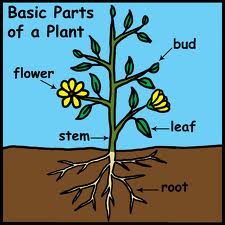
All organisms, or living things, have external structures. A plant’s external, or outer, structures include roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. Meanwhile, most animals have a body, arms, legs, and a head.
What are the 5 parts of a plant?
Parts of a Flowering Plant
- Angiosperms. Flowering plants, also called angiosperms, are the most numerous of all the divisions in the Plant Kingdom.
- Root System. The roots of a flowering plant are very important. ...
- Shoot System. Flowering plant stems, leaves, and flowers make up the plant shoot system. ...
- Sexual Reproduction and Flower Parts. ...
- Asexual Reproduction. ...
- Summary. ...
What are three major parts of a plant?
- Leaves produce food for the plant
- Leaves help to filter dust and other particles present in the air, thus keep the air clean
- Leaves keep the plant cool through the loss of water by evaporation
- Twigs help to give rise to new plants
What are the most important parts of a plant?
The important functions of a stem include:
- A stem carries out a number of functions essential for various processes such as photosynthesis.
- Provides a definite framework and structure to a plant which later develops into a tree.
- Support: Primary function of the stem is to hold up buds, flowers, leaves, and fruits to the plant. ...
What are the parts of plant and their uses?
What are Plants?
- Plant Ecology. Plants can synthesize their own food by combining light energy, atmospheric carbon dioxide, and hydrogen atoms.
- Different Parts of a Plant. Before we get into the details, first we must be aware of the similarities between plants and human beings.
- Roots. ...
- Stems. ...
- Leaves. ...
- Flowers. ...
- Fruits. ...
- Seeds. ...
- Parts of Plants and Their Functions. ...

What are the external parts of a flower?
Sepal: The outer parts of the flower (often green and leaf-like) that enclose a developing bud. Petal: The parts of a flower that are often conspicuously colored. Stamen: The pollen producing part of a flower, usually with a slender filament supporting the anther.
What are the main parts of plants internal and external?
Internal & External Parts of the PlantsRoots. Roots provide structural support for the plant to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. ... Stems. Stems offer physical support to the plant and contain the buds that develop into leaves, flowers and additional stems. ... Leaves. ... Flowers. ... Seeds.
What is the internal part of a plant?
The internal parts of plants consist of specialized cells in the plant stem and leaf that make up the plant's structure and perform functions in the plant tissues. Cells that provide structure have thick cell walls that support the plant.
What are the external parts of the stem?
The external features of a stem include the nodes, petioles, and leaves. The internal features of the stem consists of the vascular tissue such as xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium.
Do plants have internal and external structures?
A system can be described in terms of its components and their interactions. Plants and animals have both internal and external structures that serve various functions in growth, survival, behavior, and reproduction.
What is the difference between internal and external structures?
External structures are what you see on the outside. But, do you know what's inside? The internal structures are the inner pieces and parts that keep organisms alive, help them grow, and help them reproduce.
What are the external parts of a leaf?
A leaf's external parts are the petiole, leaf base, lamina, leaf apex, and leaf edge.
What are the internal and external parts of a leaf?
Leaves have three main internal regions; the epidermis, the mesophyll, and the veins. The epidermis is the outermost layer, being present on the top and bottom of the leaf, the upper and lower epidermis, respectively (Figure 4.2. 1).
What are the 7 parts of a plant?
The different parts of a plant include roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, and fruits. Roots have the function of absorbing water and minerals from the soil whereas the primary functions of stems are supporting, transporting, storing, and reproducing.
What are the 5 main plant parts?
The basic parts of most land plants are roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
Whats a node in a plant?
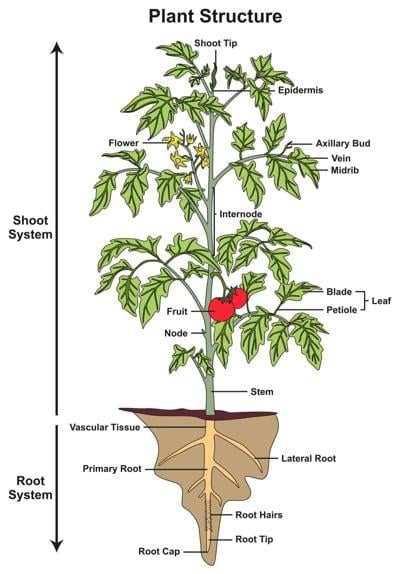
Nodes. A node is an area on a stem where buds are located (figure 6). It is a site of great cellular activity and growth. It is here that small buds develop into leaves, stems or flowers. When pruning, it is important to locate a plant's nodes.
What is the stem part of a plant?
stem, in botany, the plant axis that bears buds and shoots with leaves and, at its basal end, roots. The stem conducts water, minerals, and food to other parts of the plant; it may also store food, and green stems themselves produce food.
What are the main parts of plant?
Plants typically have six basic parts: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
What is internal features of plant?
Plant tissues are large, organized groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Examples include meristems, xylem and phloem. Almost all plant cells retain all of the genetic information necessary to develop into a complete plant.
What are the main parts of a plant and their functions?
The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. The stem supports the plant above ground, and carries the water and minerals to the leaves. The leaves collect energy from the Sun and make food for the plant, using an amazing process called photosynthesis.
What is the internal structure of a leaf?
The internal structure of the leaf is protected by the leaf epidermis, which is continuous with the stem epidermis. The central leaf, or mesophyll, consists of soft-walled, unspecialized cells of the type known as parenchyma.
How do plants reproduce?
Every part of a plant has a specific job to help it either grow, survive, or reproduce. Roots grow outward from the seed and hold the plant in place while soaking up water and nutrients from the soil. Leaves make food for the plant from the sun and carbon dioxide in a process called photosynthesis. Reproduction is helped by pollination, where animals fertilize flowers while eating or moving around on the pollen.
What does the spine do to a plant?
Your spine helps your body stand up straight. This is part of what a stem does; a stem provides support for the plant. Stems also move water and food from the roots throughout the plant, like your veins move blood throughout your body. Or, like plumbing pipes move water through a house.
What do the roots of a sage tree do?
The roots of this tree are working to soak up water and nutrients from the soil.
Why do blueberry plants have flowers?
Some flowers, like those on the blueberry bush, actually turn into fruits, which protect the seeds of the plant.
Why are leaves important?
Leaves have a very important job because all living things need oxygen. And, not only do plants use the glucose as food, but so does any animal that eats plants. Now, Maria understands why rabbits like eating the lettuce in her garden! Flowers & Fruits.
What do leaves do in the spring?
Leaves. Next, leaves begin to grow from the stem. During the spring and summer, they make food for the plant so it can continue growing. This process, called photosynthesis, is when leaves take in sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, and give off oxygen and a sugar called glucose.
Why did Maria study the parts of a plant in school?
Maria recently studied the parts of a plant in school so she wants to examine them closely in her grandmother's garden. Let's take a look at the parts of the plant that Maria is going to see and find out what their functions are and why they are important.
Why do plants have deep roots?
The roots often extend far into the ground, spreading deep and wide to ensure the plant has plenty of food and drink within its reach. Some plants, such as grasses, have shallow fibrous roots that appear similar to tiny hair-like fibers.
What is the role of roots in plants?
They are an essential part of the plant’s survival, tasked with the responsibility of anchoring the plant to the ground and also seeking out moisture and nutrients to be delivered to the plant and enable it to grow.
What is the function of the stem?
It is the midsection between the roots and the leaves or flowers, and its main function is to carry moisture and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. There are different types of cells within the stem that perform their own functions. The xylem cells transport water from root ...
What are the roots of carrots?
Taproots are another type of root that is present in some plants, such as carrots and potatoes. Taproot systems extend vertically into the soil and are quite chunky in size and appearance, storing food for the plant ( University of Illinois Extension ). For epiphytes, which are plants that live on other plants and trees in their natural habitat, ...
What organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
Chloroplast. These organelles are interesting in that they are only found in plant cells. They contain chlorophyll, giving the foliage of the plants their green color and aiding in the process of photosynthesis. The function of the chloroplast is to capture sunlight to conduct photosynthesis.
Why do succulent leaves hold water?
These swollen leaves hold onto water so that in the case of drought, the plant has enough water reserves to survive.
What is the control room of a plant cell?
The nucleus is the control room of the plant cell and is the most important part of any plant cell. It takes on a spherical shape and contains the DNA of the plant within its chromosomes, holding on to all of the plant’s genetic hereditary information. It is responsible for coordinating all of the metabolic functions, including cell growth, protein synthesis, and cell division. By taking care of this, the nucleus regulates all of the functions of the cell. Contained within the nucleus are also other organelles, some of which produce ribosomal RNA.
What is the root system?
➤ THE ROOT SYSTEM – It is located below the ground, responsible for absorbing water and minerals from the soil as well as give firmness to the whole plant/tree. The root system includes organs such as the roots, tubers, and rhizomes
What is the function of stems in plants?
Stem performs much vital work for the whole plant. They support the plant and held up towards the light. Stem acts like the plant’s transportation system. It receives water and minerals from the root and distributes it among all other parts including leaves for the food processor with the help of Xylem tissue.
Why are leaves called plant food factories?
The leaf is known as a plant food factory because it prepares food for the entire plant through the process of photosynthesis. Under this process, the leaves make glucose, or food, using sunlight, water, chlorophyll and carbon dioxide.
What is the part of a flowering plant that protects the seeds?
A fruit is part of flowering plant which protect the seeds by covering it.
What is the reproductive organ of a plant?
Flowers are the reproductive organ of flowering plants. It makes seeds, which become new plants. Along with reproduction, flowers are also a rich source of food for other living organisms such as insects, birds, animals and humans.
Which part of the cell transports food in the form of glucose produced from photosynthesis?
And then stem transports food in the form of glucose produced from photosynthesis from leaves to other parts such as roots and stems with the help of Phloem tissue.
Where is the root of a plant located?
The root is located below the ground. It helps to anchor the plant to the ground so it does not fall over. It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil and sends it to the stem.
What are the two parts of a plant?
The parts of the plant body are also differentiated into two kinds of functional plant organs: vegetative and reproductive. The vegetative structures include the root, stem, and leaves; the reproductive parts consist of the flower, fruit, and seed.
What are the two main parts of the plant body?
The parts of the plant body of the angiosperms are divided into two distinct systems: the root and shoot. In terrestrial plants, the root system is the plant organ that is normally underground (descending) while the shoot system is above ground (ascending). The root system consists of the primary root and its branches, or a mass of fibrous roots. The plant shoot system consists of the stem, leaves, and reproductive organs.
Which part of the plant absorbs water and nutrients?
In general, it is the root that provides anchorage and absorbs water and nutrient elements which are transported to the leaves via the stem (trunk, branches, and twigs). At the same time, the leaves absorb carbon dioxide from the air which is utilized in the production of carbohydrate through the process of photosynthesis. This carbohydrate is in turn transported, again via the stem, to the different parts of the plant, including the roots and the reproductive structures. At certain periods of organ development, the stored photosynthate may again be retransported to other plant organs.
How can knowing the different parts of plants help in crop production?
By knowing the different parts of plants and how each part participates in growth, development, and adaptation, it will be possible to make necessary manipulations of the plant and of the environment for improved crop production . Familiarity with the different morphological and anatomical terms will likewise enhance understanding of the concepts, practices, and advances as well as become useful in the identification, rearing, and improvement of crop plants.
What is the body part of a plant?
The stem is an above-ground part of a plant that provides structural support and connects the root system to the leaves. Stems vary in size, ranging from a small vine to the 30 foot diameter of a tree!
What is the inside of a plant stem like?
Did you know that the inside of a plant stem is like a highway? Imagine a highway where trucks are transporting food and water to different areas of the city. Before entering the highway, the trucks first have to stock their trailers with supplies from a local warehouse. The loaded trucks then travel to the highway and eventually reach their destination, a grocery store.
What is the ring on a dicot plant?
In a dicot plant stem, the xylem and phloem are separated into rings. Have you ever counted tree rings? You are actually looking at old xylem tissue of a dicot plant. Each ring represents one year the plant was alive.
What are some examples of dicot plants?
A dicot plant has a seed that sprouts out two leaves. Examples of dicot plants are most woody trees and shrubs. A monocot and dicot plant. In a monocot plant stem, the xylem and phloem are paired together and are dispersed throughout the stem. A monocot stem has a bundled vascular system.
What is the area of the stem where leaves grow from?
The area of the stem where leaves grow from is called a node. The stalk of the leaf that connects to the node is called the petiole. The area of the stem between nodes is called the internode. We also explored the vascular system of a plant stem. The vascular system includes the phloem and the xylem.
What is the phloem in a tree?
The phloem is a network of tubes in the stem that transport food to the rest of the plant. Have you ever witnessed sap oozing from a tree? You are actually witnessing sticky phloem contents leaking out. When you eat syrup, you are eating the sugary contents transported in the phloem. A way to remember the phloem transports food throughout the plant is to think of the beginning sound of phloem, which sounds like the f in food.
How do leaves transport food to the rest of the plant?
Everyone knows plants manufacture food from the sun, but how do leaves transport food to the rest of the plant? This movement of food and water is performed by the vascular system. The vascular system is comprised of two main tissues, the phloem and xylem.
What are the parts of a plant?
Root, stem, flower, leaf! In this hands-on science lesson, your students will create their own plants to help them identify and remember the parts of a plant.
How to explain the function of each plant?
One by one, explain the function of each plant part. Tell your class that roots hold the plant into the soil. They take in water and minerals to help the plant stay alive. Define the stem as the part that carries water from the roots to the other parts of the plant. Explain that the flower helps the plant reproduce, ...
What are some examples of plants with different leaves?
For example, maple trees have star-shaped leaves, magnolia trees have obovate leaves, and birch trees have deltoid leaves. Use this as a jumping off point for a class discussion about what plants need to survive. After some suggestions, remind your students that plants need sun, ...
What are the cells that make up a plant's growing points called?
Specialized groups of cells called meristems are a plant's growing points. Meristems are the site of rapid, almost continuous cell division. These cells either continue to divide or begin to differentiate into other tissues and organs. How they divide, and whether they ultimately become a tissue or an organ, are controlled by a complex array of internal plant hormones but also can be influenced by environmental conditions. In many cases, you can manipulate meristems to make a plant do something you want, such as change its growth pattern, flower, alter its branching habit, or produce vegetative growth.
What are the basic structures of plants?
Cells are the basic structural and physiological units of plants. Most plant reactions (cell division, photosynthesis , respiration, etc.) occur at the cellular level. Plant tissues ( meristems , xylem , phloem, etc.) are large, organized groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
What is the unique feature of plant cells?
A unique feature of plant cells is that they are readily totipotent. In other words, almost all plant cells retain all of the genetic information (encoded in DNA) necessary to develop into a complete plant. This characteristic is the main reason that vegetative (asexual) reproduction works.
Can you manipulate meristems?
In many cases, you can manipulate meristems to make a plant do something you want, such as change its growth pattern, flower, alter its branching habit, or produce vegetative growth. This piece is part of the collection Botany Basics. January 2008.