Some of the potential effects of trauma include:
- Development of unhealthy habits with food and fitness
- More likely to use drugs and alcohol and develop dependence
- Chronic stress from past trauma leads to inflammation throughout the body
- Autoimmune and cardiovascular disease risks are higher
- Anxiety-provoking complications include heart-related damage
- Increased risk of strokes and heart attack
What is the difference between penetrating and blunt trauma?
Penetrating trauma occurs when a foreign object pierces the skin and enters the body creating a wound. In blunt or non-penetrating trauma the skin is not necessarily broken. In penetrating trauma, the object remains in the tissue or passes through the tissues and exits the body.
What are the physiological effects of trauma trauma?
The Physiological Effects of Trauma Trauma sensitizes the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is the body’s central stress response system. You can think of this as the juncture of our central nervous system and endocrine system, which makes us more reactive to stress and more likely to increase the stress hormone cortisol.
What is penetrating trauma and how is it treated?
Penetrating trauma often causes damage to internal organs resulting in shock and infection. The severity depends on the body organs involved, the characteristics of the object, and the amount of energy transmitted. Assessment includes x-rays, CT scans, and MRI. Treatment involves surgery to repair damaged structures and remove foreign objects.
What is the difference between penetrating and Perforating trauma?
In penetrating trauma, the object remains in the tissue or passes through the tissues and exits the body. An injury in which an object enters the body and passes through is called a perforating injury.
What are the three different levels of penetrating trauma?
The mechanism of injury may be categorized as low, medium, or high velocity.
What abdominal organ is commonly injured during penetrating trauma?
The liver is the most commonly injured organ in blunt abdominal trauma and the second most commonly injured organ in penetrating abdominal trauma [3-6]. The liver is a highly vascular organ located in the right upper quadrant (figure 1) of the abdomen and is susceptible to injury from traumatic mechanisms.
What kind of injury causes a penetrating trauma?
Penetrating trauma is an injury caused by a foreign object piercing the skin, which damages the underlying tissues and results in an open wound. The most common causes of such trauma are gunshots, explosive devices, and stab wounds.
Which organ is most susceptible to penetrating trauma?
The intestines were most commonly impacted by penetrating trauma (70.1% of cases), followed by the liver and spleen (19.4% and 17.9%, respectively). The most common mode of injury in penetrating trauma cases was gunshot (85%) and stab wounds (15%).
What are four signs and symptoms of an abdominal injury?
Symptoms and signs – Not all may be presenthistory of injury to the abdominal area.bleeding wound or other obvious injury, possibly with visible intestines.severe pain and possible muscle spasm across the abdominal wall.nausea or vomiting.bruising of the skin.More items...
What are the five most reliable signs & symptoms of blunt abdominal trauma?
Early indications of abdominal trauma include nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine, and fever. The injury may present with abdominal pain, tenderness, distension, or rigidity to the touch, and bowel sounds may be diminished or absent.
What are the elements of penetrating trauma?
The major elements that make up the sum injury seen with penetrating trauma are crushing, stretching, and cavitating injuries. The exact combination of these three components depends heavily on the shape, size, mass, and velocity of the penetrating object along with the type(s) of tissue the object traverses.
How penetrating injuries can cause infection?
Skin penetrating injuries can introduce infectious agents directly into the blood stream, e.g. tetanus and blood borne viruses such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV. It is very important that skin penetrating injuries are minimised e.g. through safe handling and disposal of sharps.
What action should be taken in case of a penetrating wound?
Puncture wounds: First aidWash your hands. This helps prevent infection.Stop the bleeding. Apply gentle pressure with a clean bandage or cloth.Clean the wound. Rinse the wound with clear water for 5 to 10 minutes. ... Apply an antibiotic. ... Cover the wound. ... Change the dressing. ... Watch for signs of infection.
What happens to the body during blunt force trauma?
Blunt impact injuries result from direct contact of a blunt object with a body. A contusion results from the blunt impact of significant force to rupture capillaries underneath the skin surface while leaving the skin surface intact, while an abrasion results from scraping off of the superficial epidermis.
Which solid organ is most frequently injured in a penetrating trauma quizlet?
What organ is most likely involved in blunt trauma? The liver.
Is penetrating trauma can pose a risk to the airways?
Penetrating facial trauma can pose a risk to the airway and breathing; airway obstruction can occur later due to swelling or bleeding. Penetrating eye trauma can cause the globe of the eye to rupture or vitreous humor to leak from it, and presents a serious threat to eyesight.
Which solid organ is most frequently injured in a penetrating trauma quizlet?
What organ is most likely involved in blunt trauma? The liver.
What is the most common cause of abdominal trauma?
Abdominal trauma caused by blunt force is a common presentation in the emergency room seen in adults and children. The chief cause of blunt abdominal trauma in the United States is motor vehicle accidents.
What organs are the primary sources of exsanguination during abdominal trauma?
One of the main causes of death after trauma, with numbers ranging from 40 to 80%, is exsanguination caused by injuries to the abdominal organs. The spleen and liver are the most commonly injured organs as a result of blunt trauma [2].
Where in the body is it most likely to find a visceral wound?
A direct blow from blunt trauma can lead to solid organ rupture and visceral damage causing haemorrhage, contamination with the visceral contents, peritonitis and associated pelvic injuries. The most common organs injured are the spleen, liver and small bowel.
What causes a penetrating trauma?
Penetrating trauma involving the ureter occurs in approximately 4% of patients and is most often caused by a stab or gunshot wound.
What is a penetrating injury?
Penetrating injuries can be broadly divided into high-velocity mechanisms, typically caused by gunshots or other missiles, or low-velocity mechanisms, typically associated with sharp objects such as knives, axes, and glass. This distinction is important because of the different underlying mechanisms of cerebrovascular injury and the vastly greater extent of tissue damage seen with high-velocity penetrating trauma.
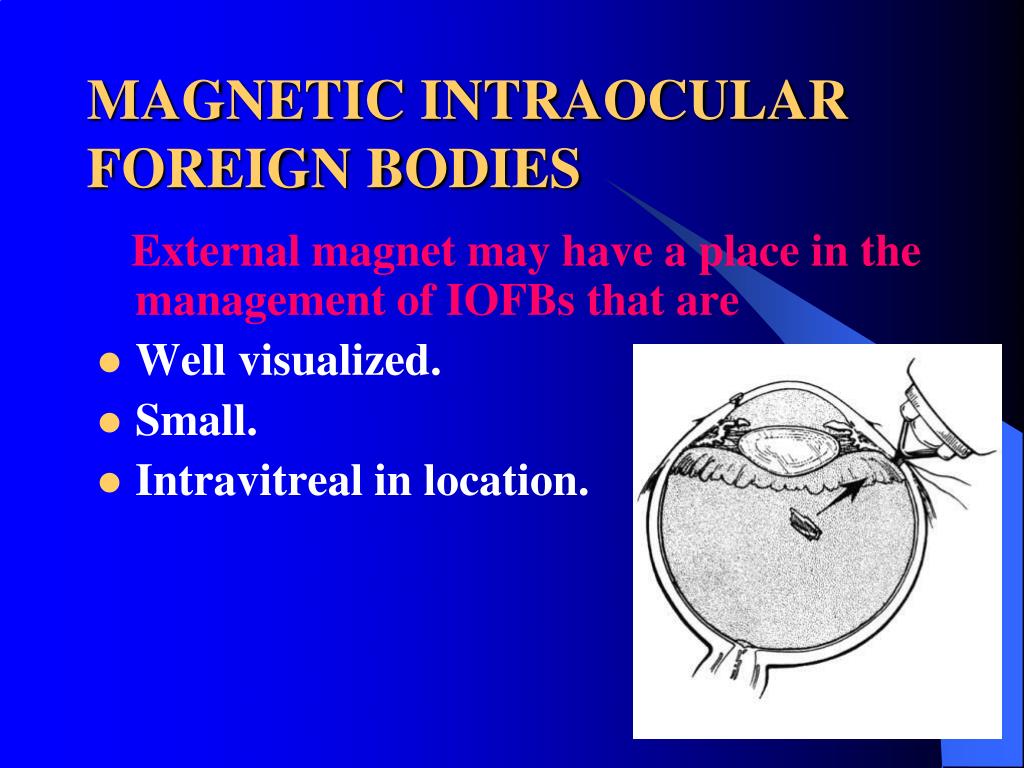
What is the three port technique for vitrectomy?
We employ the standard three-port technique for vitrectomy, proceeding from anterior to posterior, clearing vitreous opacities ( Fig. 140-18 ). As in vitrectomies for penetrating injuries, it is important to identify the posterior hyaloid and, if it is still adherent to the retina, create a PVD. The stump of proliferation growing through the exit site should be reduced but not eliminated, so that the posterior exit site is not reopened. Retinal breaks are managed with air–fluid exchange and endo-photocoagulation or scleral buckling with cryopexy. We routinely advocate an encircling scleral buckle, even in eyes without retinal detachment.
How to repair a penetrating aorta?
Penetrating injuries to the thoracic aorta are usually treated with urgent surgical repair via an anterolateral thoracotomy. Endovascular repair with stent grafts may be possible for penetrating injuries in selected patients (see TAI section).
What is the most common mechanism of upper extremity vascular injury?
Penetrating trauma is the most common mechanism in upper extremity vascular injury. A penetrating mechanism of injury in military series is greater than 90% routinely, and consists of explosive shrapnel and high-velocity gunshot wounds.
How does high velocity trauma affect cerebrovascular injury?
High-velocity penetrating trauma can induce cerebrovascular injury-based predominantly on three underlying mechanisms: (1) direct soft tissue injury, (2) shock wave effects, and (3) thermal injury. Direct soft tissue injury occurs due to direct contact with the penetrating object, such as when a bullet passes through blood vessels, or by the creation of bony fracture fragments, which can act as secondary projectiles ( Moeng and Boffard, 2002; Steenburg et al., 2010 ). Shock wave effects result from the dissipation of kinetic energy into the soft tissues surrounding the penetrating trajectory, as well as the associated cavitation. Thermal injury to blood vessels can be caused by the intrinsically high temperatures of many projectiles.
What causes a thoracic injury to be punctured?
Most penetrating thoracic injuries are due to missile or knife wounds, but the intrathoracic organs are occasionally punctured by a bony fragment resulting from nonpenetrating trauma.
How does trauma affect your body?
Because many traumatic events involve violation of a person’s bodily integrity, they often have adverse influences on physical and mental health and attitudes toward medical care.
What to do if you have experienced trauma?
If you have experienced trauma or violence, you may want to talk to your healthcare provider about what you’ve gone through. You don’t need to go into detail, but it’s important to remember that stressful life experiences influence the way we cope, and our overall health. A good provider will want to be part of your healing journey and will help you find the resources you need. Remember that asking for help is courageous, and that you can survive and thrive after trauma.
Why do people have more ACEs?
For example, people who experience more ACEs are at an increased risk of heart disease and liver disease. This may be due in part to the fact that repeated trauma and violence can change our physiology and influence the way we cope (e.g., smoking, over eating, substance use, or sexual risk taking).
Can you heal alone?
One key to healing is finding people who can support you—these people can be a combination of friends, family, and professionals. No one heals alone.
How does trauma affect the human body?
Actual injuries and wounds are normally outwardly quantifiable and can prompt injury-related actual agony, yet passionate emotional trauma and PTSD can likewise profoundly affect the human body.
How does trauma affect your future?
Untreated past emotional trauma can immensely affect your future wellbeing. The enthusiastic and actual responses it triggers can make you more inclined to genuine ailments including coronary failure, stroke, stoutness, diabetes, and disease, as per Harvard Medical School Study.
What does emotional trauma mean?
At the point when your conviction that all is good has been broken by an unfathomably unpleasant occasion, your body can frequently respond suddenly. Emotional trauma may happen when you experience the accompanying circumstances: Incidents that happen all of a sudden.
How does emotional trauma affect your self esteem?
Low confidence – emotional trauma can influence how you esteem and see yourself. Sadness – encountering a misfortune can be horrendous, including somebody kicking the bucket yet also different sorts of misfortune. Numerous individuals experience distress because of how an emotional trauma has completely changed them.
What chemicals are released when you feel pushed?
At the point when we feel pushed or undermined, our bodies discharge chemicals called cortisol and adrenaline. This is the body’s programmed method of getting ready to react to peril, and we do not influence it.
Is emotional trauma intellectual?
The indications of emotional trauma can show both genuinely and intellectually. The brain is, all things considered, part of the body. Our mind can affect our reaction to torment, our capacity to mend, and our capacity to feel refreshed a lot.
Can pressure signs continue after trauma?
Studies have shown that pressure signs can proceed long after the emotional trauma is finished. This may influence your psyche and body, including how you think, feel and carry on.
What is the healing process of trauma?
Every trauma, whether it occurs in a physiological, cognitive, emotional, or interpersonal form, affects the physical body. The healing of trauma begins in the body. Our body is the accurate history of our experiences in life; therefore, it is essential that we include the body in the healing process.
Why do muscles contract during trauma?
Muscle contractions protect the physical body. Trauma causes very deep muscle contractions designed to protect the body from harm or possible death during a traumatic episode. The contraction in these muscles must be released to restore the body back to its relaxed state.
Why does overemphasis affect body sensitivity?
Overemphasis on thought distorts body sensitivity. Due to an overemphasis on the mind, the result of social and politically ingrained opinions, programming, and stigma, we have deadened this shaking mechanism so that it no longer reduces the muscular tension, causing us to continue to carry it in our bodies long after the trauma is over.
How does PTSD occur?
PTSD is caused by the lack of release of the high excitement or anxiety (biochemical energy) that was generated at the time of the traumatic event. The body continues to seek a discharge from this overstimulation, so the brain unconsciously reproduces situations similar to the original trauma. This is the mind’s attempt to replay the traumatic scenario so that that the energy can be discharged, in the hope that the victim will now become the survivor. The most common example of this is when abused children enter into abusive relationships as adults.
What is the term for the continuation of disturbing thoughts, emotions, and feelings that persist even after the trauma is over?
PTSD is the term used to explain the continuation of disturbing thoughts, emotions, and feelings that persist even after the trauma is over.
What happens if you don't fight or flee?
If you did not have the opportunity to fight or flee, or process the trauma, it is likely you froze and became stuck. Trauma side effects/symptoms are signs of a deregulated nervous system, and this is why natural healing is very useful and a necessary tool in trauma recovery. Written by Erin Paterson.
Why does the body store memories?
Because the experience is emotionally and physiologically overwhelming, the body stores the memories, thoughts, and emotions of the trauma in order to process them at a later date. The high chemical charge left in the body after trauma continually seeks to discharge.
What is the treatment for penetrating trauma?
Assessment includes x-rays, CT scans, and MRI. Treatment involves surgery to repair damaged structures and remove foreign objects.
How much mortality is associated with abdominal trauma?
The literature reveals mortality rates from 0-100%. The lowest mortality is in patients who sustain just a superficial injury to the abdominal wall but if the injury penetrated the peritoneum and is associated with hypotension, acidosis, and hypothermia, the mortality rates are more than 50%. The mortality is greatest in those who suffer a concomitant vascular injury of the abdominal vessels. When the patient is brought promptly to a trauma center, a 5% mortality rate can be expected. The majority of deaths occur within the first 24 hours of injury. Risk factors that predict mortality include female gender, the presence of shock on arrival, delay in treatment and associated head injury. Firearms are usually associated with a much higher morbidity and mortality compared to knife wounds. [17][18][19](Level V)
What is the standard management of penetrating abdominal trauma?
The standard management of penetrating abdominal trauma is a laparotomy. A greater understanding of mechanisms of injury and improved imaging has resulted in conservative operative strategies in some cases.
What determines the severity of an abdominal injury?
The characteristics of the damaged tissue determine the severity of the injury: the denser the tissue, the greater the amount of energy transmitted to it. History and Physical. Penetrating abdominal trauma is due to stabbings, ballistic injuries, and industrial accidents.
What is the most common cause of abdominal trauma?
Penetrating abdominal trauma is seen in many countries. The most common cause is a stab or gunshot. The most common organs injured are the small bowel (50%), large bowel (40%), liver (30%), and intra-abdominal vascular (25%). When the injury is close range, there is more kinetic energy than those injuries sustained from a distance. Even though most gunshot wounds typically have a linear projection, the high-energy wounds are associated with unpredictable injuries. There may also be secondary missile injuries from bone or bullet fragments. Stab wounds that penetrate the abdominal wall are difficult to assess. Occult injuries can be missed, resulting in delayed complications that can add to the morbidity.[1][2][3]
What are the most common causes of occult injuries?
The most common cause is a stab or gunshot. The most common organs injured are the small bowel (50%), large bowel (40%), liver (30%), and intra-abdominal vascular (25%).
How does kinetic energy affect a projectile?
As a projectile passes through tissue, it decelerates and transfers kinetic energy to the tissue. Increased velocity causes more damage than mass. Kinetic energy increases with the square of the velocity.
How long does it take for a trauma patient to fall off?
Although some medical professionals in trauma and emergency medicine counter that there is insufficient evidence that results for a patient involved in trauma fall off after precisely 60 minutes, the principle remains the same: Rapid intervention can make all the difference in patient morbidity and mortality. And in a 2015 editorial in Injury: International Journal of the Care of the Injured, Rogers and colleagues stated: "There is an aspect to trauma care that is very time dependent."
When caring for a patient who's experienced penetrating trauma, hemorrhage control, either?
When caring for a patient who's experienced penetrating trauma, hemorrhage control, either externally by applying pressure or tourniquet, or surgical control is the next order of business after controlling the patient's air and ensuring adequate oxygen delivery. This is often the case even when a concomitant devastating neurological injury is present.
What is the importance of a paper clip in trauma?
Paper clips at the puncture site aid in matching up possible organ involvement on plain films. When available, a focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) scan is an invaluable adjunct. Mapping the path of the bullet or knife and, by inference, the injured organs, forms the basis for timing and type of intervention.
Does hemorrhage control require immediate blood transfusion?
Along with hemorrhage control, a patient who's experienced penetrating trauma needs immediate blood transfusion. Data suggest timely blood administration in a balanced ratio makes a difference, indicates Dr. Turay.
Is IV insertion anxiety normal?
Dr. Turay says that anxiety during IV insertion in high-stakes scenarios is normal. He encourages trauma providers to sharpen IV access skills, remembering that the intraosseous route is equally effective and relatively easier to attain in patients with profound shock.
Is CPR helpful after a heart attack?
Although CPR is a common tool, especially in the field, if the person doesn't have a pulse after penetrating trauma, CPR is not helpful. Unlike a heart attack or a choking incident, the heartbeat's cessation is due to blood loss, rendering this resuscitative method ineffective.
Can you touch an impaled object?
Dr. Turay recommends not touching or removing an impaled object, as it could worsen the injury. Also, he explains it's impossible to know what the object may touch inside the patient's body, perhaps compressing a vessel enough to prevent bleeding out. He suggests waiting for a surgeon to address it, as interference may worsen the injury. Trauma professionals may help the patient, however, with wound packing or a tourniquet for hemorrhage control.
What is a penetrating trauma?
Supporting Author (s): Penetrating trauma is an injury caused by a foreign object piercing the skin, which damages the underlying tissues and results in an open wound. The most common causes of such trauma are gunshots, explosive devices, and stab wounds.
What percentage of penetrating injuries are male?
Males constituted a majority of persons with penetrating injuries, particularly when caused by firearms (88%) and explosives (80-85%). Two-thirds of penetrating injuries (66%-67%) occurred to persons age 18-44, even though this age group represents on 36% of the population.
What are the most common causes of trauma in the US?
The most common causes of penetrating trauma in the US are gunshots and stabbings. One recent study found approximately 40% of homicides and 16% of suicides by firearm involved injuries to the torso. 1 As recently as 2003, the US led in firearms-related deaths in all economically developed countries. 2.
What causes low energy penetrating trauma?
Low-energy penetrating trauma may be caused accidentally by impalement or intentionally by a knife, ice pick, or other weapon.
What is the result of force to the body that causes injury without anything penetrating the soft tissues or internal organ?
Blunt trauma is the result of force to the body that causes injury without anything penetrating the soft tissues or internal organs and cavities.
What to do with a Pt who has experienced a nonsignificant MOI?
With a pt who has experienced a nonsignificant MOI, focus on the chief complaint while assessing the pt as a whole.
What is the most concerning pulmonary blast injury?
One of the most concerning pulmonary blast injuries is arterial air embolism, which occurs on alveolar disruption with subsequent air embolization into the pulmonary vasculature.
What happens when you are close to a blast wave?
When the victim is close to the blast, the blast wave may cause disruption of major blood vessels and rupture of eardrums and major organs, including the lungs.
What happens when a bullet is cavitated?
Cavitation, which results from the rapid changes in tissue and fluid pressure that occur with the passage of the projectile, can result in serious injury to internal organs distant to the actual path of the bullet.
Can broken ribs cause chest wall to expand?
Broken ribs can interfere with the ability of the chest wall to expand normally during breathing.
