
Female specific Effects:
- Male pattern hair growth and baldness
- Menstruation disturbances
- Decreased size of breast
- Deeper voice (hoarseness)
...
Athletes who use synthetic oxygen carriers have an increased risk of:
- heart disease.
- stroke.
- heart attack.
- blood clot.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of blood doping?
Thus blood doping:
- Increases muscle mass
- Increases one’s overall weight gain
- Increases strength
- Offers Feelings of confidence and positivity (euphoria)
- Increases aggressiveness
- Increases muscle definition and leanness
What negative effects does blood doping have on athletes?
Too many red cells can cause blood to sludge and clot in arteries and veins, causing bad things like stroke and heart attack. Blood doping has the same end result as using EPO. In effect, the athlete donates a unit (about a pint) or two of blood to himself.
How unhealthy is blood doping?
Blood doping, including having blood transfusions to change the way your blood carries oxygen to the rest of your body, may result in: an increased risk of heart failure, stroke, kidney damage and high blood pressure. problems with your blood like infections, poisoning, overloading of your white cells and reduction of your platelet count.
What is the affect of doping on XRD peak intensity?
Yes, there will be shifting of XRD peaks during doping. The main reason in your case is the increase/decrease in the lattice parameters that is reflected by the shift of diffraction peaks. This effect is mainly due to the difference in ionic radii between the main element and the dopant ion.
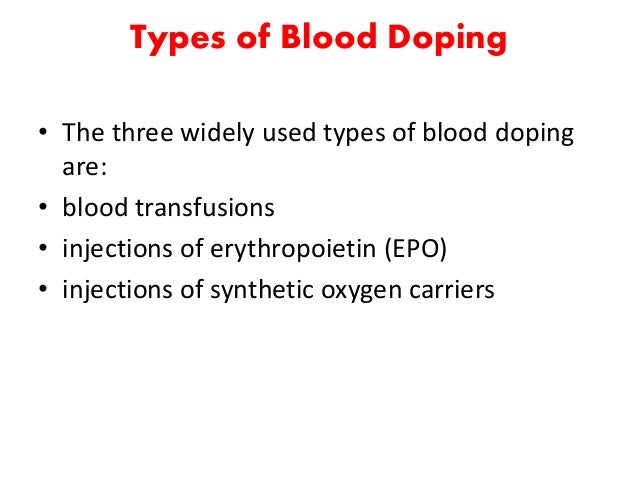
What is blood doping?
Blood doping is the practice of misusing certain techniques and substances to increase the red blood cells in the body. There are three widely known substances or methods used for blood doping, namely, erythropoietin (EPO), synthetic oxygen carriers and blood transfusions*.
Can withdrawal from anabolic steroids cause depression?
Withdrawal from anabolic steroid use can be associated with depression, and in some cases, suicide.
How does exercise affect the body?
In the human body, exercise can be a source profound physiological changes. In particular, its impacts the release of fundamental hormones in the body. The adrenal glands is the body 's main site of steroid hormone release and it responds to increased physical activity through the release of hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone. (Buono & Yeager, 1991) Aldosterone is an essential hormone used by the body to maintain sodium and fluid balance. It exerts it effects by increasing sodium re-absorption and potassium secretion in the kidneys and in turn this also increases water resorption.
Why is the pressure in the arteries higher?
So in the arteries of the human being, if its pathway is blocked by fatty deposits, the walls becomes smaller and the heart has to pump a higher amount of pressure to get the blood flowing through, resulting in hypertension. In order to check if a patient is suffering from hypertension or abnormal levels of blood pressure, there are four indirect and non-invasive methods to assess the patient.
Do steroids affect the heart?
Steroids also affect the heart. The heart is a muscle, and steroid usage can causes changes in the heart. One of these changes is a decrease in HDL cholesterol and an increase in LDL cholesterol, resulting in overall raised
Does aerobic exercise increase myocardial function?
In general, whether it is short-term or long-term, aerobic exercise can increase the myocardial MnSOD activity (Demirel et. al., 2001) which also plays a role against irregular heartbeat (Hamilton, Quindry, French, Staib, Hughes, Mehta, Powers,
Why is it important to increase red blood cells in the body?
More efficiency and more power yield better athletic performance. Increasing the number of red blood cells in the body increases the ability to deliver oxygen to tissues and that's where blood doping and EPO come in.
What Are the Risk and Benefit of Erythropoietin (EPO)?
Now he has fallen, admitting that he blood doped, used steroids and erythropoietin (EPO), and exhibited disdain to those around him, both friend and foe. The problem, however, is that sports are always filled with cheating, and the public accepts some acts of dishonesty as part of the game. The distinction between what is ethically acceptable and what is not continues to be a blurred line.
Can throwing a spitball get you into the Hall of Fame?
Throwing a spitball and not getting caught might get you into the baseball hall of fame, but as seen in the latest writers' vote, drugs are a nonstarter. Repeated studies have asked athletes whether they would choose steroid use and die early or win an Olympic medal, and the temptation of gold wins every time.
Is blood doping the same as EPO?
Blood doping has the same end result as using EPO. In effect, the athlete donates a unit (about a pint) or two of blood to himself. The blood can be stored for a month or two while the body replenishes it and just before competition, the saved blood is transfused back into the athlete, increasing the red blood cell count and the oxygen delivery capacity. The risk? The same as using EPO – blood clots and potential death.
What is blood doping?
According to the World Anti-Doping Agency (Wada) blood doping is defined as the “misuse of certain techniques and/or substances to increase one’s red blood cell mass, which allows the body to transport more oxygen to muscles and therefore increase stamina and performance”.
What are the most common methods of blood doping?
There are three most commonly used methods for blood doping and these include erythropoietin (EPO), synthetic oxygen carriers and blood transfusions, all of which are prohibited under Wada’s List of Prohibited Substances and Methods.
What does EPO do to your body?
EPO is a naturally occurring hormone that stimulates bone marrow to up your red blood cell count. Simply put, more red blood cells means more oxygen traveling to muscles. Pro athletes may be able to dose themselves precisely, with small amounts every day, but if you take too much EPO you end up with too many red blood cells, which actually thicken the blood and slow it down in your veins.
Does hematocrit increase risk of stroke?
The same blood-thickening effect also increases the risk for blood clots, stroke and heart attack. “The most dangerous side effect relates to an increased risk of a thromboembolic event (clot),” says Amit Momaya a surgeon at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. The cellular components of the blood, or “hematocrit,” usually make up about 40 percent of blood volume when centrifuged. As red blood cells accrue, hematocrit goes up as well and along with it, the risk of blood clots and heart attacks.
Does EPO cause cancer?
As a growth hormone, EPO also has antiapoptotic effects, meaning that it slows down the body’s natural system of killing and removing damaged cells. “It doesn’t cause cancer, but it might prevent the body from killing cancer cells, or it might aggravate growth of cancer cells,” says Franz. Some long-term studies of kidney patients have found an increased incidence of cancer for those treated with EPO, and experts hypothesize that the hormone may stimulate tumor growth.
Can EPO cause blood clots?
In 2014, researchers in The Netherlands noted that four recent trials of kidney transplant patients receiving high doses of EPO after surgery found an increased risk of blood clots. “EPO is known to induce hypertension, so if you are a more mature male you might already have hypertension and taking EPO could have long-term risks,” says doctor Stefan Franz.
What is doping misconduct?
Likewise, doping includes other forms of misconduct, such as assisting, encouraging, provoking, inciting or covering up an anti-doping rules violation or any attempted violation either by an athlete or a member of their team, such as their doctor or physical trainer.
What is the role of EPO in the body?
The blood cells that are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to cells throughout the body and to return the carbon dioxide from those cells back to the lungs.
Is EPO used for anemia?
EPO is produced synthetically and is used as a clinical practice in patients with some types of anemia, especially in those who must undergo dialysis processes, or some types of tumors, it is even used preventively in premature children or with very low birth weight, to prevent them from developing anemia.
What is blood doping?
Blood doping has been defined as the misuse of substances or certain techniques to optimize oxygen delivery to muscles with the aim to increase performance in sports activities.
Why is blood doping so common?
The main reasons for the widespread use of blood doping include: its availability for athletes (erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and blood transfusions), its efficiency in improving performance, and its difficult detection.
What is blood doping?
Blood doping refers to a handful of techniques used to increase an individual's oxygen-carrying red blood cells, and in turn, improve athletic performance.
What happens to the starting gun at an Olympic event?
Once any starting gun is fired at an Olympic event, every split second counts to the elite athletes. And that's where blood doping comes in, particularly in endurance sports.
Why do you need EPO?
RECOMMENDED VIDEOS FOR YOU... When used for legitimate medical reasons, EPO helps with the treatment of anemia related to cancer or kidney disease. Blood transfusions involve drawing out your own blood and storing it for a few months while your body replenishes its red blood-cell supplies.
How long does EPO last?
In addition, EPO is short-lived, remaining in the body for as short a time as two days.
How do red blood cells help the body?
Red blood cells shuttle oxygen through a person's blood, so any boost in their numbers can improve the amount of oxygen the blood can carry to the body's muscles. Then end result is more endurance.
How many urine samples were positive after EPO?
Three weeks after the last EPO injection, only two out of 48 urine samples showed up as positive in lab tests. Nonetheless, the total red blood cells and aerobic capacity of the participants were still elevated at that time.
What does the extra bump mean?
For athletes, the extra bump can mean the difference between a gold and silver medal, or whether or not you break a world record.
What does blood doping do to your body?
Blood doping is meant to raise the amounts of hemoglobin (oxygen-carrying protein in the blood) in the blood stream. A high amount of hemoglobin means that the muscles are able to get enough oxygen required for respiration for energy to be released consequently improving performance as well as stamina. Here are the major pros and cons of blood ...
What are the pros and cons of blood doping?
Athletes and bodybuilders choose to do blood doping to reduce fatigue, enhance performance and build muscles mass enabling them to perform tirelessly even at the most physically demanding activity. Doping does not only assist one in becoming ...
Why is blood doping illegal?
Blood doping is considered an illegal method of enhancing an athlete’s performance by boosting the blood’s ability to carry more oxygen to muscles artificially. The method has been banned by various sports organizations and also by the international Olympic committee as it raises numerous issues. Blood doping is meant to raise the amounts of hemoglobin (oxygen-carrying protein in the blood) in the blood stream. A high amount of hemoglobin means that the muscles are able to get enough oxygen required for respiration for energy to be released consequently improving performance as well as stamina. Here are the major pros and cons of blood doping.
How does blood doping affect endurance?
Thus blood doping: 1. Increases muscle mass. 2. Increases one’s overall weight gain. 3. Increases strength. 4.
Is blood doping good for you?
Finding a fastest and quickest way to winning is human nature and in sports this applies too. Even though blood doping has immediate short term advantages, its side effects and disadvantages outweighs any good that might have possibly come with it. The obsession of winning has prompted people into doing things to their bodies to gain advantage now and immediate without thinking of the compromises they might be getting themselves into in the long ran. Some of the disadvantages that come with blood doping include:
