learn to do everyday activities such as dressing and going to school. Recreational therapy. Participating in art programs, cultural activities, and sports can help improve a child’s physical and intellectual skills. Speech and language therapy.
What is physical therapy?
It involves exercises and activities that can maintain or improve muscle strength, balance, and movement. A physical therapist helps the child learn skills such as sitting, walking, or using a wheelchair. Other types of therapy include: Occupational therapy.
How many different types of treatment do children need?
A child may need one or several different types of treatment depending on how severe the symptoms are and what parts of the body are affected. The treatment differs from person to person, depending on each one’s specific needs.

Why So Confusing?
Classification Preference Changes Based on The Intended Use
The Move Toward A Universal Classification System
What Types of Cerebral Palsy Are there?
Classification Based on Severity Level
Classification Based on Topographical Distribution
Classification Based on Motor Function
- The brain injury that causes Cerebral Palsy affects motor function, the ability to control the body in a desired matter. Two main groupings include spastic and non-spastic. Each has multiple variations and it is possible to have a mixture of both types. Spastic Cerebral Palsyis characterized by increased muscle tone. Non-spastic Cerebral Palsywill ...
Muscle Tone
Pyramidal, Or Spastic Cerebral Palsy
Extrapyramidal, Or Non-Spastic Cerebral Palsy