
Despite the numerous different traits of pea plant, Mendel chose seven main traits to conduct his experiments:
- Flower colour: Red & White
- Flower position: End & Side.
- Seed colour: Yellow & green.
- Seed shape: Smooth & Wrinkled.
- Stem height: Tall & short.
- Pod ( fruit) colour: Green & Yellow.
- Pod (fruit) shape: Swollen & Sinuous.
| Trait | Dominant Expression | Recessive Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Form of ripe seed (R) | Smooth | Wrinkled |
| Color of seed albumen (Y) | Yellow | Green |
| Color of flower (P) | Purple | White |
| Form of ripe pods (I) | Inflated | Constricted |
What was the main aim of Mendel’s experiments?
The main aim of Mendel’s experiments was: 1 To determine whether the traits would always be recessive. 2 Whether traits affect each other as they are inherited. 3 Whether traits could be transformed by DNA. More ...
What did Mendel mean by expressed and latent traits?
Upon compiling his results for many thousands of plants, Mendel concluded that the characteristics could be divided into expressed and latent traits. He called these dominant and recessive traits, respectively. Dominant traits are those that are inherited unchanged in a hybridization.
What did Mendel's experiment show about segregation and dominance?
Mendel even conducted this experiment with other contrasting traits like green peas vs yellow peas, round vs wrinkled, etc. In all the cases, he found that the results were similar. From this, he formulated the laws of Segregation And Dominance. In a dihybrid cross experiment, Mendel considered two traits, each having two alleles.
What did Mendel find out about hybrid plants?
Mendel then crossed these pure-breeding lines of plants and recorded the traits of the progeny. He found that all of the first-generation (F1) hybrids looked like 1 of the parent plants. For example, all the progeny of a purple and white flower cross were purple (not pink, as blending would have predicted).
See more
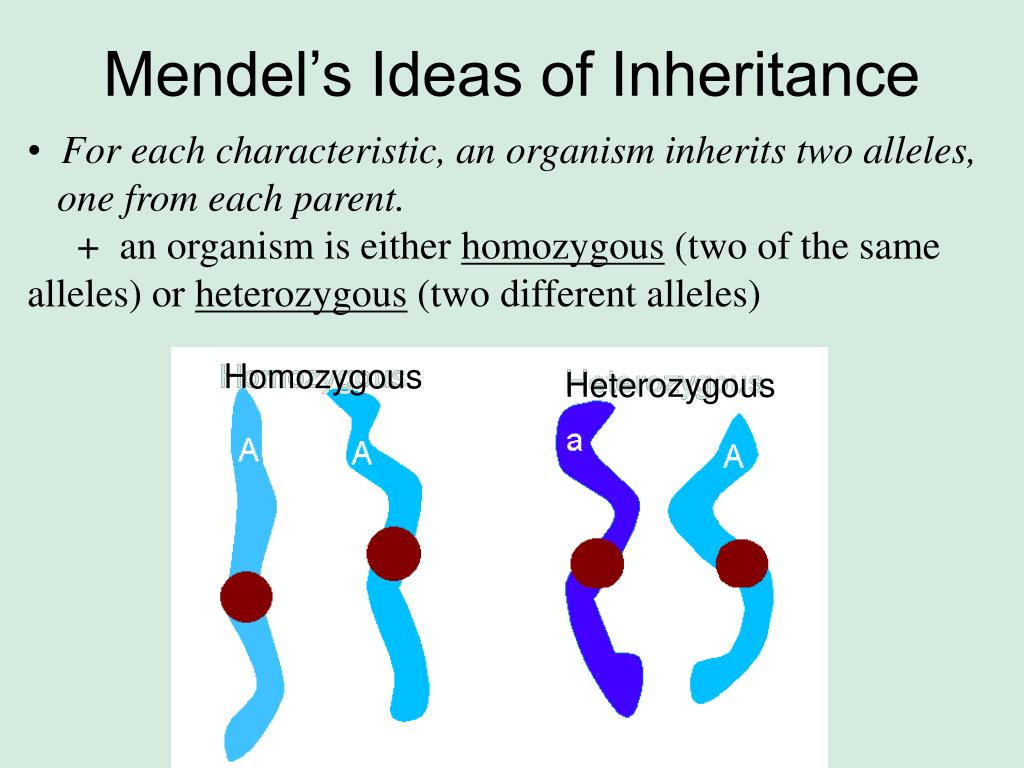
What is a dominant trait in Mendelian genetics?
A dominant trait is an inherited characteristic that appears in an offspring if it is contributed from a parent through a dominant allele.
What is the dominant traits of pea plant?
Yellow seed colour is the dominant trait and green seed colour is the recessive trait.
How did Mendel prove dominant and recessive traits?
He selected homozygous tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants. He crossed the tall pea plant with the dwarf pea plant. It was observed that the F1 generation are all tall plants. Thus, it was concluded that the gene causing tallness is dominant while the gene causing dwarfness is recessive.
What were the 7 traits Mendel studied?
Mendel used seven pea plant traits in his experiments which include flower color (purple or white), flower position (axil or terminal), stem length (long or short), seed shape (round or wrinkled), seed color (yellow or green), pod shape (inflated or constricted), and pod color (yellow or green).
Which is a dominant trait?
dominant trait. In genetics, a trait that will appear in the offspring if one of the parents contributes it.
What are the dominant and recessive characters of pea plant?
ExploreTraitDominant ExpressionRecessive ExpressionColor of seed albumen (Y)YellowGreenColor of flower (P)PurpleWhiteForm of ripe pods (I)InflatedConstrictedColor of unripe pods (G)GreenYellow3 more rows
What are dominant and recessive traits class 10?
Complete Answer: - Dominant refers to the relationship between two versions of a gene. If the alleles (two versions of each gene) of a gene are different, one allele will be expressed as Dominant gene while the other allele effect is called recessive.
How did Mendel explain the inheritance of traits?
Genes located on different chromosomes will be inherited independently of each other. Mendel observed that, when peas with more than one trait were crossed, the progeny did not always match the parents. This is because different traits are inherited independently – this is the principle of independent assortment.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits Maybe dominant or recessive traits are inherited independently?
At the same time there tall plants, but had wrinkled seeds, while others were short, but had round seeds. Thus, Mendel's experiments show that the tall/short trait and the round seed/wrinkled seed trait are independently inherited.
How many dominant characteristics are present in pea plant from given list?
Axial flower, yellow pod, flower position, pod shape, terminal flower, wrinkled seed, tall plant, white flower, seed shape.
Is hybrid dominant or recessive?
A hybrid is called heterozygous, as it has two different alleles. The offspring from a pure tall pea plant, cross-pollinated with a pure short pea plant, will result in a heterozygous plant for tallness. No organism has all dominant or all recessive genes....DominantRecessiveWidow's peak hairlineStraight hairline7 more rows
What are the 3 laws of Mendel?
The law of inheritance was proposed by Gregor Mendel after conducting experiments on pea plants for seven years. Mendel's laws of inheritance include law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment.
What color is dominant in pea plants?
Heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with green seeded plant.
What is the dominant color of the flower of a pea plant?
purple colourIn the pea plant, purple colour of flower is dominant over white colour. Progeny obtained by crossing pure purple flowered plants with white flowered plants are self-pollinated.
How many traits did each pea plant characteristics have?
During this time, Mendel observed seven different characteristics in the pea plants, and each of these characteristics had two forms (Figure 3). The characteristics included height (tall or short), pod shape (inflated or constricted), seed shape (smooth or winkled), pea color (green or yellow), and so on.
Is green or yellow dominant in pea plants?
Since yellow is dominant to green, all of the offspring were yellow.
What did Mendel's choice of traits allow him to see experimentally?
Mendel’s choice of these kinds of traits allowed him to see experimentally that the traits were not blended in the offspring as would have been expected at the time, but that they were inherited as distinct traits . In 1868, Mendel became abbot of the monastery and exchanged his scientific pursuits for his pastoral duties.
How does Mendel perform hybridization?
Mendel performed hybridizations, which involve mating two true-breeding individuals that have different traits. In the pea, which is naturally self-pollinating, this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety.
What pollen did Mendel use to make a plant with white flowers?
Once these validations were complete, Mendel applied the pollen from a plant with violet flowers to the stigma of a plant with white flowers. After gathering and sowing the seeds that resulted from this cross, Mendel found that 100 percent of the F 1 hybrid generation had violet flowers.
What is true breeding peas?
By experimenting with true-breeding pea plants, Mendel avoided the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring that might occur if the plants were not true breeding.
What did Mendel show about pea plants?
He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring in specific patterns.
What is Mendel's seminal work?
Mendel’s seminal work was accomplished using the garden pea, Pisum sativum, to study inheritance. This species naturally self-fertilizes, meaning that pollen encounters ova within the same flower. The flower petals remain sealed tightly until pollination is completed to prevent the pollination of other plants.
Did Mendel's experiment stop?
Instead, Mendel’s results demonstrated that the white flower trait had completely disappeared in the F 1 generation. Importantly, Mendel did not stop his experimentation there. He allowed the F 1 plants to self-fertilize and found that 705 plants in the F 2 generation had violet flowers and 224 had white flowers.
How many traits did Mendel have?
Mendel followed the inheritance of 7 traits in pea plants, and each trait had 2 forms. He identified pure-breeding pea plants that consistently showed 1 form of a trait after generations of self-pollination.
What did Mendel find?
Mendel did thousands of cross-breeding experiments. His key finding was that there were 3 times as many dominant as recessive traits in F2 pea plants (3:1 ratio).
How many pairs of purebred peas are there in Mendel crossbred peas?
Mendel cross-bred peas with 7 pairs of pure-bred traits. First-generation (F1) progeny only showed the dominant traits, but recessive traits reappeared in the self-pollinated second-generation (F2) plants in a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits.
Why did Mendel study peas?
Mendel studied inheritance in peas ( Pisum sativum ). He chose peas because they had been used for similar studies, are easy to grow and can be sown each year. Pea flowers contain both male and female parts, called stamen and stigma, and usually self-pollinate. Self-pollination happens before the flowers open, so progeny are produced from a single plant.
How many peas did Mendel grow?
He may have grown as many as 30,000 pea plants over 7 years.
Why is Mendel known as the father of genetics?
Mendel’s experiments. Mendel is known as the father of genetics because of his ground-breaking work on inheritance in pea plants 150 years ago. Explore topics.
What is the result of each parent passing along 1 factor for every trait?
In 1866, Mendel published the paper Experiments in plant hybridisation ( Versuche über plflanzenhybriden ). In it, he proposed that heredity is the result of each parent passing along 1 factor for every trait. If the factor is dominant, it will be expressed in the progeny. If the factor is recessive, it will not show up but will continue to be passed along to the next generation. Each factor works independently from the others, and they do not blend.
What is the dominant trait of Mendel's experiment?
He crossed wrinkled-green seed and round-yellow seeds and observed that all the first generation progeny (F1 progeny) were round-yellow. This meant that dominant traits were the round shape and yellow colour.
What were the two experiments Mendel conducted?
Mendel conducted 2 main experiments to determine the laws of inheritance. These experiments were: Monohybrid Cross Experiment. Dihybrid Cross Experiment. While experimenting, Mendel found that certain factors were always being transferred down to the offspring in a stable way.
How did Mendel find the first generation of pea plants?
In this experiment, Mendel took two pea plants of opposite traits (one short and one tall) and crossed them. He found the first generation offsprings were tall and called it F1 progeny. Then he crossed F1 progeny and obtained both tall and short plants in the ratio 3:1. To know more about this experiment, visit Monohybrid Cross – Inheritance Of One Gene.
Why did Mendel pick a pea plant?
Mendel picked pea plant in his experiments because the pea plant has different observable traits. It can be grown easily in large numbers and its reproduction can be manipulated. Also, pea has both male and female reproductive organs, so they can self-pollinate as well as cross-pollinate.
What is the law of dominance?
This is also called Mendel’s first law of inheritance. According to the law of dominance, hybrid offsprings will only inherit the dominant trait in the phenotype. The alleles that are suppressed are called as the recessive traits while the alleles that determine the trait are known as the dormant traits.
How many alleles are there in segregation?
The law of segregation states that every individual possesses two alleles and only one allele is passed on to the offspring.
Why is heredity dependent on inheritance?
This simply means that due to inheritance, the members of the same family possess similar characteristics. It was only during the mid 19th century that people started to understand inheritance in a proper way.
How does Mendel avoid the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring?
By experimenting with true-breeding pea plants, Mendel avoided the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring that might occur if the plants were not true breeding. The garden pea also grows to maturity within one season, meaning that several generations could be evaluated over a relatively short time.
How does Mendel perform hybridization?
In the pea, which is naturally self-pollinating, this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety.
What pollen did Mendel use to make a plant with white flowers?
Once these validations were complete, Mendel applied the pollen from a plant with violet flowers to the stigma of a plant with white flowers. After gathering and sowing the seeds that resulted from this cross, Mendel found that 100 percent of the F 1 hybrid generation had violet flowers.
What did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color?
What results did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color? First, Mendel confirmed that he was using plants that bred true for white or violet flower color. Irrespective of the number of generations that Mendel examined, all self-crossed offspring of parents with white flowers had white flowers, and all self-crossed offspring of parents with violet flowers had violet flowers. In addition, Mendel confirmed that, other than flower color, the pea plants were physically identical. This was an important check to make sure that the two varieties of pea plants only differed with respect to one trait, flower color.
What did Mendel show about pea plants?
He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring in specific patterns.
What is a trait in biology?
A trait is defined as a variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic. The characteristics included plant height, seed texture, seed color, flower color, pea-pod size, pea-pod color, and flower position.
What is Mendel's seminal work?
Mendel’s seminal work was accomplished using the garden pea, Pisum sativum, to study inheritance. This species naturally self-fertilizes, meaning that pollen encounters ova within the same flower. The flower petals remain sealed tightly until pollination is completed to prevent the pollination of other plants.
What are Mendel's traits?
The seven traits Mendel identified as being useful to his aims and their different manifestations were: Flower color: Purple or white. Flower position: Axial (along the side of the stem) or terminal (at the end of the stem). Stem length: Long or short. Pod shape: Inflated or pinched.
How did Mendel determine the traits of plants?
Once Mendel had two sets of plants that differed only at a single trait, he performed a multigenerational assessment in an effort to try to follow the transmission of traits through multiple generations. First, some terminology: 1 The parent generation was the P generation, and it included a P1 plant whose members all displayed one version of a trait and a P2 plant whose members all displayed the other version. 2 The hybrid offspring of the P generation was the F1 (filial) generation. 3 The offspring of the F1 generation was the F2 generation (the "grandchildren" of the P generation).
How many pea plants did Mendel grow?
Mendel would end up growing and studying nearly 29,000 pea plants between 1856 and 1863.
Why did Mendel examine pea plants?
He examined them in order to understand which characteristics could be passed on to future generations and exactly how this occurred at a functional level, even if he didn't have the literal tools to see what was occurring at the molecular level.
Why did Mendel perform a multigenerational assessment?
Once Mendel had two sets of plants that differed only at a single trait, he performed a multigenerational assessment in an effort to try to follow the transmission of traits through multiple generations. First, some terminology:
Why did Mendel assess genetic crosses from the three generations?
Mendel assessed genetic crosses from the three generations to assess the heritability of characteristics across generations. When he looked at each generation, he discovered that for all seven of his chosen traits, a predictable pattern emerged.
What questions did Mendel ask himself?
When Mendel began to formulate specific ideas about what he hoped to test and identify, he asked himself a number of basic questions. For example, what would happen when plants that were true-breeding for different versions of the same trait were cross-pollinated?
