During anaphase, the following key changes occur:
- The paired centromeres in each distinct chromosome begin to move apart.
- Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a "full" chromosome. ...
- Through the spindle apparatus, the daughter chromosomes move to the poles at opposite ends of the cell.
- The daughter chromosomes migrate centromere first and the kinetochore fibers become shorter as the chromosomes near a pole.
What are the major events that occur during anaphase?
- Prophase: condensation of chromosomes begins
- Metaphase: arrangement of chromosomes at the centre often called metaphase plate or equatorial plate
- Anaphase: separation of sister chromatids and movement towards the poles
- Telophase: restoration of interphase condition
- Cytokinesis: it is the division of cytoplasm
What are facts about anaphase?
anaphase One of several stages of cell division. In mitosis the chromatids of each chromosome move apart to opposite ends of the spindle. In the first anaphase of meiosis, the paired homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends; in the second anaphase the chromatids move apart, as in mitosis.
What are four things happen in prophase?
What four things happen in prophase? 1) The nuclear membrane disintegrates 2) The nucleolus disappears 3) Chromatin condenses into chromosomes 4) abiotic spins forms between poles. Spindle apparatus. Moves and organized chromosomes prior to division; composed of spindle fibers, centrioles and aster fibers.
What is the significance of anaphase in this process?
What is the significance of anaphase in this process? answer choices . Anaphase usually ensures that each daughter cell has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Anaphase usually ensures that each daughter cell has twice as many chromosomes as the parent cell. In anaphase, the cell splits in half. ...

What are the events of telophase?
During telophase, the chromosomes begin to decondense, the spindle breaks down, and the nuclear membranes and nucleoli re-form. The cytoplasm of the mother cell divides to form two daughter cells, each containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell.
What are the 3 things happen in anaphase?
In anaphase, cohesin proteins binding the sister chromatids together break down. sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles. non-kinetochore spindle fibers lengthen, elongating the cell.
What is the most important event during anaphase?
Complete answer: Anaphase comprises of the following events : -The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate from their respective mates and begin to move toward the opposite poles.
What happens at the end of anaphase?
Once anaphase is complete, the cell moves into telophase.
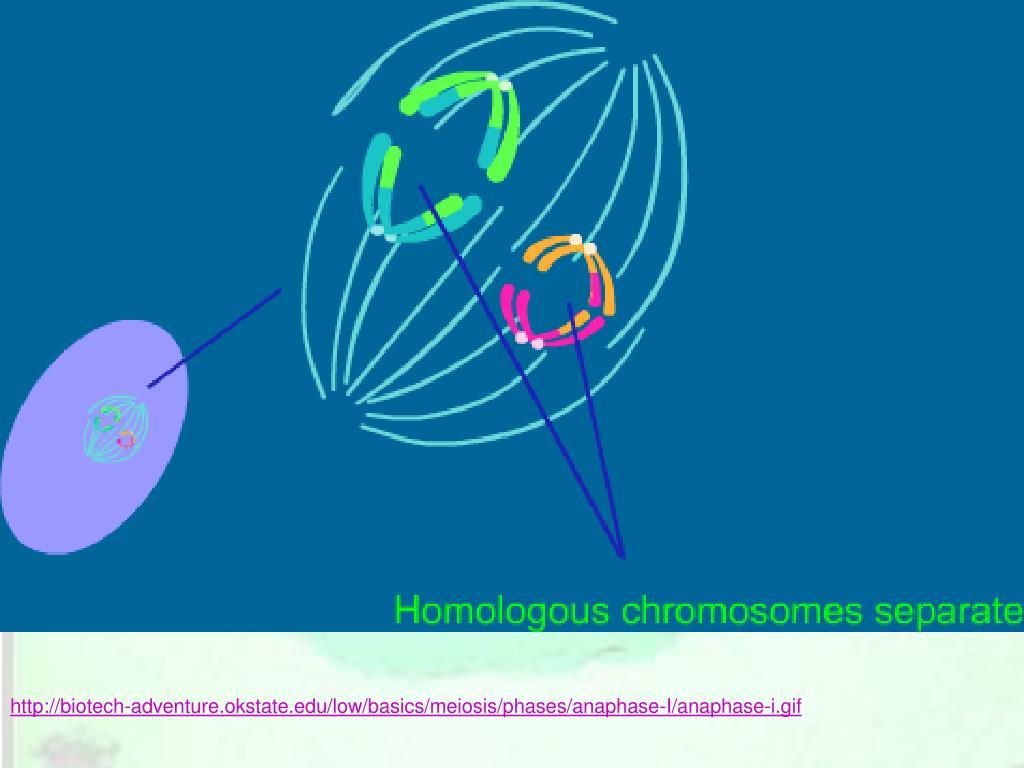
What happens in the anaphase 1?
Anaphase I begins when homologous chromosomes separate. The nuclear envelope reforms and nucleoli reappear. The chromosomes coil up, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, and the centrosomes begin moving apart. Spindle fibers form and sister chromatids align to the equator of the cell.
Which of the following is the main feature of anaphase?
So, the correct option is 'Centromeres split and chromatids separate'
What is the event that occurs during anaphase 2?
Anaphase II is the stage when sister chromatids of every chromosome separate and begin to move towards the opposite ends of the cell. The separation and the movement is due to the shortening of the kinetochore microtubules.
What is the most important change that occurs during anaphase Why is it important?
Anaphase is a very important stage of cell division. It ensures that duplicated chromosomes, or sister chromatids, separate into two equal sets. This separation of chromosomes is called disjunction. Each set of chromosomes will become part of a new cell.
Which occurs in anaphase quizlet?
What happens during Anaphase? The spindle fibers SPLIT APART the sister chromatids and move them to opposite ends of the cell, equally dividing the genetic material.
What must happen for anaphase to begin?
Anaphase begins when the cohesion proteins located between the sister chromatids disappear; the sister chromatids, located at the equator of the metaphase plate, separate and begin their migration toward the opposite poles of the mitotic spindle.
Which of the following is the main feature of anaphase?
So, the correct option is 'Centromeres split and chromatids separate'
What happens in anaphase II of meiosis?
Anaphase II: The chromatids split at the centromere and migrate along the spindle fibers to opposite poles. Telophase II: The cells pinch in the center and divide again. The final outcome is four cells, each with half of the genetic material found in the original. In the case of males, each cell becomes a sperm.
What Happens During Anaphase I?
How the chromosomes are brought to each side of the cell during anaphase is now understood as a breakdown of the microtubule network, shortening the microtubule (MT) fibers and hence bringing each chromosome closer to its final destination. Kinetochore function is therefore crucial, as these keep the chromosomes attached, like abseiling rope clips, to a rope that may fray at any moment. As most kinetochores are attached to more than one microtubule – usually a bundle – the breakdown of single sections of microtubule does not lead to the detachment of a chromosome from the spindle, yet this attachment must still be strong. Some scientists liken the kinetochore to microtubule bundle connection to the Chinese finger trap, where any traction forces create an even stronger attachment.
What happens to the spindle during meiosis?
An improperly attached chromosome or incompletely developed spindle network during meiosis leads to infertility or miscarriage. The dissolving of the nuclear membrane, allowing centrosomes to migrate to both cell poles, is not timed according to spindle development. This means that the spindle network might not be completed in time for the separation of the chromosome pairs in meiosis I, or of the single chromosomes in meiosis II. Alternatively, early disintegration of the nuclear membrane means that the spindle apparatus can be completely formed prior to anaphase.
What happens to the two socks in meiosis?
In meiosis, the outcome will be a new human and a combination of two completely different people. However, the replication method is the same, and there are two black, white and yellow socks clipped together, and two red, blue and green socks clipped together. During meiosis, an exact copy is not the desired outcome, so the red of one sock swaps with the white of one of the other colored socks (crossing over). We now have one black, white and yellow sock, one red, blue and green sock, one black, red and yellow sock, and one white, blue and green sock. They remain clipped together, but are no longer exact pairs – they have undergone recombination and therefore represent a tetrad – two completely different sock pairs. The pairs are now ready to be pulled to different sides of the cell during anaphase I. This means that the resulting two daughter cells both contain a slightly different but complete set of genetic information – two clipped-together socks each. Of course, this is extremely oversimplified, as hundreds of alleles will be swapped between chromosomes. But this analogy is meant to keep a confusing subject simple to understand.
What is a pair of chromosomes that are recombinated during meiosis?
Upon recombination, a pair of chromosomes is referred to as a tetrad . In mitosis, crossing over does not occur and the resulting replicated chromosome pairs are just that, chromosome pairs. So the tetrad refers solely to a pair of recombined chromosomes during meiosis. Crossing over – tetrad formation.
Which stage of meiosis is the third stage?
Anaphase I is the third stage of meiosis I and follows prophase I and metaphase I. This stage is characterized by the movement of chromosomes to both poles of a meiotic cell via a microtubule network known as the spindle apparatus. This mechanism separates homologous chromosomes into two separate groups.
Is the dissolving of the nuclear membrane timed?
The dissolving of the nuclear membrane, allowing centrosomes to migrate to both cell poles, is not timed according to spindle development. This means that the spindle network might not be completed in time for the separation of the chromosome pairs in meiosis I, or of the single chromosomes in meiosis II.
Is mitosis anaphase?
Firstly, there is no anaphase I in mitosis, only anaphase. Mitosis is a single-step process where one cell becomes two. Meiosis is a two-step process, first creating two cells out of one, and then four cells out of those two.
Abstract
Aneuploidy results from the malsegregation of one or more chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis.
Citation Formats
Sluder, G, and Rieder, C L. The events and regulation of anaphase onset. United States: N. p., 1993. Web.
What is the term for the early metaphase?
Prometaphase is often referred to as “late prophase.” (Though it’s also sometimes called “early metaphase” or referred to as a distinct phase entirely!) Regardless, some really important things occur during prometaphase that propel cell division along and that help explain what happens in metaphase.
What happens during prometaphase?
The short version of what happens during prometaphase is that the nuclear membrane breaks down .
What Is Mitosis?
Mitosis is a process that occurs during the cell cycle. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two new cells, known as “daughter cells.” In order to pass its genetic material to the two new daughter cells, a parent cell must undergo cell division, or mitosis. Mitosis results in two new nuclei—which contain DNA—that eventually become two identical cells during cytokinesis .
What is the line that divides the sister chromatids down the middle of the cell called?
This imaginary line dividing the cell down the middle is called the metaphase plate or equatorial plane .
How many phases does mitosis occur in?
In order to accomplish this goal, mitosis occurs in four discrete, consistently consecutive phases: 1) prophase, 2) metaphase, 3) anaphase, and 4) telophase . We have an overview of mitosis here, which is more of an intro to what mitosis is and how it works. If you're a little shaky on mitosis still, that's definitely where you should start.
What is interphase in biology?
We can think of interphase as a transitional phase. Interphase is when the parent cell prepares itself for mitosis. This phase isn’t considered part of mitosis, but understanding what happens during interphase can help the steps of mitosis make a little more sense.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The main purpose of mitosis is to accomplish cell regeneration, cell replacement, and growth in living organisms. Mitosis is important because it ensures that all new cells that are generated in a given organism will have the same number of chromosomes and genetic information. In order to accomplish this goal, mitosis occurs in four discrete, consistently consecutive phases: 1) prophase, 2) metaphase, 3) anaphase, and 4) telophase .
What happens during prophase?
In prophase, the chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles form at opposite poles of the cell. Prophase (versus interphase) is the first true step of the mitotic process. During prophase, a number of important changes occur:
What is the S phase in biology?
S phase: The period during which DNA is synthesized. In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized. The S stands for synthesis.
How are chromosomes held in the metaphase plate?
Chromosomes are held at the metaphase plate by the equal forces of the polar fibers pushing on the centromeres of the chromosomes.
What is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes are evenly divided between two cells?
Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where chromosomes in the nucleus are evenly divided between two cells. When the cell division process is complete, two daughter cells with identical genetic material are produced.
How do chromosomes move?
Chromosomes move randomly until they attach (at their kinetochores) to polar fibers from both sides of their centromeres.
When do diploid cells begin to form?
It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophase/mitosis. At the end of cytokinesis, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells, with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes.
Why do centrioles move away from each other?
The two pairs of centrioles (formed from the replication of one pair in Interphase) move away from one another toward opposite ends of the cell due to the lengthening of the microtubules that form between them.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/meiosis_anaphase_1-56a09b4c5f9b58eba4b2052b.jpg)