Difference Between Fatty Acids and Triglycerides
- Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with -COOH parts, whereas triglycerides are organic esters.
- Fatty acids are derived from triglycerides.
- Three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule undergo esterification to form one triglyceride molecule.
Do triglycerides always contain 3 fatty acids?
Some triglycerides molecules are composed of three identical fatty acids. However, in most cases two or three different fatty acids molecules are found in triglyceride molecules. Triglyceride is insoluble in water due to the presence of large hydrocarbon chains.
Why are fats and oils called triglycerides?
Fats and oils are called triglycerides (or triacylcylgerols) because they are esters composed of three fatty acid units joined to glycerol, a trihydroxy alcohol: Figure 7.2. 1 : Chemical reaction for the formation of a triglyceride. If all three OH groups on the glycerol molecule are esterified with the same fatty acid, the resulting ester is ...
Is the triglyceride simplest fat?
Triglycerides are the basic chemical form of fat,Simple lipids 2 are composed of esters of long-chain carboxylic acids ( fatty acids) which are called triglycerides, the enzyme lipase catalyzes their complete hydrolysis. What Are Triglycerides?
What is the breakdown of triglycerides?
What are triglycerides broken down into during digestion? In the stomach, gastric lipase starts to break down triglycerides into diglycerides and fatty acids. Within two to four hours after eating a meal, roughly 30 percent of the triglycerides are converted to diglycerides and fatty acids.

What type of fatty acid is a triglyceride?
Triglycerides are a combination of: three fatty acids (i.e. saturated fat, unsaturated fat or both – these are the building blocks of fats) glycerol, a form of glucose (a simple sugar).
What are the two types of fatty acids found in triglycerides?
There are many different types of triglycerides, with the main division being between those that contain saturated fatty acids and those that contain unsaturated fatty acids.
What are the 3 components of triglyceride?
A triglyceride is composed of glycerol and three fatty acids. When all of the fatty acids in a triglyceride are identical, it is termed a "simple" triglyceride. The more common forms, however, are the "mixed" triglycerides in which two or three kinds of fatty acids are present in the molecule.
Do triglycerides have fatty acids?
A. Triglycerides are the most common form of fat in the bloodstream. They consist of three fatty acid chains linked by a molecule called glycerol. When you eat food, enzymes in your gut break down fats into their component fatty acids, which are then reassembled to create triglyceride particles.
What elements are found in triglycerides?
Answer and Explanation: The chemical elements that make up triglycerides are hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. These are the components of the glycerol molecule, as well as the components of the three fatty acids that bond to the glycerol.
What are the 3 types of fatty acids?
Dietary fats contain a mixture of saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Foods are often categorized by the predominant type of fatty acids they contain, even though foods contain all three types.
What are the 4 components of triglyceride fats?
There are three important parts to a triglyceride molecule, the glycerol backbone, the ester linkage and. the esterified fatty acids.
What are the 4 molecules in triglyceride?
Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organic acids join to form esters.
Does triglyceride have 3 fatty acids?
Triglycerides (see Fig. 37.3) comprise three fatty acids esterified with a glycerol backbone. 'Triacylglycerols' is the correct chemical name but they are more commonly known as 'triglycerides' and this term will be used throughout this chapter. Triglycerides are the major dietary fat.
What are fatty acids made of?
Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―COOH) at the other end.
What 3 elements make up fatty acids?
Fats and oils are organic compounds that, like carbohydrates, are composed of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O), arranged to form molecules.
Why are fatty acids stored as triglycerides?
Fatty acids as an energy source Fatty acids, stored as triglycerides in an organism, are a concentrated source of energy because they contain little oxygen and are anhydrous.
What are the two types of fatty acids?
Fatty acids can be divided into four general categories: saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and trans fats. Saturated fatty acids and trans fats are associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease.
What are the two main fatty acids?
Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid) and linoleic acid (an omega-6 fatty acid).
What are the 2 types of fatty acids How are they different?
Unsaturated fatty acids have relatively low melting points, which explains why they are liquids at room temperature. Plants use unsaturated fatty acids to store energy. Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one less hydrogen atom than the same-length saturated fatty acid chain.
What are the main 2 types of fats?
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats tend to be more liquid (like canola oil). Fats can also have different effects on the cholesterol levels in your body. A diet high saturated fats and trans fats raise bad cholesterol (LDL) levels in your blood.
What causes triglyceride?
A triglyceride is formed when the three hydroxyls (OH-) groups of a single glycerol molecule react with the carboxyl group (COOH-) of three fatty a...
What type of structure are triglycerides?
Triglycerides are triesters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have...
What does it mean if your triglycerides are high?
High triglycerides may contribute to hardening of the arteries or thickening of the artery walls (arteriosclerosis) — which increases the risk of s...
What are the 3 types of triglycerides?
The three types of fatty acids that compose triglycerides are saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. The three types of trigly...
What causes triglycerides to rise?
The most common causes of high triglycerides are obesity and poorly controlled diabetes. If you are overweight and are not active, you may have hig...
What is a triglyceride?
Triglyceride is an organic ester formed by esterification of glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains. A mixture of triglyceride molecules that contain a high percentage of long-chain saturated fatty acids is called fats, whereas a mixture of triglycerides that contain a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acids or short-chain saturated fatty ...
What are fatty acids made of?
Fatty acids are organic substances made up of a long carbon chain with hydrogen atoms attached and a methyl group (-CH3) at one end and an acid group (-COOH) at the other end. Depending on the presence of C=C double bonds, fatty acids can be divided into two types; saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids do not contain any C=C ...
How many carbon atoms are in a fatty acid?
Most natural fatty acids contain even numbers of carbon atoms, up to 24 atoms in length. However, the structure and function of fatty acid may vary depending on their length of the carbon chain, amount, and the location of double bonds present in the chain.
What are some examples of fatty acids?
Fatty acids are derived from the triglycerides and phospholipids. Some examples for fatty acids are linoleic acid, stearic acid, and oleic acid.
Why is triglyceride insoluble in water?
Triglyceride is insoluble in water due to the presence of large hydrocarbon chains.
Which type of fatty acid lacks two H atoms?
The monounsaturated fatty acids are the fatty acids which lack two H atoms and contain one double bond between two adjacent carbon atoms. This types of fatty acids forms the monounsaturated fat.
What are the lipids?
Lipids are a class of nutrients that mainly include triglycerides (fats and oils), phospholipids, and sterols. Fatty acid and triglycerides are organic substances; contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
What is considered high triglycerides?
For healthy adults, normal triglyceride levels are under 150 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Values of 151 to 200 mg/dL are considered borderline high; those 201 to 499 are high, and those 500 and higher are very high (and increase the risk of inflammation of the pancreas gland, called pancreatitis). Growing evidence suggests that above-normal triglyceride levels can raise the risk of cardiovascular disease independent of cholesterol levels.
What happens to triglycerides after eating?
Triglycerides can provide energy to fuel your body, while the extras are deposited in fat tissue. After a very heavy, fatty meal, your bloodstream may contain so many triglyceride particles that a blood sample may have a milky tint. But within a few hours, they're mostly cleared out.
What are the two types of lipoproteins?
So they combine with cholesterol and protein to form lipoproteins. Your lipid profile lists two of these lipoproteins: low-density lipoprotein (better known as LDL cholesterol) and high-density lipoprotein (also called HDL cholesterol).
What is the most common form of fat in the bloodstream?
A. Triglycerides are the most common form of fat in the bloodstream. They consist of three fatty acid chains linked by a molecule called glycerol. When you eat food, enzymes in your gut break down fats into their component fatty acids, which are then reassembled to create triglyceride particles.
How to get triglycerides back to normal?
To get your triglycerides back into a normal range, start with lifestyle changes. Aim for a healthy weight, get regular exercise, and eat more whole, unprocessed grains. Eat fewer refined carbohydrates, and cut back on saturated fat from meat.
Do lipoproteins have triglycerides?
But there are actually several other types of lipoproteins, including some that contain mainly triglycerides. Triglycerides can provide energy to fuel your body, while the extras are deposited in fat tissue. After a very heavy, fatty meal, your bloodstream may contain so many triglyceride particles that a blood sample may have a milky tint. But within a few hours, they're mostly cleared out. When you need energy between meals, hormones release the stored triglycerides into the bloodstream.
What are triglycerides made of?
Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organic acids join to form esters. The glycerol molecule has three hydroxyl (HO–) groups and each fatty acid has a carboxyl group (–COOH).
Why are triglycerides present in the blood?
They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils. Many types of triglycerides exist. One specific classification focuses on saturated and unsaturated types. Saturated fats lack C=C groups.
What is the left part of a triglyceride?
Left part: glycerol; right part, from top to bottom: palmitic acid, oleic acid, alpha-linolenic acid. A triglyceride ( TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from tri- and glyceride ). Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, ...
What are the different types of fatty acids?
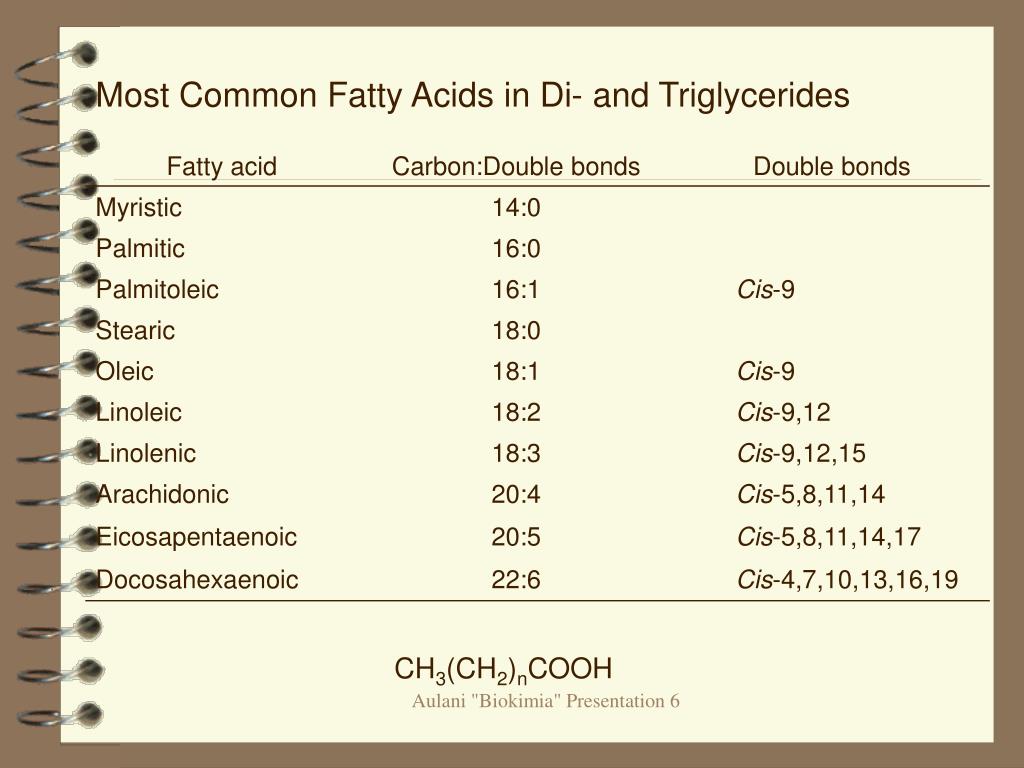
Some common examples of fatty acids: 1 Butyric acid with 4 carbon atoms (contained in butter) 2 Lauric acid with 12 carbon atoms (contained in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and breast milk) 3 Myristic acid with 14 carbon atoms (contained in cow's milk and dairy products) 4 Palmitic acid with 16 carbon atoms (contained in palm oil and meat) 5 Stearic acid with 18 carbon atoms (also contained in meat and cocoa butter)
How many carbons are in a medium chain fatty acid?
Medium-chain fatty acid ( MCFA) with 6 to 12 carbons (e.g. capric acid ). Long-chain fatty acids ( LCFA) with 13 to 21 carbons (e.g. petroselinic acid ). A triglyceride molecule may have fatty acid elements of different lengths, and a fat product will often be a mix of various triglycerides.
What is the role of the pancreatic lipase in the lipid bond?
The pancreatic lipase acts at the ester bond, hydrolyzing the bond and "releasing" the fatty acid. In triglyceride form, lipids cannot be absorbed by the duodenum. Fatty acids, monoglycerides (one glycerol, one fatty acid), and some diglycerides are absorbed by the duodenum, once the triglycerides have been broken down.
What are the names of fatty acids?
In chemistry and biochemistry, dozens of saturated fatty acids and of hundreds of unsaturated ones have traditional scientific/technical names usually inspired by their source fats (butyric, caprylic, stearic, oleic, palmitic, and nervonic ), but sometimes their discoverer ( mead, osbond ).
What are the three types of fatty acids that make up triglycerides?
The three types of fatty acids that compose triglycerides are saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids . From these three types of fatty acids come the three types of triglycerides, or fats; saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated tri glycerides.
Which fatty acids are saturated?
Saturated Triglycerides. In saturated triglycerides, or satura ted fats, most of the fatty acids are saturated, which technically means that each carbon atom has the maximum number of attached hydrogen atoms. Saturated fats are the biggest dietary cause of high LDL, or 'bad', cholesterol levels.
What foods lower cholesterol?
Foods that contain polyunsaturated fats include many vegetables oils and fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, herring and trout.
What type of fat is most fatty?
Most of the fatty acids are polyunsaturated in polyunsaturated fats. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are two or more pairs of hydrogen atoms short of saturation; two examples are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Polyunsaturated fat is another type of unsaturated fat, and they too can help lower your cholesterol levels when you consume them instead of saturated fats. Foods that contain polyunsaturated fats include many vegetables oils and fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, herring and trout.
What are hydrogenated trans fats?
You may be wondering where hydrogenated trans fats fit into the picture. These trans fats are not naturally occurring; an industrial process adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils, making them solid at room temperature. The American Heart Association reports that trans fats raise your bad LDL cholesterol while lowering your good HDL levels, and they also increase your risk of developing heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes. Trans fatty acids are found in fried foods and commercial baked goods such as cookies, donuts and crackers, as well as in processed foods and many margarines.
What foods have monounsaturated fats?
Foods with high levels of monounsaturated fats include vegetable oils such as olive oil, canola oil, peanut oil and sesame oil. You can also get monounsaturated fats by eating avocados, peanut butter and a variety of nuts and seeds. Advertisement.
What is the lipid in your blood?
Triglycerides are a type of lipid, or fat, found in your blood. When you eat, your body converts calories it does not use right away into triglycerides, which your body later stores in your fat cells. Between meals, hormones release triglycerides to provide you with energy. Regularly eating more calories than you burn may lead to high triglyceride levels in your blood. There are three different types of triglycerides.
How many fatty acids are in glycerol?
One molecule of glycerol and three fatty acids
Which tissue stores triglycerides?
Fat cells of the adipose tissue readily take up and store triglycerides. Unlimited capacity
What is the goal of fat digestion?
Goal of fat digestion is to dismantle triglycerides into small molecules the body can absorb and use. End result are fatty acids and glycerol
How many carbons are in a polyunsaturated fatty acid?
Polyunsaturated fatty acid with its closest double bond six carbons away from the methyl end
What is the transport vehicle for lipids?
Within the intestinal cells, the newly made triglycerides and other lipids (cholesterols and phospholipids) are packed with protein into transport vehicles called chylomicrons that glide through the lymph until they reach the bloodstream (thoracic duct)
What is the third site of glycerol?
One glycerol with two of its three attachment sites occupied by fatty acids. Third site is occupied by a phosphate group and a molecule of choline. Both hydrophobic and hydrophilic. Used as an emulsifier to mix fats with water in such products as mayo, salad dressings, and candy
How many types of fat are there in the bloodstream?
Solve the body's challenge of transporting fat through the watery bloodstream. 4 main types, distinguished by size and density. Each contains different amounts of lipids and proteins. More lipids, less dense and vise versa
Why do high triglycerides matter?
High triglycerides may contribute to hardening of the arteries or thickening of the artery walls (arteriosclerosis) — which increases the risk of stroke, heart attack and heart disease. Extremely high triglycerides can also cause acute inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
Why are triglycerides important?
Triglycerides are an important measure of heart health. Here's why triglycerides matter — and what to do if your triglycerides are too high. If you've been keeping an eye on your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, there's something else you might need to monitor: your triglycerides.
What are the different types of lipids that circulate in your blood?
Triglycerides and cholesterol are different types of lipids that circulate in your blood:
What is the name of the fat that is found in the blood?
Triglycerides are a type of fat (lipid) found in your blood.
What are the risks of high triglycerides?
High triglycerides are often a sign of other conditions that increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, including obesity and metabolic syndrome — a cluster of conditions that includes too much fat around the waist, high blood pressure, high triglycerides, high blood sugar and abnormal cholesterol levels.
What medications lower triglycerides?
Fibrates. Fibrate medications, such as fenofibrate (TriCor, Fenoglide, others) and gemfibrozil (Lopid), can lower your triglyceride levels. Fibrates aren't used if you have severe kidney or liver disease.
What foods increase triglycerides?
Avoid sugar and refined carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, such as sugar and foods made with white flour or fructose, can increase triglycerides.

Overview
Classification
Fats can be classified according to the lengths of the carbon chains of their constituent fatty acids. Most chemical properties, such as melting point and acidity, vary gradually with this parameter, so there is no sharp division. Chemically, formic acid (1 carbon) and acetic acid (2 carbons) could be viewed as the shortest fatty acids; then triformin would be the simplest triglyceride. However, the terms "fatty acid" and "fat" are usually reserved for compounds with su…
Chemical structure
Triglycerides are tri-esters consisting of a glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules. Alcohols have a hydroxyl (HO–) group. Organic acids have a carboxyl (–COOH) group. Alcohols and organic acids join to form esters. The glycerol molecule has three hydroxyl (HO–) groups and each fatty acid has a carboxyl group (–COOH). In triglycerides, the hydroxyl groups of the glycerol join the ca…
Nomenclature
Fats are usually named after their source (like olive oil, cod liver oil, shea butter, tail fat) or have traditional names of their own (like butter, lard, ghee, and margarine). Some of these names refer to products that contain substantial amounts of other components besides fats proper.
In chemistry and biochemistry, dozens of saturated fatty acids and of hundreds of unsaturated ones have traditional scientific/technical names usually inspired by their source fats (butyric, ca…
Industrial uses
Linseed oil and related oils are important components of useful products used in oil paints and related coatings. Linseed oil is rich in di- and tri-unsaturated fatty acid components, which tend to harden in the presence of oxygen. This heat-producing hardening process is peculiar to these so-called drying oils. It is caused by a polymerization process that begins with oxygen molecules attacking the carbon backbone.
Staining
Staining for fatty acids, triglycerides, lipoproteins, and other lipids is done through the use of lysochromes (fat-soluble dyes). These dyes can allow the qualification of a certain fat of interest by staining the material a specific color. Some examples: Sudan IV, Oil Red O, and Sudan Black B.
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
See also
• Diglyceride acyltransferase, enzyme responsible for triglyceride biosynthesis
• Medium-chain triglycerides
• Lipid profile
• Lipids