Brain Coverings: Meninges
- The outermost layer, the dura mater, is thick and tough. ...
- The arachnoid mater is a thin, weblike layer of connective tissue that does not contain nerves or blood vessels. ...
- The pia mater is a thin membrane that hugs the surface of the brain and follows its contours. ...
What are the six major structures of the brain?
cerebrum, diencephalon, mesencephalon, pons, medulla oblongata, cerebellum. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. what are the six major regions of the brain? Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Nice work!
What is the internal structure of the brain?
The cerebrum consists of the outer grey matter (cerebral cortex), an inner mass of white matter made up of myelinated axons, which forms the bulk of the deeper structures of the cerebral hemispheres, and subcortical structures which include the diencephalon, pituitary gland, limbic structures and the basal ganglia.
What are the major brain structures?
- Like the cerebrum, it is made up of two, highly convoluted hemispheres.
- The cerebellum coordinates ongoing muscular movements and helps maintain proper posture, equilibrium, and muscle tone.
- The fourth major division of the adult brain is called the brainstem (or brain stem), which lies anterior to the cerebellum and inferior to the diencephalon.
What are the three major regions of the brain?
Other Brain Regions and Their Functions
- Cerebral Cortex. The outermost layer of the cerebral hemisphere, also known as the gray matter. ...
- Corpus Callosum. The corpus callosum connects right and left hemisphere and allows communication between the two hemispheres.
- Frontal Lobe. ...
- Parietal Lobe. ...
- Occipital Lobe. ...
- Temporal Lobe. ...
- Limbic System. ...
- Basal Ganglia. ...
- Internal Capsule. ...
- Reticular Activating System. ...

What are the three main exterior parts of the brain?
The brain has three main parts:The cerebrum fills up most of your skull. It is involved in remembering, problem solving, thinking, and feeling. ... The cerebellum sits at the back of your head, under the cerebrum. It controls coordination and balance.The brain stem sits beneath your cerebrum in front of your cerebellum.
What is the external brain?
An external brain is an organized and reliable system for capturing, clarifying, organizing, reviewing, and executing your open loops.
What are the structures of the brain?
The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem.Cerebrum: is the largest part of the brain and is composed of right and left hemispheres. ... Cerebellum: is located under the cerebrum. ... Brainstem: acts as a relay center connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord.
What are the 4 external lobes of the brain named after?
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into five lobes, four of which have the same name as the bone over them: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the temporal lobe. A fifth lobe, the insula or Island of Reil, lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
What is an example of an external brain?
Assess the level of need by making an inventory of your child's needs: Your child may need all, some, or few of the following External Brain functions - time-keeper, friend-chooser, money-manager, information-interpreter, hygiene-monitor, and decision-maker.
Is the brain internal or external?
Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex....Human brainSystemCentral nervous systemArteryInternal carotid arteries, vertebral arteries13 more rows
How many structure are there in the brain?
The brain is composed of three main structures , the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The brain sends chemical and electrical signals throughout the body to regulate different biological functions and sense environmental changes. The brain communicates with the majority of the body through the spinal cord.
What is the structure and function of brain?
It is responsible for vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure. The brain stem is made of the midbrain, pons, and medulla. Pons – The primary role of the pons is to serve as a bridge between various parts of the nervous system, including the cerebellum and cerebrum.
What are the five parts of the brain?
We're going to talk about these five parts, which are key players on the brain team:cerebrum (say: suh-REE-brum)cerebellum (say: sair-uh-BELL-um)brain stem.pituitary (say: puh-TOO-uh-ter-ee) gland.hypothalamus (say: hy-po-THAL-uh-mus)
What are the four parts of the brain?
Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Although we now know that most brain functions rely on many different regions across the entire brain working in conjunction, it is still true that each lobe carries out the bulk of certain functions.
What are the 4 lobes of the brain and their function?
The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 2). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a fissure known as the central sulcus . The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language.
What is the inner brain called?
Cerebrum. The cerebrum, which forms the major portion of the brain, is divided into two major parts: the right and left cerebral hemispheres. The cerebrum is a term often used to describe the entire brain. A fissure or groove that separates the two hemispheres is called the great longitudinal fissure.
What part of the brain controls decision making?
The Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) and hippocampus are the most critical parts of the human brain for decision making.
What part of the brain is for overseas vision?
The occipital lobes sit at the back of the head and are responsible for visual perception, including colour, form and motion. Damage to the occipital lobe can include: Difficulty with locating objects in environment.
Where is the brain located?
The brain is housed inside the bony covering called the cranium. The cranium protects the brain from injury. Together, the cranium and bones that protect the face are called the skull. Between the skull and brain is the meninges, which consist of three layers of tissue that cover and protect the brain and spinal cord.
What are the 3 fissures of the brain?
The cerebrum is divided into a left and right hemisphere by a longitudinal fissure that goes by many different names: longitudinal fissure, cerebral fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
Which layer of the brain is thick and tough?
The outermost layer, the dura mater, is thick and tough. It includes two layers: The periosteal layer of the dura mater lines the inner dome of the skull (cranium) and the meningeal layer is below that. Spaces between the layers allow for the passage of veins and arteries that supply blood flow to the brain.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
How many nerves are in the cranium?
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
What organ controls memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger, and every other process?
The brain is a complex organ that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger and every process that regulates our body. Together, the brain and spinal cord that extends from it make up the central nervous system, or CNS.
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. Supported by the vertebrae, the spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain and the rest of the body.
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
What is the outermost layer of the brain?
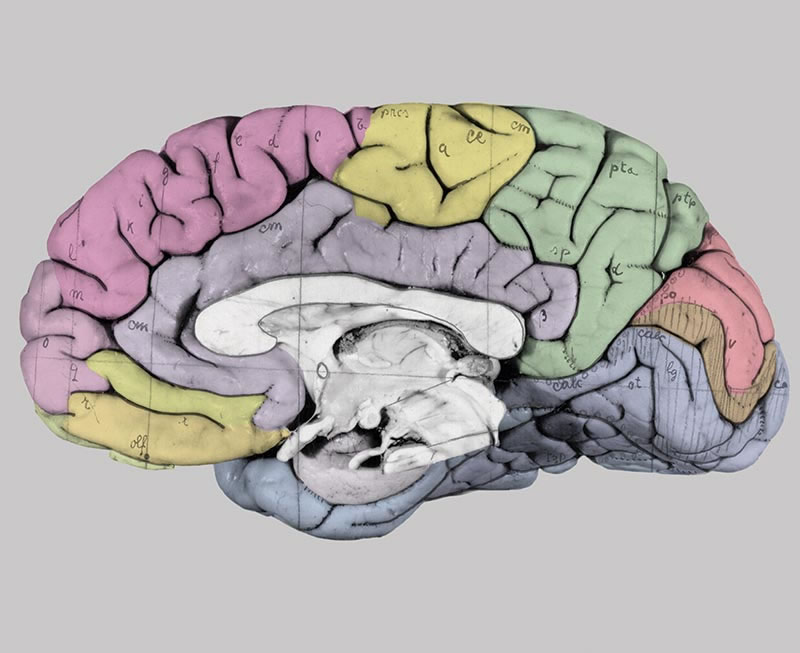
This schematic image refers mainly to the cerebral cortex, the outermost layer that overlies most of the other brain structures like a fantastically wrinkled tissue wrapped around an orange. The preponderance of the cerebral cortex (which, with its supporting structures, makes up approximately 80 percent of the brain's total volume) is actually a recent development in the course of evolution. The cortex contains the physical structures responsible for most of what we call ''brainwork": cognition, mental imagery, the highly sophisticated processing of visual information, and the ability to produce and understand language. But underneath this layer reside many other specialized structures that are essential for movement, consciousness, sexuality, the action of our five senses, and more—all equally valuable to human existence. Indeed, in strictly biological terms, these structures can claim priority over the cerebral cortex. In the growth of the individual embryo, as well as in evolutionary history, the brain develops roughly from the base of the skull up and outward. The human brain actually has its beginnings, in the four-week-old embryo, as a simple series of bulges at one end of the neural tube.
What is the middle bulge of the brain?
What had been the middle bulge in the neural tube develops into the midbrain, which functions mainly as a relay center for sensory and motor nerve impulses between the pons and spinal cord and the thalamus and cerebral cortex. Nerves in the midbrain also control some movements of the eyeball, pupil, and lens and reflexes of the eyes, head, and trunk.
How are the two hemispheres connected?
The two hemispheres are connected mainly by a thick bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum, or "hard body," because of its tough consistency. A smaller bundle, the anterior commissure, connects just the two temporal lobes. Although the corpus callosum is a good landmark for students of brain anatomy, its contribution to behavior has been difficult to pin down. Patients in whom the corpus callosum has been severed (a way of ameliorating epilepsy by restricting seizures to one side of the brain) go about their everyday business without impairment. Careful testing does turn up a gap between sensations processed by the right brain and the language centers of the left brain—for instance, a person with a severed corpus callosum is unable to name an object placed unseen in the left hand (because stimuli perceived by the left half of the body are processed in the right hemisphere). On the whole, though, it appears that the massive crossing-over of nerve fibers that takes place in the brainstem is quite adequate for most purposes, at least those related to survival.
What is the control center for the stimuli that underlie eating and drinking?
The hypothalamus is the control center for the stimuli that underlie eating and drinking. The sensations that we interpret as hunger arise partly from a degree of emptiness in the stomach and partly from a drop in the level of two substances: glucose circulating in the blood and a hormone that the intestine produces shortly after the intake of food. (Receptors for this hormone gauge how far digestion has proceeded since the last meal.) This system is not a simple "on" switch for hunger, however: another portion of the hypothalamus, when stimulated, actively inhibits eating by promoting a feeling of satiety. In experimental animals, damage to this portion of the brain is associated with continued excessive eating, eventually leading to obesity.
What is the limbic system responsible for?
The limbic system is responsible for most of the basic drives and emotions and the associated involuntary behavior that are important for an animal's survival: pain and pleasure, fear, anger, sexual feelings, and even docility and affection. As with the rhinencephalon, the sense of smell is a powerful factor. Nerves from the olfactory bulb, by which all odor is perceived, track directly into the limbic system at several points and are then connected through it to other parts of the brain; hence the ability of pheromones, and perhaps of other odors as well, to influence behavior in quite complex ways without necessarily reaching our conscious awareness.
Which hemisphere of the brain is responsible for the movement of the left arm?
For example, nerve impulses concerned with movement of the left arm originate in the right cerebral hemisphere, and information about the orientation, speed, and force of the movement is fed back to the right cerebral hemisphere, through the left half of the cerebellum. The nerves responsible for movement at the ends of the arms and legs tend to have their origin near the outer edges of the cerebellum. By contrast, nerves that have their origin near the center of the cerebellum serve to monitor the body's overall orientation in space and to maintain upright posture, in response to information about balance that is transmitted by nerve impulses from the inner ear, among other sources.
Where is the cerebellum located in birds?
Its great surface area is accommodated within the skull by elaborate folding, which gives it an irregular, pleated look. In relative terms, the cerebellum is actually largest in the brain of birds, where it is responsible for the constant streams of information between brain and body that are required for flight.
What are the major structures of the brain?
The brain contains various structures that have a multitude of functions. Below is a list of major structures of the brain and some of their functions. Basal Ganglia. Involved in cognition and voluntary movement. Diseases related to damages of this area are Parkinson's and Huntington's. Brainstem.
What is the anatomy of the brain?
The anatomy of the brain is complex due its intricate structure and function. This amazing organ acts as a control center by receiving, interpreting, and directing sensory information throughout the body. The brain and spinal cord are the two main structures of the central nervous system. There are three major divisions of the brain.
What are the two major divisions of the forebrain?
There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon contains structures such as the thalamus and hypothalamus which are responsible for such functions as motor control, relaying sensory information, and controlling autonomic functions. The telencephalon contains the largest part of the brain, ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for processing sensory information?
The forebrain is the division of the brain that is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the telencephalon.
Which part of the brain is responsible for thinking, perceiving, and evaluating sensory information?
The forebrain is responsible for a number of functions related to thinking, perceiving, and evaluating sensory information. The midbrain, also called the mesencephalon, connects the hindbrain and the forebrain. It is associated with motor functions and auditory and visual responses. The hindbrain contains both the metencephalon and ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for balance and balance?
The hindbrain extends from the spinal cord and is composed of the metencephalon and myelencephalon. The metencephalon contains structures such as the pons and cerebellum. These regions assists in maintaining balance and equilibrium, movement coordination, and the conduction of sensory information.
What are the two main structures of the central nervous system?
The brain and spinal cord are the two main structures of the central nervous system. There are three major divisions of the brain. They are the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.
What are the parts of the brain?
There are three main parts of the brain: the cerebrum, cerebellum and the brain stem.
What Are the Regions of the Brain and How Do They Fit Into the Brain Structure?
The three main parts of the brain are split amongst three regions developed during the embryonic period: the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Together, these regions act as a useful map to understanding the various parts of the brain's structure and functions.
What Is the Brain and Why Does It Matter?
The brain is a three-pound organ that serves as headquarters for our bodies. Without it, we wouldn't be able to process information, move our limbs, or even breathe. Together with the spinal cord, brain structure and function helps control the central nervous system—the main part of two that make up the human nervous system. (The other part, the peripheral nervous system, is made up of nerves and neurons that connect the central nervous system to the body's limbs and organs.) The human nervous system is responsible for helping us think, breathe, move, react and feel.
What Are the 4 Lobes of the Brain?
The cerebrum's left and right hemispheres are each divided into four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes . The lobes generally handle different functions, but much like the hemispheres, the lobes don't function alone. The lobes are separated from each other by depressions in the cortex known as sulcus (or sulci) and are protected by the skull with bones named after their corresponding lobes.
What Are the Main Parts of the Brain Stem?
The brain stem is made up of three parts: the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
What Is the Cerebellum?
The cerebellum stands for "little brain" in Latin. It looks like a separate mini-brain behind and underneath the cerebrum (beneath the temporal and occipital lobes) and above the brain stem. The cerebellum (along with the brain stem) is considered evolutionarily to be the oldest part of the brain.
How many nuclei are there in the cerebellum?
Earlier, we learned how four nuclei are responsible for connecting the cerebellum to the body. To connect the cerebellum to the brain stem, the brain depends on nerve tracts called cerebellar peduncles. The cerebellar peduncles help process and analyze motor and sensory information, such as the position of our joints and limbs. There are six cerebellar peduncles (three for each hemisphere) with both white and gray matter. The six cerebellar peduncles are: superior (2), middle (2) and inferior (2).
What are the structures of the brain?
After learning the structure of the brain, here are the fun facts: 1 Weight – Your brain weighs some three pounds, which is half the weight of your skin. 2 Gray matter- The brain’s gray matter is made up of neurons, which gather and transmit signals. There are about 100 Billion neurons in the brain. It takes up 40% of brain matter. 3 White matter- The white matter is made up of dendrites and axons that create the network by which neurons send their signals. It takes up 60% of brain matter. 4 Numbers- The brain is made up of 75% water. It has 60% fat thus making it the fattest organ in the body. It has at least some 100,000 miles of blood vessels in the brain. The brain generates between 10 -23 watts of energy whilst you are awake and this is sufficient to light up a bulb.
What are the parts of the brain?
There are 3 major parts of the brain: cerebrum (Latin for brain), cerebellum (little brain), and brainstem. The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. It is divided into two, the right and the left hemisphere, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers. The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the cerebrum ...
What is the forebrain part of?
Each section contains fluid filled cavities known as ventricles.The midbrain becomes part of the brainstem, the forebrain becomes the cerebrum and other underlying structures and the hindbrain develops into regions of the brainstem and cerebrum. Additionally, the limbic system (or the emotional brain) is buried within the cerebrum.
What is the largest part of the brain?
The Cerebrum (Thought and Action) The cerebrum/cortex is the largest part of the brain and is divided into four sections called lobes. The function of these lobes is listed below: Frontal lobe- Associated with planning of speech, reasoning, emotions, problem solving and movement.
Which lobe of the brain is associated with the perception of auditory stimuli?
Parietal lobe- It’s associated with recognition, movement, orientation, perception of stimuli, speech and memory. Temporal lobe- It’s associated with memory, speech, and the perception and recognition of auditor stimuli. The cerebral cortex is wrinkled, which increases the brain surface and neurons within it, thus making the brain more efficient.
How much does the brain weigh?
After learning the structure of the brain, here are the fun facts: Weight – Your brain weighs some three pounds, which is half the weight of your skin. Gray matter- The brain’s gray matter is made up of neurons, which gather and transmit signals. There are about 100 Billion neurons in the brain. It takes up 40% of brain matter.
How many neurons are there in the brain?
There are about 100 Billion neurons in the brain. It takes up 40% of brain matter. White matter- The white matter is made up of dendrites and axons that create the network by which neurons send their signals. It takes up 60% of brain matter. Numbers- The brain is made up of 75% water.
