
Ans. Petiole In botany, the petiole is the stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem. The petiole is the transition between the stem and the leaf blade. Outgrowths appearing on each side of the petiole in some species are called stipules. Leaves lacking a petiole are called sessile or epetiolate.Petiole
What are the internal parts and function of a leaf?
Various internal structures of the leaf facilitate the process of photosynthesis, transpiration, gaseous exchange, and transfer of prepared food to other parts of the plant. Angiosperms can be divided into two types, i.e. monocots and dicots, and the internal structure of a leaf also varies depending upon the type of plant too.
What are the parts of a typical leaf?
The leaf:
- Leaf base: The part of the leaf with which it is attached to the stem is called the leaf base. ...
- Petioles: The stalk of the leaf is called petiole. ...
- Lamina or leaf blade: The green and expanded portion of the leaf beyond the petiole is called the lamina. ...
- Shape of the leaf: The general outline or shape of the leaf may be of following types. ...
What is the internal structure of a leaf?
The internal structure of the leaf is protected by the leaf epidermis, which is continuous with the stem epidermis. The central leaf, or mesophyll, consists of soft-walled, unspecialized cells of the type known as parenchyma. Oxygen is passed into the atmosphere through stomata—pores in the leaf surface.
What are the two main parts of the external leaf?
Parts of a Leaf. Leaves have two main parts: The leaf blade and the Stalk or the petiole. The leaf blade: It is also called the lamina. It’s generally broad and flat. It is in this layer that photosynthesis occurs. It contains a prominent midrib at the center of the leaf blade which is the main vein. From this midrib arise branches called veins.
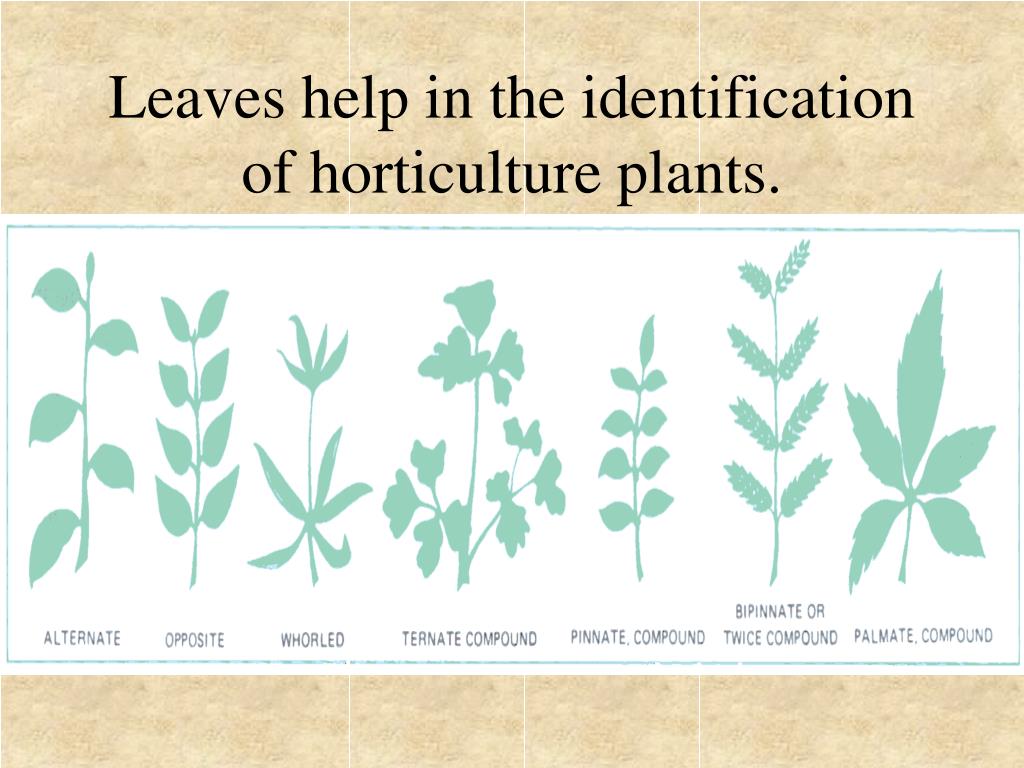
What are the external parts of leaves?
What are the external parts of a plant leaf? Ans. Petiole, leaf base, lamina, leaf apex, and leaf margin are the external parts of a leaf.
What is the function of external structure of a leaf?
Epidermis: It is the outermost layer and secretes a waxy substance called the cuticle. The cuticle helps retain water inside the leaf cells. The epidermis houses the guard cells which regulate the movement of water into and outside the cell. Guard cells do so by controlling the size of the pores also called stomata.
What are the external and internal parts of leaf?
Leaves have three main internal regions; the epidermis, the mesophyll, and the veins. The epidermis is the outermost layer, being present on the top and bottom of the leaf, the upper and lower epidermis, respectively (Figure 4.2. 1).
What are the different structures within a leaf and what are their functions?
Structure-Function Relationship: LeavesName of StructureStructureFunctionPithParenchyma with vacuoles and plastidsStorage, supportPlasmodesmataOpenings between sieve tubes connecting cytoplasmTransport of sapSpongy cellsRounded, widely spaced, near stomataAllow gas exchangeSuberinWaxy moleculeWaterproofing9 more rows•Dec 11, 2015
What are the 8 external parts of a leaf?
Apex: tip of the leaf • Margin: edge of the leaf • Veins: carry food/water throughout leaf; act as a structure support • Midrib: thick, large single vein along the midline of the leaf • Base: bottom of the leaf • Petiole: the stalk that joins a leaf to the stem; leafstalk • Stipule: the small, leaf-like appendage to a ...
What are the external structures?
All animals have external structures, which means outside parts of the body. Most animals have a head, body covering, limbs, and some form of a tail. Although these body parts may look different on different animals, they are all crucial to helping them live and reproduce.
What is the three external part of the leaves?
The leaf is divided into three parts: i) leaf apex – a tip of the leaf blade; ii) leaf margin – edge of the leaf; and iii) leaf veins – tiny capillaries. Leaf veins are divided into two parts: the main/ central vein and the side veins. It helps in transporting water and nutrients throughout the leaf.
What are the main parts of plants internal and external?
Internal & External Parts of the PlantsRoots. Roots provide structural support for the plant to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. ... Stems. Stems offer physical support to the plant and contain the buds that develop into leaves, flowers and additional stems. ... Leaves. ... Flowers. ... Seeds.
What are the 4 functions of leaves?
CONTENTSPhotosynthesis.Transpiration.Guttation.Storage.Defense.
What are the 10 functions of a leaf?
Leaf contains minute pores called stomata where gaseous exchange and transpiration occurs. The main functions of leaves are photosynthesis, exchange of gasses and transpiration.
What is the function of stomata?
Stomata regulate gas exchange between the plant and environment and control of water loss by changing the size of the stomatal pore. This stomatal movement is affected by several environmental stimuli, such as relative humidity, CO2 concentration, and light intensity.
What are the external adaptations of a leaf?
Leaves are adapted for photosynthesis and gaseous exchange. They are adapted for photosynthesis by having a large surface area, and contain openings, called stomata to allow carbon dioxide into the leaf and oxygen out....Features of leaves.AdaptionPurposeChlorophyllAbsorbs sunlight to transfer energy into chemicals4 more rows
What is the function of leaf stomata?
This evolutionary innovation is so central to plant identity that nearly all land plants use the same pores — called stomata — to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Stomata are tiny, microscopic and critical for photosynthesis. Thousands of them dot on the surface of the plants.
What are the types of lines?
In geometry there are four types of lines: Horizontal Line Vertical lines Parallel lines Perpendicular lines
What is a ray?
A ray is a part of a line with one endpoint (i.e., starting point) and continues forever in the other direction.
What is perpendicular lines?
When two straight lines meet or intersect at an angle of 90 degrees, they are perpendicular to each other.
What is parallel lines?
Parallel lines are two straight lines that are always the same distance apart. They never meet or intersect at any point, even at infinity.
Which side of a leaf is continuous?
the lower side of the leaf. Some are continuous, and some are divided
What is the auricle?
auricle- is a pair of tiny appendages between the leaf blade and the sheath.
What are scale-like leaves?
Scale-like leaves overlap one another like fish scales or shingles on a roof.
What is a lobe in a leaf?
A lobe is a projecting part or segment of the leaf. The space between two
What does "serrate" mean in a leaf?
Serrate means saw-tooth with the teeth pointing forward. Margin-one of many forms: wavy, toothed, lobed, and entire or smooth. A lobe is a projecting part or segment of the leaf. The space between two.
Which cell controls the opening and closing of the stomata?
guard cells control the opening and closing of the stomata.
What is a leaf?
A leaf is a plant organ that is flat, thin, and usually green in color.
B. Leaf-blade or Lamina
It is the thin, flat part of the leaf that is typically green in color. It is characterized by green color, thinness, and smoothness. The leaf is divided into three parts: i) leaf apex – a tip of the leaf blade; ii) leaf margin – edge of the leaf; and iii) leaf veins – tiny capillaries.
What are the two types of mesophyll cells?
There are two types of Mesophyll cells, the Palisade and spongy cells. Palisade Cells: These cells are where the majority of photosynthesis happens. The cells are at the top of the leaf packed in closely. The Palisade cells have lots of chloroplasts in them to help with the process of photosynthesis. Spongy Cells: Although theses cells are not ...
What is the space in a plant that allows the gases to move around freely?
Air Space : This space allows the gases to move around freely. Vein (vascular bundle): Made up of Xylem and Phloem tubes these veins transport the sugar and water the plant needs. Xylem: This is an important part of the leaf, it brings the water from the roots through to the leaves of the plant.
Why do my leaves feel waxy?
Waxy Cuticle: The point of leafs being or feeling waxy, is so that the water doesn’t drown the plant. It is sort of like a shield against the water, the water usually gets into the plant through the roots. There are two types of Mesophyll cells, the Palisade and spongy cells.
What are the internal parts of a leaf?
The Stoma also is in control of how much water leaves the leaf. Guard Cells: Guard cell just protects the Stoma from opening up to far.
What is the name of the plant that transports sugar from the leaf?
Phloem: The Phloem is similar to the Xylem, but it transports this sugar (which was made from the photosynthesis) to various parts of the leaf.
Which cells have chloroplasts?
The Palisade cells have lots of chloroplasts in them to help with the process of photosynthesis. Spongy Cells: Although theses cells are not at the top of the leaf (they are in the middle) they still do photosynthesis. These cells have more space in between them to allow the gases inside the leaf to move around freely.
What is the outer edging of a leaf?
Margin : This is the outer edging of the leaf. They can be in many different forms, i.e. serrated, parted. Lateral Veins: These veins are one of the most important parts of the leaf, they transport the food and water the leaf needs to all it’s necessary places. Petiole: This part attaches the leaf to the actual plant stalk.
External parts
If we examine the leaf externally, there are six most important parts of a leaf as mentioned below:
Internal parts
There are several important parts of a leaf that functions internally. These parts usually include:
CONCLUSION
There are several parts of a leaf located on the external and internal levels that collectively work to facilitate the normal functioning of a leaf and support the survival of the plant eventually. Our private tutors provide ideal services of home tuition related to biology and all other relevant subjects.
What is a Leaf?
A leaf is the main part of vascular plants that are responsible for making food. Vascular plants contain cells or vessels to carry the fluid. Leaves get their green color due to the presence of chlorophylls that helps in making food. Leaves carry out many important functions like making food with the help of sunlight and handling the exchange process of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
What is the arrangement of veins on a leaf blade that function as a food and water carrier?
There are mainly two types of venation; Reticulate Venation and Parallel Venation.
What is the uppermost part of a leaf?
Lamina is the uppermost part of a leaf that contains veins and chloroplast. The main functions of a leaf such as photosynthesis and transpiration start from the lamina through its internal parts.
What control the process of transpiration in which water passage takes place from roots through the vascular system?
Guard cells control the process of transpiration in which water passage takes place from roots through the vascular system. They are present around the stomata.
What is the function of a leaf?
The main function of the leaf is to fetch food from the root for the plant and carry out photosynthesis for its growth. Following are the few functions:
What is the function of leaves in plants?
The food storage function of leaves often takes place in Cabbage, Lettuce, Spinach, and various other vegetable plants. A leaf stores starch as its food. The function of food storage is carried out by vascular bundles.
Which cells allow the exchange of gases in and out of a leaf?
The exchange of gases is the function mainly done by stomata in the leaf through its small openings. Then mesophyll cells, which lie under epidermal cells, allow the diffusion of gases in and out of a leaf.
What are the structures of the leaf?
Leaf morphology. Typically, a leaf consists of a broad expanded blade (the lamina ), attached to the plant stem by a stalklike petiole. In angiosperms leaves commonly have a pair of structures known as stipules, which are located on each side of the leaf base and may resemble scales, spines, glands, or leaflike structures.
How long do leaves last in a tree?
Leaves are essentially short-lived structures. Even when they persist for two or three years, as in coniferous and broad-leaved evergreens, they make little contribution to the plant after the first year. The fall of leaves, whether in the first autumn in most deciduous trees or after several years in evergreens, results from the formation of a weak zone, the abscission layer, at the base of the petiole. Abscission layers may also form when leaves are seriously damaged by insects, disease, or drought. As a result, a zone of cells across the petiole becomes softened until the leaf falls. A healing layer then forms on the stem and closes the wound, leaving the leaf scar, a prominent feature in many winter twigs and an aid in identification.
What is a leaf called when it is inserted directly on the petiole?
When only a single blade is inserted directly on the petiole, the leaf is called simple.
What is a spine in a cactus?
Spines are also modified leaves. In cacti, spines are wholly transformed leaves that protect the plant from herbivores, radiate heat from the stem during the day, and collect and drip condensed water vapour during the cooler night. In the many species of the spurge family ( Euphorbiaceae ), the stipules are modified into paired stipular spines and the blade develops fully. In ocotillo ( Fouquieria splendens ), the blade falls off and the petiole remains as a spine.
Why is Pain Bush poisonous?
Pain bush, or African poison ivy ( Smodingium argutum ). The species is poisonous because of the sap it emits.
Why do leaves fall off trees?
The fall of leaves, whether in the first autumn in most deciduous trees or after several years in evergreens, results from the formation of a weak zone, the abscission layer, at the base of the petiole. Abscission layers may also form when leaves are seriously damaged by insects, disease, or drought.
What are the margins of simple leaves?
The margins of simple leaves may be entire and smooth or they may be lobed in various ways. The coarse teeth of dentate margins project at right angles, while those of serrate margins point toward the leaf apex. Crenulate margins have rounded teeth or scalloped margins.
