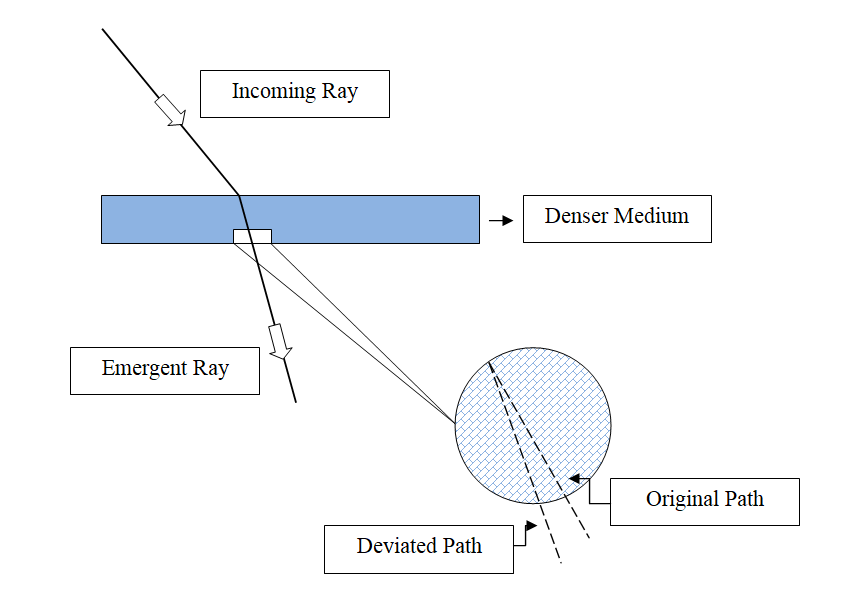
The major effects of refraction of lights are:
- Bending of light.
- Change in wavelength of light.
- Splitting of light rays if it is polychromatic in nature.
What is a real life example of refraction?
- A prism uses refraction to form a spectrum of colors from an incident beam of light.
- Refraction is responsible for the ability of the cornea and lens of the eye to form a real image on the retina.
- Spectacles are worn by people with defects of vision use refraction for providing correct vision.
What happens to the speed of light when refraction occurs?
Refraction occurs when waves travel from one material to another. For light, this can change both the speed and direction. Refraction of light takes place in many places, including lenses and prisms. When a wave or light ray moves from one medium to another its speed changes. The direction of the ray may also change.
What are some things that refract light?
- Your eyes
- Rainbows
- Light bending in a glass of water
- Glasses
- Camera lenses
- Object dislocation in water
- Binoculars
Which of the following changes when light is refracted?
When light travels from air into glass, the light slows down and changes direction slightly. When light travels from a less dense substance to a denser substance, the refracted light bends more towards the normal line. If the light wave approaches the boundary in a perpendicular direction, the light ray doesn’t refract despite the change in speed.
What are three effect of refraction of light?
Ans: The significant effects of refraction of lights are: bending of light, change in wavelength of light, splitting of light rays if it is polychromatic in nature.
What are the effects of reflection and refraction?
Reflection involves a change in direction of waves when they bounce off a barrier. Refraction of waves involves a change in the direction of waves as they pass from one medium to another. Refraction, or the bending of the path of the waves, is accompanied by a change in speed and wavelength of the waves.
What causes refraction?
Refraction is caused due to the change in speed of light when it enters from one medium to another. When the light goes from air into water, it bends towards the normal because there is a reduction in its speed.
How do reflection and refraction affect light differently?
Reflection is when the light goes back to the previous medium, but changes direction. On the flip side, Refraction is when the light is absorbed by the medium, but the direction and speed are affected.
What are 3 differences between reflection and refraction?
Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it strikes a smooth surface. Refraction is the bending of light rays when it travels from one medium to another. Generally occurs on shinny surfaces that only allow rebounding of light without permitting penetration through it.
What are examples of reflection and refraction?
Display different types of objects that reflect and refract. Common objects include mirrors (reflect); glass of water with spoon in it (refract); foil (reflect); oil in a glass bottle (refract); prism (refract); glass (refract); lens (refract); or any shiny surface (reflect).
How do reflection and refraction allow us to appreciate things around us?
Rays of light reflect, or bounce off, objects just like a ball bounces on the ground. This reflection of light is what enables us to see everything around us. Take a look out your window: you see everything in the natural world (that doesn't produce its own light) because it reflects the light of the Sun.
What are the similarities of reflection and refraction?
In reflection of light, the incidence ray, the reflected ray, the normal and the point of incidence lies on the same plane. Similarly In refraction of light, the incidence ray, the refracted ray, the normal and the point of incidence lies on the same plane.
What is Refraction of Light?
Refraction in simple terms is the bending of light when it passes from one transparent substance to another. It also happens with water, sound and other waves. Due to this bending, which causes refraction of light, we are able to have magnifying glasses, prisms, lenses and rainbows. Our eyes would not be able to focus, without the refraction of light.
Why is a lens used for refraction?
A lens is used for refraction in order to form an image like magnification.
What is the bending of light when it passes from one transparent substance to another?
Refraction in simple terms is the bending of light when it passes from one transparent substance to another. It also happens with water, sound and other waves. Due to this bending, which causes refraction of light, we are able to have magnifying glasses, prisms, lenses and rainbows.
Why does a white light split into seven colors?
Whenever a white light passes through a glass prism it splits into seven colour components because of refraction of light.
What are the main aspects of light that fall under the ray optics?
Further. reflection and refraction are the main aspects of the light that fall under the ‘ ray optics’. When light travels in a single direction, it follows a straight path while when it bends, refraction of light happens. Let’s understand the concept of refraction of light and its related components through this blog.
How to find the speed of light in a medium?
The formula is n=c/v where ‘n’ denotes as the index of refraction, ‘c’ as the velocity of light in vacuum and ‘v’ velocity of light in the medium.
How to find the index of refraction?
The formula is n=c/v where ‘n’ denotes as the index of refraction, ‘c’ as the velocity of light in vacuum and ‘v’ velocity of light in the medium.
How does refraction affect light?
Effect of refraction of light is to change the direction in which light is travelling. If a ray of light is incident at a plane boundary at an angle of incidence i then according to Snell’s law, sin (i)/v1 = sin (r)/v2 where r is the angle of refraction and v1 and v2 are velocities of light on either side of the boundary. So, after refraction at the boundary, light travels in a different direction away from the boundary. If the velocity changes continuously in the medium, the angle of refraction also changes continuously and the ray path becomes curved.
What is the first major effect of refraction?
Our eye lens is makes an inverted image of the object which is sent to brain and then it is made erect their and we see can see the things easily.
Why are rainbows so beautiful?
Each droplet produces a cone of light waves, however the maximum angle which the different colours of light refract is slightly different (red has a refraction index of 1.334 I believe, while blue’s is closer to 1.34). Because different colours move at different speeds through the same droplet they refract at different angles, the result is that red refracts the most of all the colours - and thus leaves the drop at the greatst angle. Aka, the outside of the bow. Why the speed is different is a property of refraction, but really you need quantum mechanics to go further.
When light is diffracted, it spreads out onto the exiting space at the end of the diffracting?
The width of the diffracting channel must be equal to or less than the wavelength of the light wave. If the with of the diffracting channel is greater than the wavelength of the light wave, it will simply travel through without spreading out at the exit end.
How does light change direction?
The light wave not only changes directions at the boundary, it also speeds up or slows down and transforms into a wave with a larger or a shorter wavelength. The only time that a wave can be transmitted across a boundary, change its speed, and still not refract is when the light wave approaches the boundary in a direction that is perpendicular to it. As long as the light wave changes speed and approaches the boundary at an angle, refraction is observed.
What is a beam of light made of?
A beam of light is made up of tiny waves. When a beam of light consisting of light waves and travelling in a certain medium falls obliquely on the boundary of another medium, then one part of light waves enters into the other medium first and it's speed changes but the rest of waves enter the other medium a little later and hence it's speed changes a little later. The fact that the speed of light waves on one side of a beam changes a little before th
Does frequency change in light?
No changes are seen in frequency of light.
What is an example of refraction?
An example of refraction is a prism.
What happens when light moves into the eye?
it means that when the light moves from air into the eye (cornea --> lens) it encounters a change of refractive index. this means the speed of light changes and that the angle changes - which is what causes the light to then focus on the retina.
What direction does reflected light fall on?
Now, instead of taking unpolarised light, you take P-polarised light (blue lines in the diagram) and let it fall on the surface of the dielectric at the glorious Brewster angle. The reflected light must be polarized in the S- direction (green dots in the figure). But the intensity in that direction is already zero. Thus, the reflected light has zero intensity, i.e, no light is reflected. The complete light is refracted. You have achieved 100% refraction.
What is the bending of a light wave?
Refraction is the bending of a light or sound wave, or the way the light bends when entering the eye to form an image on the retina.
Why does light split into 7 primary colors?
like white light which on refraction splits up into 7 primary colors upon refraction because different colors have different speeds in different medium other than air or vaccum.
How to see city lights in the evening?
Works really well specially if you are in an urban area. Go to the terrace of a tall building in the evening, which has at least 6 floors. Feast your eyes upon the city lights, preferably the ones which is the farthest within your range of vision.
Is the flickering of the lights a physical refraction?
This is very much the physical approach of expressing refraction!
How does refraction affect the rainbow?
Effects of Refraction in Nature. Rainbow is formed after a shower due to the refraction of sunlight by surfaces of water droplets. When the sun rises, the light coming from the sun refracts through the Earth’s atmosphere and reaches our eye before the sun actually crosses the horizon.
What is the angle of refraction of light rays?
For a particular incident angle namely the critical angle, the refracted ray passes along the interface i.e. the angle of refraction is 90.
What is the relative refractive index of a denser to rarer medium?
Refraction from denser to rarer medium: The relative refractive index is less than 1. The angle of refraction is less than the angle of refraction i.e. the refracted ray shifts away from the normal. Refraction from glass to air falls in this category.
What is the ratio of the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction?
Snell’s Law: The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (angle between the incident ray and the normal) to the sine of the angle of refraction (angle between the refracted ray and the normal) is constant. The constant depends on the two media and the wavelength of the incident light.
What is the phenomenon of light traveling at different speeds?
This phenomenon is known as the refraction of light . Light travels with different speeds in different media. This causes refraction. For refraction from rarer to denser medium, the light ray shifts towards the normal whereas for refraction from denser to rarer medium, light shifts away from the normal. 2.
What happens when light rays are incident?
When a light ray is incident on the surface separating two media, the direction of the ray changes. This phenomenon is known as the Refraction of light. The speed of light is maximum in the vacuum. In any medium, light travels with less speed. Due to this, the direction of light changes at the interface of two different media. The frequency of the incident light remains constant but the speed and wavelength change. When a light ray enters a denser medium, it bends closer to the normal whereas for a lighter medium, the ray shifts away from the normal.
What happens to the frequency of light rays when they enter a denser medium?
When a light ray enters a denser medium, it bends closer to the normal whereas for a lighter medium, the ray shifts away from the normal.
What is the index of refraction in a medium?
Anisotropy. In some special cases, the index of refraction in a medium can depend on the direction in which light passes through the medium. Certain mineral crystals have two distinct indices of refraction along two directions and are known as birefringent materials.
What determines the angle of light rays?
There are several factors that determine at what angle a light ray will bend when passing from one medium into another. Angle of Incidence. If a light ray crosses over from one medium to another -- from air to glass for instance -- perpendicular to the surface between the media, it does not change direction, it passes right through. ...
What is the angle of incidence of light rays?
The angle the light ray makes with the perpendicular in the first medium is called the angle of incidence. The angle the light ray makes with the perpendicular in the second medium is called the angle of refraction.
