
Explore
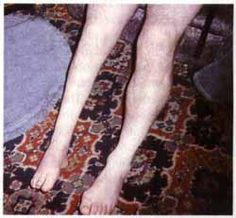
How does polio affect you later in life?
Causes of late effects of polio muscle fatigue and pain due to reduced muscle tissue. pain, and sleep or breathing problems, from postural abnormalities (such as scoliosis or kyphosis) increased stress on joints, leading to arthritis and pain (this may be worsened by weight gain)
Does post-polio syndrome get worse?
Post-polio syndrome (PPS) can cause a wide range of symptoms that can significantly affect everyday life. These tend to develop gradually and get worse very slowly over time.
What is the life expectancy of someone with post-polio?
Outlook. In most cases, post-polio syndrome life expectancy is good. PPS is rarely life-threatening, though symptoms can vary from mild to severe. If you have PPS, talk to your doctor about how to manage your condition.
Does Post-Polio go away?
There's currently no cure for post-polio syndrome (PPS), so treatment focuses on helping you manage your symptoms and improving your quality of life. People with the condition are often treated by a team of different healthcare professionals working together.
Does post-polio syndrome affect brain?
Autopsies in some polio patients have found damage to the brainstem and motor cortex as well as to spinal motor neurons.
Can you regain muscle after polio?
Answer: Research studies have demonstrated that muscle strength and endurance can be improved among polio survivors, even those diagnosed with PPS, through individually designed exercise programs that are monitored and advanced slowly over three to six months.
What parts of the body does polio affect?
Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a disabling and life-threatening disease caused by the poliovirus. The virus spreads from person to person and can infect a person's spinal cord, causing paralysis (can't move parts of the body).
Should post polio patients exercise?
If you have Post Polio Syndrome (PPS), it's vital to exercise moderately every second day to keep the muscles we have and avoid obesity, diabetes, stroke and heart disease. Exercise also helps us accomplish more of those activities of daily living and can improve how we feel.
Which signs are indicative of post-polio syndrome?
Post-polio SyndromeMuscle weakness.Feeling tired (mental and physical fatigue)Joint pain.
What does post-polio feel like?
Common signs and symptoms of post-polio syndrome include: Muscle and joint weakness and pain that gets worse over time. Feeling easily fatigued and exhausted. Losing muscle tissue (atrophy)
How do you test for post-polio syndrome?
Post-polio syndrome (PPS) can be difficult to diagnose because there are no specific tests for it and symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions. Your GP may suspect post-polio syndrome based on your medical history and the results of a physical examination.
What type of doctor treats post-polio syndrome?
Neurologists are physicians who diagnose and treat disorders of the nervous system. They address diseases of the spinal cord, nerves, and muscles that affect the operation of the nervous system.
What are the symptoms of polio?from betterhealth.vic.gov.au
New symptoms recognized by the medical community that may relate to prior polio include: unaccustomed fatigue – either rapid muscle tiring or feeling of total body exhaustion; new weakness in muscles, both those originally affected and those seemingly unaffected; and/or decreased ability to tolerate cold temperatures.
What is Post-Polio Health International?from post-polio.org
Post-Polio Health International recommends that all polio survivors receive consistent, basic medical evaluations. If a patient's symptoms are not explained and alleviated by general medical approaches and the symptoms persist or worsen, a referral is in order.
Why do polio survivors need a neuromuscular exam?from post-polio.org
Post-Polio Health International recommends that all polio survivors have yearly medical examinations and that those who are experiencing any of the persistent new symptoms of weakness, pain, fatigue and breathing problems obtain a comprehensive neuromuscular examination. Some survivors are reluctant to seek medical attention. Reasons for avoiding a physician can include early memories of polio, a recent visit that was not helpful, belief that no physician today understands the late effects of polio, or an inaccessible office or examination table.
How long does it take to forget polio?from post-polio.org
Some patients may describe these symptoms and "forget" to tell you they had polio. This triad of symptoms is typically presented at least fifteen years after the acute case of poliomyelitis, as the North American, Western European and Australasian experience documents. Individuals, now in their seventh or eighth decade, are facing a combination of new polio problems and aging. Because poliomyelitis has not yet been eradicated from the world, survivors will be seeking assistance for years to come.
What is the most serious form of poliomyelitis?from post-polio.org
Paralytic poliomyelitis can be classified as spinal, bulbar or spino-bulbar. Bulbar is the most serious form of polio and involves the part of the brain dealing with the vital functions of respiration and swallowing.
How long does it take for polio to show symptoms?from betterhealth.vic.gov.au
Polio symptoms generally appear between 3 and 21 days after infection. However, many people infected with poliovirus have no symptoms and may not even know they are affected.
How to help a compromised neuromuscular system?from post-polio.org
Heed general advice about eating well, getting the proper amount of sleep, avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking and overeating, and exercising appropriately. Many symptoms result from the overuse and misuse of muscles and joints. Carefully consider which muscles to exercise and how often.
