4 Essential Elements For A Healthy Plant Growth
- Carbon Dioxide. Plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. ...
- Light. Photosynthesis cannot take place without light since that’s what drives the. ...
- Temperature. Plants cannot survive in extreme temperatures. ...
- pH Level of Soil/Water. Plants need a well-balanced pH level in order to absorb all the nutrients it needs for healthy growth.
What minerals are essential for plant growth?
What minerals are essential for plant growth?
- Nitrogen (N) – used in larger quantities than any other mineral nutrient.
- Phosphorus (P) a.
- Potassium (K) It is used in larger amounts than any other element except N. May have "luxury consumption" plants take up more than is needed.
- Magnesium. a.
- Sulfur (S) a.
- Manganese (Mn) a.
- Iron. a.
- Copper. a.
What are the three nutrients for plant growth?
What are the three most important nutrients for plant growth?
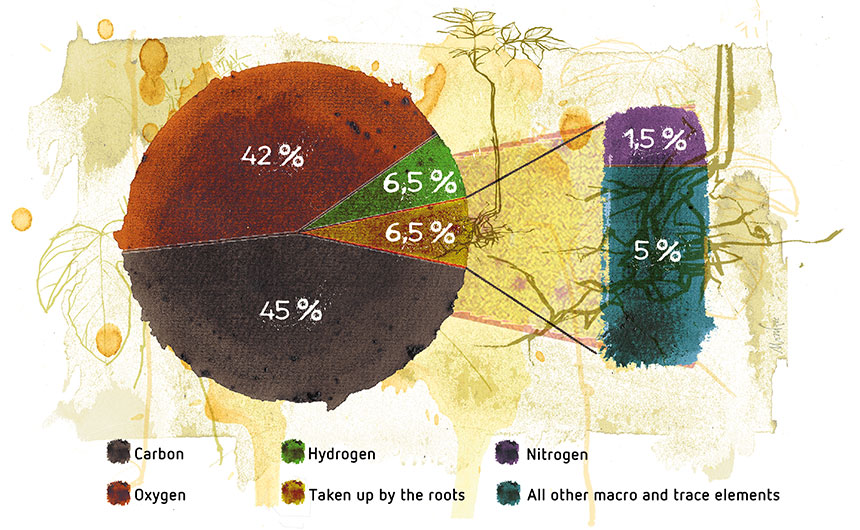
- Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are provided by air and water.
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the macronutrients.
- Calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are examples of secondary nutrients.
- A variety of micronutrients are present, including the elements boron, chlorine, copper, copper alloy, ferrous iron, manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), and zinc (Zn).
What are the four elements plants need to grow?
water, space in which to live, air, and optimal temperatures in order to grow and reproduce. For most plants, these needs are summarized as light, air, water, and nutrients (known by the acronym LAWN). Students will conduct an experiment to evaluate whether plants need air in order to survive and grow. II. Objectives
What is the best nutrient for plant growth?
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2) – Plants absorb CO 2 from the air, combining it with water and light to make carbohydrates—a process more commonly known as photosynthesis.
- Hydrogen (H) – Hydrogen is a part of water ( H2O). ...
- Oxygen (O) – Along with what has been described above, plants consume oxygen through their pores—even at night. ...

What are the three elements essential for plant growth?
The primary nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. You may be most familiar with these three nutrients because they are required in larger quantities than other nutrients. These three elements form the basis of the N-P-K label on commercial fertilizer bags.
What is the most essential element for the growth of plant?
Nitrogen (N) is made available to the plant from the air and soil. But most of the needed elements that are nutrients for plants come from the soil. They are not all equally important but all play a role in plant growth. Most needed are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), and sulphur (S).
What are the essential elements of a plant?
Plants require 17 essential elements for growth: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur (S), cal- cium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), and zinc (Zn).
What are the 20 essential elements for plant growth?
There are actually 20 mineral elements necessary or beneficial for plant growth. Carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) are supplied by air and water. The six macronutrients, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S) are required by plants in large amounts.
Why are essential elements essential to plants?
Key Points An element is essential if a plant cannot complete its life cycle without it, if no other element can perform the same function, and if it is directly involved in nutrition.
What is the essential for plant growth and survival?
Plants, like all living organisms, have basic needs: a source of nutrition (food), water, space in which to live, air, and optimal temperatures in order to grow and reproduce. For most plants, these needs are summarized as light, air, water, and nutrients (known by the acronym LAWN).
What are the 18 essential elements in plants?
Summary. Plants require 18 essential nutrients to grow and survive, classified by their importance into macronutrients (C, H, O, N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S) and micronutrients (B, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Mo, Cl, Co, Ni).
What are 16 essential elements of plants?
Plants require 17 essential elements for growth: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur (S), cal- cium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), boron (B), chlorine (Cl), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), and zinc (Zn).
Why do plants need the 16 essential elements?
Like humans, plants require certain key nutrients to grow well, develop, reproduce and remain healthy. The performance of a crop in the field depends on the genetic makeup of the variety grown, fertility and pesticides programs, and interaction with the environment.
What are the 18 essential elements in plants?
Summary. Plants require 18 essential nutrients to grow and survive, classified by their importance into macronutrients (C, H, O, N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S) and micronutrients (B, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Mo, Cl, Co, Ni).
What are essential and non essential elements in plants?
The 17 Essential Plant Elements include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, boron, chlorine, iron, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and nickel. The non-mineral essential plant elements include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. These are either taken up as a gas or water.
What are the 5 essential elements of life?
1. Note that most living matter consists primarily of the so-called bulk elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur—the building blocks of the compounds that constitute our organs and muscles. These five elements also constitute the bulk of our diet; tens of grams per day are required for humans.
What does essential element mean?
Legal Definition of essential element : an element of a tort or especially a crime that must be alleged in the complaint or charging instrument (as the indictment) in order to make out a prima facie case.
What are essential elements?
These elements have specific structural or physiological roles. These are required for plants to complete their life cycle—examples: Carbon, hydrog...
What are the six most important elements?
The six most important elements are C, H, O, N, P and S.
What are non-essential elements?
These elements are required in some plants but not all. Their absence does not produce any major deficiency symptoms in plants—examples: cobalt, si...
Write down the role of potassium in plants?
a. Potassium maintains osmotic balance in cells and anion-cation balance in the cells. b. It is needed for stomatal opening and closing and synthes...
Write the deficiency symptoms of magnesium?
The deficiency symptoms of magnesium are necrosis, chlorosis, stunted growth, and improper synthesis of protein.
How many elements are needed for plant growth?
Plant growth is solely dependent on 17 different elements. The presence of all these chemical elements in perfect proportion is primarily responsible for the healthy growth of a plant. As a gardener, you must know about these 17 essential elements. All these elements have been classified into specific categories.
What are the three elements that are essential to plant life?
Some essential elements are primarily derived from fertilizers . Nitrogen (N), Potassium (K), and Phosphorus (P) are three elements.
What is Plant Nutrition?
Every living thing needs nutrients for its survival and so do plants. These nutrients facilitate the life cycle of the plant and its growth. There are 16 such nutrients, which the plant might need, and out of these sixteen, nine are essential and the other seven are required by the plants but in the absence of the remaining seven, the plant would not die. The nutrients can be further classified into the following:
What are the secondary nutrients in plants?
The Secondary Nutrients consist of Magnesium (Mg), Sulfur (S), and Calcium (Ca) which though are required in smaller amounts are required by the plant for various reasons. Magnesium is a part of Chlorophyll pigment without which Photosynthesis would not be possible and the plant would fail to prepare food and energy.
What is the most important component of the cell wall?
Boron is an important component of the cell walls. Besides sit also helps in the transportation of sugar and cell division. Manganese helps in the building of Chloroplasts and it also activates enzymes. Iron also helps in photosynthesis and enzyme reactions. It also helps in the synthesis of chlorophyll.
Why is zinc important for plants?
These nutrients are required in very small quantities as the name suggests. Zinc has a huge role to play in the stimulation and activation of enzymes; therefore it is required though in a small amount for the proper functioning of the plant. Copper is also important for Photosynthesis and it a part of various enzymes.
What is the best way to replenish soil?
These elements are responsible for the maximum growth of the plants. Adding fertilizers to the soil is one of the best methods to maintain a minimum required level of replenishment. As the name suggests, secondary micronutrients are added with primary micronutrients.
What are the nutrients that plants need?
A very few plants need five other nutrients: cobalt, nickel, silicon, sodium, and vanadium.
What are the five essential nutrients that plants need?
A very few plants need five other nutrients: cobalt, nickel, silicon, sodium, and vanadium. Each essential nutrient affects specific functions of plant growth and development (Table 1). Plant growth is limited by the nutrient that is in the shortest supply (Fig. 1).
How do plants get nutrients?
Plants take in almost all of the essential nutrients through their roots. The exception is carbon, which is taken in through leaf pores, or stomata. Two types of organisms living in the soil help the roots take up nutrients: 1 Microorganisms, or microbes, break down organic compounds into inorganic compounds in a process called mineralization. 2 Fungi enable some plants to take up phosphorus by increasing the size of the roots and providing more soil-to-root contact.
How to tell if soil has nutrient problems?
It is hard to tell whether the soil has a nutrient problem just by looking at the plants. Symptoms vary by nutrient and plant species. Common symptoms include: Little or no growth. Dead tissue at the leaf tips, on the leaf edges, or within the leaves. Yellow or dead leaves on one part of the plant only.
What happens if a plant doesn't have a nutrient?
A plant that lacks an essential nutrient cannot complete its life cycle—the seed may not germinate; the plant may not be able to develop roots, stems, leaves, or flowers properly; or it may not be able to produce seeds to create new plants. Often the plant itself will die.
What is the essential nutrient?
To be used by a plant, an essential nutrient must be broken down into its basic form. The nutrient must be in the form of either a positively charged ion (cation) or a negatively charged ion (anion). A plant cannot use organic compounds, such as those in manure or dead leaves, until they are broken down into their elemental or ionic forms.
How do fungi take up phosphorus?
Fungi enable some plants to take up phosphorus by increasing the size of the roots and providing more soil-to-root contact.
What are the essential elements for plants?
This article throws light upon the functions of various essential elements in the growth of plants. The essential elements are: 1. Carbon, Oxygen and Hydrogen 2.
Why is phosphorus important for plants?
Phosphorus is essential for cell division and development of the meristematic tissues at the growing points and for root growth. It offsets the harmful effects of excess nitrogen in plants.
What is the phosphorus in the cell?
Phosphorus is a constituent of the cell nucleus, and metabolically active compounds like nucleic acids, adenosine di and triphosphate etc. Nucleic acids are essential for the transfer of genetic information and A.D.P. and A.T.P. are involved in energy transfer, A.D.P. is involved in basic reactions of photosynthesis.
What is the main structural component of the cell?
Nitrogen: Nitrogen is a major structural constituent of the cell. It is also an essential constituent of metabolically active compounds like proteins, nucleic acids, chlorophyll, enzymes, adenosine di and triphosphates (A.D.P. and A.T.P.) hormones etc. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Why is boron important?
Boron is required for proper development of tissues, particularly the vascular elements. Boron deficiency causes the necrosis of tissues and sterility and malformation of the reproductive organs. It is also involved in the translocation of sugars in plants.
How does potassium affect crops?
Potassium increases the resistance of crops to hot and dry conditions and insect pests and disease s. It increases the stiffness of straw in cereals and therefore the lodging of cereals is reduced. It improves the quality of fruits and grains. 5.
What are the constituents of all organic compounds?
1. Carbon, Oxygen and Hydrogen: Carbon, oxygen and hydrogen are the major constituents of all organic compounds, of which crops are made and they are concerned with different metabolic reactions which are vital for the growth of plants. Carbohydrates fats and proteins are oxidized to liberate energy which is essential for all living organisms.
What are the elements that promote plant growth?
Further, Pilon-Smits et al. (2009) consider cobalt (Co), sodium, selenium (Se), and silicon, as well as aluminum (Al), as merely beneficial elements. Accordingly, these elements can promote plant growth and may in fact be essential to some species. They have been reported to enhance plant resistance to some biotic stresses (like pests and diseases) and abiotic stresses (like drought and those stresses associated with soil properties).
Why is it important to have an element in a plant?
Based on the first criterion, an element is considered essential if, in its absence, a normal plant is unable to complete its life cycle which includes the production of viable seed. In other words, the presence of the element must ensure the formation of a seed that possesses the natural capability to germinate and develop into a mature plant under favorable conditions for growth.
How Many Essential Elements Are There?
Quantitative analysis has in fact shown that plant tissues can contain any or a combination of more than 60 elements.
How many elements are needed for plants to reproduce?
Plants require for their growth and reproduction at least 16 essential elements. At least 16 is highlighted because some authorities strongly argue the inclusion of other elements into the original list of 16. Clearly, some elements have been shown essential at least in some species. For example, the essentiality of cobalt has been established for nitrogen fixation in legumes.
How many elements are in Ni?
Based on these criteria, Hopkins (1999) concluded that there has been a general agreement for the inclusion of nickel (Ni) into the list of essential micronutrients, thus increasing the number of essential elements to 17 from Arnon and Stout-compliant’s 16.
How many elements are considered essential?
According to nutrients.ifas.ufl.edu (2004), the number of chemical elements that are considered essential ranges from 16 to 20 or even more largely because of differences in the definition of essential elements. Citing D.J.D. Nicholas (1961), an element should be considered essential if its addition enhances plant growth even though it merely substitutes for one of the 16 elements that Arnon declares to be essential. Accordingly, Nicholas listed 20 essential elements including sodium (Na) and vanadium (V).
Why are elements essential?
Based on the third criterion, an element is essential because it is indispensable to plant nutrition and does not merely correct some unfavorable conditions of the soil or culture medium. For example, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and magnesium are essential elements because they are part of the chlorophyll molecule (Chl a = C55H72O5N4Mg) and the presence of chlorophyll is essential in photosynthesis.
What are the elements that plants need to survive?
Plants require several different chemical elements in order to thrive. Oxygen, carbon and hydrogen are found in water and air; secondary nutrients that plants need include magnesium, calcium and sulfur. Beyond that, plants also need such micronutrients as zinc, molybdenum, copper, manganese, cobalt, iron and boron.
What are the three elements that are found in fertilizers?
Potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen are created in nature from decomposing plants that have died. To stimulate plant growth, gardeners and farmers use fertilizers that contain the three essential macronutrients. Most fertilizers on the market contain large amounts of potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen. Since the other chemical elements aren't as ...
What are the building blocks of plants?
The reason for this is that the basic building blocks of every plant are ATP, cell membranes and amino acids. Nitrogen is an element in every amino acid; ATP, which is the primary source of energy for all cells, contains phosphorus. Potassium is essential to a plant's ability to metabolize.
What is the importance of potassium in plants?
Potassium is essential to a plant's ability to metabolize. This element also comprises up to two percent of a plant's weight. Plants that don't receive enough of these three essential macronutrients will be severely limited in their ability to grow since they would also be deprived of the basic building blocks.
Is nitrogen in fertilizer?
Since the other chemical elements aren't as crucial to plant growth, as well as being found abundantly in most soils, they're not included in most fertilizers. Every bag of fertilizer has printed on it the exact percentages of potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen that are contained in the fertilizer mix. The remaining material in a standard bag of ...
How many essential plant elements can be remembered?
The 17 essential plant elements can be remembered using a clever Mnemonic device that my botany professor Dr. Max Bell taught me in my undergraduate days at Truman State University. Here is the mnemonic device to remember the 17 essential plant nutrients of higher plants:
What are the non-mineral elements in plants?
The non-mineral essential plant elements include hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. These are either taken up as a gas or water. There are 4 elements that are beneficial to promote plant growth but are not considered to be necessary for completion of the plant life cycle. They are silicon, sodium, cobalt, and selenium.
What are the elements that are considered macronutrients?
The macronutrients include nitrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and sulfur. The micronutrients are chloride, iron, boron, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and nickel.
Where do the minerals in hydroponics come from?
In hydroponics, these mineral elements come from either the fertilizer salts you add to your source water or are already present in your source water. The macronutrients carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen come from either water or gases in the air.
How many clusters of elements are there in the periodic table?
Figure 1 illustrates the essential and beneficial elements location on the periodic table. You can see that there are three clusters of elements within the periodic table.
What are the elements that plants need to grow?
Did you know that there are over 18 elements plants need in order to grow? Macronutrients plants need are those elements that your plants will use lots of, whereas micronutrients are used in small amounts to grow. We'll start with the big three macronutrients: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O). These may seem like a no-brainer, but these elements are essential to all life on earth, especially planets. Do they look familiar? That's because plants get these elements from the air (CO2) and from water (H2O), and these two compounds create the basis for sugars and starches your plants need. These will give strength to and build cellular walls, leaves, and stems. The second set of macronutrients are the three we're all aware of: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). These elements are what help your plant break down elements it needs to survive, help turn light and water into food for your plants, and help build the strength of your plants. Specifically, (N) is found in chlorophyll, amino, and nucleic acids, and in proteins and enzymes. (P) helps cell membranes and has a big role in the ATP (energy system) of a plant. (K), on the other hand, is heavily involved in photosynthesis and resilience especially when it comes to droughts. The last set of macronutrients your plants need are Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), and Sulfur (S). While not used as much as their macronutrient counterparts, these elements are vital in assuring your plant's survival. (Ca), for example, helps strengthen cell walls and helps deliver nutrients when your plants are stressed. (Mg) is vital in chlorophyll production, function, and breaking down enzymes, whereas (S) is important in creating chlorophyll and creating proteins for your plant.
What are the elements that help plants grow?
No matter what they are, you'll want to make sure that your plants receive these elements at the right stage in growth: Boron that helps the structure of your plant as well as assisting the functions of plant cells. Iron helps energy transfer and helps nitrogen go where it needs to in your plants.
What are the two macronutrients that plants need to survive?
The second set of macronutrients are the three we're all aware of: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). These elements are what help your plant break down elements it needs to survive, help turn light and water into food for your plants, and help build the strength of your plants.
Why is nickel important to plants?
Nickel is important to the metabolism of plants because it helps turn urea nitrogen into useable ammonia. Without it, nitrogen would probably toxify your plant.
What are the micronutrients that grow?
Micronutrients vital for your grow are Iron (Fe), Boron (B), Copper (Cu), Chlorine (Cl), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mo), Zinc (Zn), Cobalt (Co), and Nickel (Ni). They may not be absorbed as much as macronutrients, but their presence in your feeding regimen is important to the growth of your plants. Some micronutrients are needed ...
Why do plants need cobalt?
Cobalt’s needed to create buds, leaves, and stems in order to get more light and make CO2 available for your plant . Remember: without all of these essential elements your plants are going to struggle to give you the yield you're looking for.
How many elements are essential for plants?
However, among the mineral elements absorbed by the plants, not all are essential. Out of 105 or more elements discovered so far, only 20 elements have been found to be essential for growth and development of the plant.
What is the role of essential elements in plant life?
An essential element is known, without which the plant cannot complete its life cycle. It has clear physiological role to play.
What are the micronutrients in plants?
The micronutrients or trace elements are: iron, manganese, copper, molybdenum, zinc, boron and chlorine. Recently some other such elements have also been discovered, e.g., cobalt, vanadium and nickel.
What are the two forms of nitrogen in soil?
They fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil in the form of nitrites (NO 2 ), and nitrates (NO 3 ). These heterotrophic organisms, occurring in the soil convert nitrogen gas (N 2) to anionic forms such as nitrates (NO 3) or nitrite (NO 2– ), or a reduced cationic form such as NH 4+ (ammonium).
How do nitrogenous compounds enter plants?
These nitrogenous compounds enter plants as nutrients through the roots and are assimilated as organic nitrogen. The plants, in turn, provide organic nitrogen to heterotrophic organisms. The other elements are absorbed from the soil, such as phosphorus (P) as phosphate (PO 4 ), and sulphur (S) mainly as sulphate (SO 4).
Why is chlorine needed in photosynthesis?
It is required for cell division in roots and leaves. It is needed to perform water-splitting reaction in photosynthesis, which evolves oxygen.
Why is phosphorus important?
This is needed for all phosphorylation reactions. It plays a very important role in the ripening of the grains and fruits. This also helps a lot in the development of root system. For the development of underground parts of radish, beet root, and potato, etc., this element is required. Phosphorus is absorbed from the soil in the form of phosphate H 2 PO − ions.
Which element imparts vigorous vegetative growth and also results delay in maturity of plants?
A single magnesium atom is bonded in the centre of each porphyrin ring. (iii) Nitrogen also imparts vigorous vegetative growth dark green colour to plants. (iv) It produces early growth and also results delay in maturity of plants. (v) It governs the utilization of potassium, phosphorus and other elements.
What is the role of magnesium in plants?
Magnesium increases the affinity of the enzyme for carbon dioxide. (ix) Magnesium brings about significant increases in the oil content of several crops. (x) Magnesium regulates the uptake of other nutrients and the base economy of plants. Plant Nutrient # 6. Sulphur:
Why is phosphorus important for plants?
An adequate supply of phosphorus early in plant life is important for the reproductive parts of the plants. (iii) It is also an essential constituent of majority of enzymes which are of great importance in the transformation of energy, in carbohydrate metabolism, in fat metabolism and also in respiration of plants. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the role of boron in plants?
(ii) Boron increases the solubility of calcium as well as mobility of calcium in the plant. (iii) It acts as a regulator of K/Ca ratio in the plant. (iv) It helps in the absorption of nitrogen.
What is the function of nitrogen?
The important functions of it are as follows: (i) Nitrogen is an essential constituent of proteins and is present in many other compounds of great physiological importance in plant metabolism e.g. nucleotides, phosphatides, alkaloids, enzymes, hormones, vitamins, etc. It is, therefore, a basic constituent of “life.”.
What is the function of sulphur in plants?
One of the main functions of sulphur in proteins or polypeptides is the formation of disulphide bonds between polypeptide chains.
Why is the vegetative portion of a plant more succulent?
Less carbohydrate is thus deposited in the vegetative portion, more protoplasm is formed, and, because protoplasm is highly hydrated, a more succulent plant results. Excessive supply of nitrogen develops excessive succulence which results harmful effects in some crops like weakening of fibre in case of cotton, lodging in case of grain crops etc.