
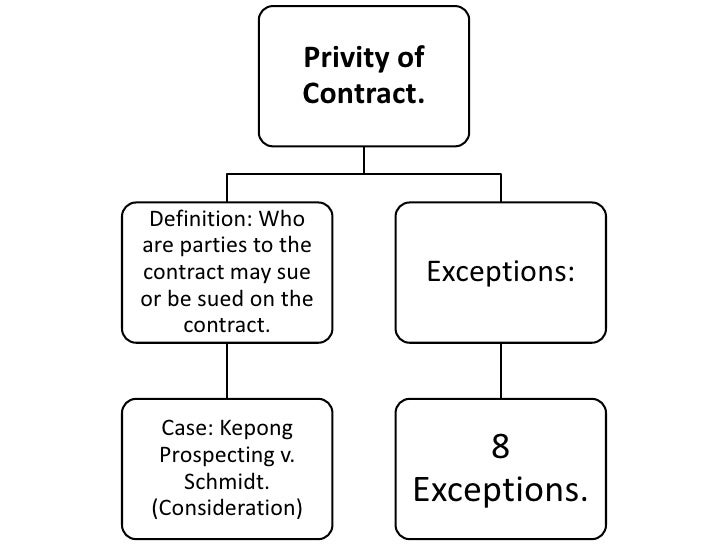
Exceptions to Privity of Contract
- Covenants running with the land
- Contracts for the hire of a chattel
- Interference with contractual rights
- Restrictions upon price
- Insurance contracts
- Privity and trust concept
- Banker’s commercial credits.
How can I create and enforce contracts for exceptions?
Contracts are formed through written or oral agreement. Understandably, oral agreements are far more difficult to enforce than written contracts. Nevertheless, the law provides for oral contract formation, including oral rescission, and modifications. The Statute of Frauds provides the framework to contract amendment. Oral modifications are binding amendments to contract, in so far as the change is acknowledged by both parties.
What is the doctrine of privity of contract?
Privity of contract is a doctrine of contract law that states that contracts should not give rights or obligations to entities other than those who are parties to the contract.
What do you need to know about privity of contract?
Privity of Contract Meaning: Everything You Need to Know
- Privity of Contract Meaning
- Horizontal Privity Contract vs. Vertical Contract
- When a Third Party has Rights
What are the rules of contract law?
- The contract should be valid. The aggrieved party must prove that the contract in question is legal and meets all the requirements of an enforceable contract.
- The aggrieved party lived up to his end of the deal. ...
- The contract was breached. ...
- The offending party was informed of the breach. ...
What are exceptions to a contract?
EXCEPTION, contracts. An exception is a clause in a deed,. by which the lessor excepts something out of that which he granted before by the deed.
What is an example of privity of contract?
“The doctrine of privity means that a contract cannot, as a general rule confer rights or impose obligations arising under it on any person other than the parties to it.” For example, if a party 'A' promised 'B' to pay Rs. 100 to the third party 'C'. Thus, 'A' and 'B' can sue each other in case of a breach of contract.
What is privity of contract and consideration What are the exceptions of privity of contract in India?
It means that under Indian Law a person may not have himself given any consideration but he can enforce the contract if he is a party to the contract. In India the rule “stranger to contract cannot sue” (Privity of Contract) has to be distinguished from the rule “stranger to consideration can sue”.
What do you understand by the doctrine of privity of contract state exceptions if any?
The doctrine of privity of a contract is a common law principle which implies that only parties to a contract are allowed to sue each other to enforce their rights and liabilities and no stranger is allowed to confer obligations upon any person who is not a party to contract even though contract the contract have been ...
What are the rules of privity of contract?
The principle of privity of contract provides that, as a general rule, a contract cannot confer rights or impose obligations arising under it to any person who is not a party. The doctrine has long been criticized as artificial and contrary to the parties' intention to benefit a third party.
What is an exception in business law?
In contracts, statutes, and deeds,an exception is a statement that something is not included, as in "Landlord rents to Tenant the first floor, with the exception of the storage room.” To "take exception" to a judge's ruling, is a way a lawyer might tell a judge that they disagree.
What are the exceptions to the doctrine of caveat emptor?
If the seller obtains the consent of the buyer by fraud then caveat emptor will not apply. Also if the seller conceals any material defects of the goods which are later discovered on closer examination then again the buyer will not be responsible.
What is privity of contract?
Privity of contract is a concept stating that contracts should not give rights or obligations to entities other than those who are parties to the contract. The principle helps to protect third parties to a contract from lawsuits arising from that contract. There are some exceptions to the privity principle and these include contracts involving ...
When does privity apply?
The privity principle also applies when a tenant subleases a property he is renting. The landlord may not be able to sue the tenant to whom the property was subleased. In contract law, privity and consideration are closely related and any contract that does not follow both principles is not enforceable. Any contract with privity, but without ...
What happens when a tenant finds out that the AC is faulty?
The tenant finds out that, contrary to the contract she signed with the landlord, the house's air conditioning system is faulty. The new tenant raises the issue with the landlord who tells him that the AC fault is the responsibility of the previous tenant.
What happens if Andrew defaults on his payments?
If Andrew defaults on his payments and John sues him for breach of contract, courts would likely not enforce the contract. This is because, although the contract is in line with the privity concept, there is no consideration in the contract.
Why does Andrew promise to pay John a fee?
Andrew promises to pay John a monthly fee because John is such a nice person. In such a contract there is no consideration, there is nothing John is giving back in return for the payments from Andrew. If Andrew defaults on his payments and John sues him for breach of contract, courts would likely not enforce the contract. ...
When is horizontal privity brought up?
Horizontal privity can be brought up if benefits in a contract are given to another party that is not a party to the contract. This may be raised when another contract is made arising from one of the parties to another contract.
Can a negligent party be sued?
In the case of personal injury resulting from negligence, the negligent party may generally be sued by third parties who are not parties to any contract with the negligent party. Assignment of the Contract. In some cases, benefits from a contract may be assigned to another party. Insurance Companies.
What is Privity of Contract?
Imagine that you visit your local supermarket and buy a frozen dinner. You come home, heat it up, and get sick immediately after eating the dinner. It turns out that the dinner was tainted with bacteria. You want to sue the supermarket and the manufacturer of the meal. However, you also want to sue the middleman who delivered the meal to the store.
Exceptions to Privity of Contract
There are some exceptions to privity of contract, meaning that even though someone was not directly involved in the contract, that person might still be able to sue. For example, there is a trust exception.
What is the doctrine of prudence of contract?
INTRODUCTION Doctrine of Privity of contract is a common law principle or mechanism by which contractual rights and liabilities are limited to the contracting parties. The logic behind this is simple, that only contracting parties have accepted the terms and responsibilities stipulated in the agreement.
What is a trust of a contractual right?
Trust of a contractual right A third party can enforce a contract, if it can be established that the promise intended to create a trust. “A trust is an obligation, enforceable in equity, by which a person, the trustee, holds property on behalf of another, the beneficiary16”.
What did the judges say about privity of contract?
Two judges said the doctrine of privity of contract produced injustice where third parties were intended to benefit from the contract and could not enforce it directly. They allowed the intended beneficiaries in this case to get the benefit.
When does the doctrine of privity of contract apply?
The doctrine of privity of contract applies when a contract has the beneficiary clause. If the contracting parties failed to discharge the obligations towards the third person, that person has no right to sue the parties for the enforcement of rights in the beneficiary clause.
What was the doctrine of Privity of Contract in Beswick v. Beswick?
Beswick. Peter Beswick agreed to transfer his business to the defendant in consideration of the promise to employ Peter as ‘consultant’ during his lifetime and after his death, to pay an annuity of £ 5 a week to his widow.
What is the doctrine of prudence of contract?
The doctrine of Privity of contract states that any third party, which is not even distinctly related to the two involved parties, does not have a right to initiate a suit against the said parties to the contract even though he/she is the beneficiary. Apart from promisor (s) and promisee (s), all ...
What is the relationship between parties whose estates constitute one estate in law?
In a real estate context, it is the legal relationship between parties whose estates constitute one estate in law. Privity of estate exists when two or more parties hold an interest in the same real property. In a leasing context, a lease agreement is both a conveyance of an interest in real property and a contract.
Which countries have the privity doctrine?
In Australia (Western Australia and Queensland), the United Kingdom, New Zealand, the U.S., and Singapore the privity doctrine has been reformed through legislation. Further law reform commissions in Hong Kong and Ireland recently recommended legislative reforms to address this issue.
What is the principle of contract law in Malaysia?
It is a fundamental rule of the common law that apart from special circumstances, for example in cases of agency , trust , assignment or statutory exception, a person who is not a party to a contract has no right to sue on a contract. The decision of Privy Council in Kepong Prospecting Ltd &Ors v Schmidt [10] affirmed that the rule applies in Malaysia. The Court of Appeal and the High Court also uphold the application of the doctrine throughout all these years.This rule has been criticised particularly in cases where the contract is for the benefit of the third-party. At this time there has been no statute introduced and the rule persists in Malaysian Law to prevent a third-party enforcing contractual provisions made in their favour. [11]
What happens when a contract requires that a party pay a certain amount to a third party?
If a contract requires that a party pays a certain amount to a third-party and he/she acknowledges it, then it becomes a binding obligation for the party to pay the third-party. The acknowledgment can also be implied.
What does the Indian Contract Act say?
The Indian Contract Act clearly states that there cannot be a stranger to a contract. What does this exactly mean? And are there any exceptions? This is explained through the Doctrine of Privity of a Contract. Let us see.
What did Peter promise Nancy?
Peter promised Nancy’s father that he would marry Nancy else would pay Rs 50,000 as damages. Eventually, he married someone else, thereby breaching the contract. Nancy filed a case against Peter which was held by the Court since the contract was a family arrangement with Nancy as the beneficiary.
Who had the right to sue Arjun and his father?
The Court held that a trust was formed with Ravi as the beneficiary for a certain amount and share of the estate. Hence, Ravi had the right to sue upon the contract between Arjun and his father, even though he was not a party to it.
Can a stranger sue on a contract?
A stranger or a person who is not a party to a contract can sue on a contract in the following cases: Trust. Family Settlement. Assignment of a Contract. Acknowledgement or Estoppel. A covenant running with the land. Contract through an agent. Essentials of a Contract. Let’s look at each of them in details:
Can a third party file a suit against a stranger?
However, a stranger (third-party) to consideration is different from a stranger to a contract. The law does not allow a stranger to file a suit on the contract. This right is available only to a person who is a party to the contract and is called Doctrine of Privity of Contract.
Can Rajiv and Krishna file a suit?
Since there is no contract between Rajiv and Krishna about repairing the leakage, if he files a suit, it will probably be dismissed by the Court. Krishna had agreed to carry out the repairs in his purchase contract with Vidya. Hence, she can file a suit against Krishna to get the work done.
The doctrine of privity and exceptions to its application
This article is written by Adhila Muhammed Arif, a student of Government Law College, Thiruvananthapuram. This article elucidates on the Doctrine of Privity and the exceptions to its application.
Introduction
According to Section 2 (h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872, a contract can be defined as an agreement that subsists between two or more parties that is enforceable in the courts of law. When one party fails to perform their obligations provided in the contract, the other party can sue them for the breach and obtain adequate remedy.
What is privity of contract?
The doctrine of privity of contract is one of the major principles that govern the law of contracts. The word ‘privity’ means ‘with knowledge and consent’.
Doctrine of privity in english law
English law is more restrictive in comparison to Indian law in the application of the doctrine of privity. This is because English law only recognizes consideration that moves from the promisee himself and not from anyone else, which puts both strangers to contract and strangers to consideration on the same footing.
Exceptions to the rule that a Third Party to contract cannot sue
The doctrine of privity of contract is however not absolute. There are several exceptional situations in which a third party to a contract can sue. The following are the exceptions to the doctrine of privity in Indian law :
Conclusion
To sum up, the doctrine of privity of contract is not an absolute rule. There are many cases in which a person who is not a party to a contract can enforce the contract as explained above.
What is the pity of contract?
Ans: Thus, Privity of Contract states that only the two parties who have an existing relationship hold rights to sue each other and claim damage or impose terms of an agreement to the other party. However, certain exceptions and provisions such as Privity of Contract and Consideration have been introduced to benefit the third party.
What is a horizontal privilege of contract?
In horizontal Privity of Contract, the beneficiary is a third party and not one of the individuals who is a participant in said contract. On the other hand, in a vertical contract, all signatories to an agreement stand to benefit directly from the same.
What is the Indian contract act?
Indian Contract Act. The Indian contract act of 1872 was established based on these principles of Doctrine of Privity of Contract. However, the definition of Privity of Contract and Privity of Consideration is different under Indian law. It states that consideration can shift to a third party also, which means that both a promisee ...
What is the doctrine of consideration?
It also established the Doctrine of consideration which states that for a promise or agreement to be applicable, the promisee must provide something to the promisor in return for successful completion of the contract.
What is the relationship between two or more contracting parties?
The relationship or connection shared by two or more contracting parties has been defined as the Privity of Contract. When a contract is drawn, it imposes specific responsibilities and obligations to individuals who are parties to this agreement. Accordingly, the premise of the Doctrine of Privity of Contract is that only contracting parties can be ...
Who agreed to pay Tweddle's son?
The main points in this Doctrine of Privity of Contract emerged after the case of Tweddle vs Atkinson case. Here, John Tweddle and William Guy agreed that they would both pay a sum of money to Tweddle’s son who was engaged to be married to William’s daughter. However, William passed away before making any payment.
Who is the principal of a contract?
The person who engages an agent or anyone who is represented by one is called the principal. If the contract is a family arrangement such as a marriage settlement a third party or beneficiary can sue the signatories to the contract to impose the agreement under exceptions to the Doctrine of Privity of Contract.

interference with Contractual Rights
Restrictions Upon Land – Exceptions to Privity of Contract
Insurance Contracts
- In modern times, situations have arisen that have necessitated the relaxing of the privity principle. 1. Collateral Contracts and the Sale of Defective Goods A third party may sue the seller over defective goods if the third party is affected by the flaws in the goods. 2. When an Agent Is Involved An agent may enter a contract with another party on...
Privity and The Trust Concept