
Karst Topography – Erosional Landforms
| Pools | An opening at the top with water collect ... |
| Sinkholes | Depression on the limestone/dolomitic re ... |
| Lapies | It is formed due to differential solutio ... |
| Limestone Pavements | It is a smoother form of lapies |
| Caves | Cave formation is prominent in areas whe ... |
What are the three features that characterize karst topography?
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum.It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes.
Which features are usually associated with karst topography?
The following is a partial list of National Park Service units that include karst landscapes:
- Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Park, Kentucky— [ Geodiversity Atlas] [ Park Home]
- Buffalo National River, Arkansas— [ Geodiversity Atlas] [ Park Home]
- Carlsbad Caverns National Park, New Mexico— [ Geodiversity Atlas] [ Park Home]
- Cumberland Gap National Historical Park, Kentucky— [ Geodiversity Atlas] [ Park Home]
What are the characteristics of karst topography?
characteristics of karst region
- Karst formation and Skinhole. The karst formation process is linked to what is known as the “carbon dioxide cascade” . ...
- Importance of Karst Topography. The karstic formation process can result in the formation of several large or small features both at the surface and below ground.
- karst topography Map. ...
- Environmental problems induced by karst. ...
What are the features of karst?
- User-friendly screens, big fonts for important figures like, Subtotal, Total, Change and Quantity etc.
- Makes billing easier without using mouse
- Supports barcode scanning
- Scanning item on SKU/PLU/EAN
- Subtotal/Close key (to close a transaction)
- Last item void/Past item void
- Refund with authorization
- Overing (full cancellation of same day bill)
- Reprint Bill

What are 3 features of karst topography?
Features of karst landscapes include caves, springs, disappearing streams, dry valleys, and sinkholes.
What is one of the main features of karst topography?
Karst is a type of landscape where the dissolving of the bedrock has created sinkholes, sinking streams, caves, springs, and other characteristic features. Karst is associated with soluble rock types such as limestone, marble, and gypsum.
What are two common features of karst topography?
When carbonate rocks dissolve, distinctive solution features develop that are characteristic of karst terrains; the more common features are springs, sinkholes, caves, and sinking or disappearing streams (fig.
What is karst topography which kind of features can it form?
Karst topography refers to natural landscape that is largely the result of chemical weathering by water, resulting in caves, sinkholes, cliffs, and steep-sided hills called towers. These features form when water picks up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and ground to form carbonic acid.
What features are characteristic of karst topography quizlet?
The INITIAL stages of Karst Topography are: Sinkholes, potholes, and caverns. Natural void in Rock created by Solution large enough for people to enter. The dominant geomorphic agent on Earth.
What is the most common surface feature of karst landscapes?
Examples of some of the most common surface karst features encountered are as follows: Sinkhole – a topographically closed depression that is circular or elliptical in shape and with steep to vertical sidewalls.
What is karst topography in geography?
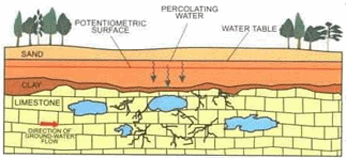
Karst Topography is the formation of landforms due to solution and deposition on any limestone or dolomitic region by the action of groundwater or surface water.
Which formation is one feature of karst topography quizlet?
One of the most spectacular features of karst topography is a cave, like those from Carlsbad National Park. This picture shows a cross-sectional view of a cave, where you can see some features of caves, like an underground lake, stalactites, and stalagmites.
Why is it called karst topography?
Why is karst topography important? Topography refers to the features of a natural area (or a description or map of those features). Karst comes from a German word for the rocky region that covers parts of Italy and Slovenia. This area is now known simply as “the Karst.”
How many landforms does karst have?
Karst Landforms – Cavern, Arch/Natural Bridge, Sink Hole/Swallow Hole, Karst Window, Sinking Creeks/Bogas, Stalactite and Stalagmite.
What karst means?
Definition of karst : an irregular limestone region with sinkholes, underground streams, and caverns.
What is karst topography?
Karst Topography is the formation of landforms due to solution and deposition on any limestone or dolomitic region by the action of groundwater or surface water. Landforms and its evolution is an important segment of the Geography syllabus of the IAS Exam. Read relevant facts about Karst landforms for the UPSC preparation.
What are the features of Karst?
The features of Karst Topography are listed down below: Swallow Hole in Section – When the stream of groundwater/surface water disappears in the hole; it is called a swallow hole. It is also called ‘Ponor’, and ‘Serbo-Coat.’. Cave in Section – Due to the erosion caused by either running water or surface water, a cavity is formed in ...
How are karsts formed?
The karsts are formed in the regions that meet the following conditions: Karst topography will be found in such regions which will have a large stretch of water-soluble rocks such as limestone at the surface or sub-surface level. The limestones of the karst topography are not porous.
What are the characteristics of karst?
The underground drainage system is one of the significant characteristics of the karst regions. Karst is most strongly developed in dense carbonate rock, such as limestone, that is thinly bedded and highly fractured. (*source – wiki) Certain other features of Karst are: Solution flutes (or rillenkarren)
What is a cave in section?
Cave in Section – Due to the erosion caused by either running water or surface water, a cavity is formed in the rock which transforms into a cave. Sink Holes – It is one of the most common features in Karst Topography. It is a depression on the limestone/dolomitic region that ranges from a shallow saucer shape to a funnel-shaped or cylindrical pipe.
What are the shapes of stalagmites?
The shapes of stalagmites range from the column, a disc, with either a smooth, rounded bulging end to a miniature crater-like depression. Pillars. The combination or fusion of stalactites and stalagmites form the pillars. The diameters of pillars vary.
Why do stalagmites rise from the floor?
Unlike stalactites those hang from the ceiling; stalagmites rise from the floor. It is formed due to the deposition of the dripping water of either the surface water or the stalactites.
How does karst topography form?
Karst topography forms when water dissolves and erodes soft rock (like limestone) and leaves landscapes behind such as caves. These areas make up ten percent of Earth's surface and provide freshwater to hundreds of millions of people.
What are some examples of karst topography?
Types of Karst Topography. Karst landscapes vary considerably. For example, some karst areas have streams and rivers that will disappear into the ground, only to reappear later as springs on the surface.
What type of landscape forms when water dissolves and erodes soft rock (like limestone) and leaves landscapes behind
One that you may not be quite as familiar with is karst topography. This is a type of landscape that forms when water dissolves and erodes soft rock (like limestone) and leaves landscapes behind such as caves, surface sinkholes, and tall, steep rock cliffs.
Why is Karst water so vulnerable to contamination?
This is because there is a lot of water moving through these regions and the soft rock doesn't provide a good filtration system to remove contaminants from the water.
What are the characteristics of karst?
Some karst regions are sharp jagged hills, while others are soft rolling hills with depressions that used to be sinkholes . These sinkholes are characteristic of karst landscapes, and are places where the surface collapses in on itself, creating a funnel-shaped hole in the ground.
Why are karsts important?
Karst regions are also important features because some 25 percent of the world's population relies on water that karst areas provide. The aquifers, springs, ground, and surface waters of karst regions provide drinking water for hundreds of millions of people all over the world, making them a valuable freshwater resource.
Why are karsts unstable?
Karst landscapes tend to be unstable because they are so susceptible to water movement and rock erosion. Communities built on karst topography may spend large amounts of money repairing road and building damage due to changes in the surface of karst landscapes. Lesson Summary.
What is the Karst topography?
Karst topography refers to a type of subterranean limestone caverns landscape, as well the mysterious-looking formations like caves, surface sinkholes, and rocky, overhanging cliffs, as a result of a specific natural occurrence. Originally known as Kras, the term was first applied to an area abundant in limestone in Slovenia, ...
What is the topography of the Karst Mountains?
The most grandiose Karst topographical features are fashioned by nature in the presence of dense limestone, abundant rainfall, and a moderate underground water system. A common feature in Karst Topography, are three-dimensional shapes, such as a monolithic limestone promontory, ...
What are the three main components of karst topography?
All types of Karst topography, from simple crevices to projecting bluffs and hollow caves, require three main components in their creation. The most grandiose Karst topographical features are fashioned by nature in the presence of dense calcium carbonate, more commonly known as limestone. Heavy rainfall and moderate groundwater circulation are ...
What are the three dimensional features of Karst?
A common feature in Karst Topography, are three-dimensional shapes, such as a monolithic limestone promontory, which is an erect protrusion out of lowland or a body of water. Discus macclintocki is a species of snails that survived the freezing temperatures during the Ice Age by flowing over buried Karst formations.
Where was the Karst Cave formed?
Early Study. Karst Cave Postojnska-Jama formed by the Pivka river in Slovenia. The origin of karst topography being carved by groundwater was based on the Dinaric Kras region and first described in literature by the Serbian geographer Jovan Cvijic in his publication "Das Karstphänomen" (1893). Discerning that aquifers were responsible for ...
What are some examples of Causses?
Some examples are Europe's gorged plateaus of south-western France, called the Causses, including the "Ares de l'Anie" in the Barétous valley, the Burren karst hills on the west coast of Ireland, and China's Kwangsi area or the Guangxi state that borders Vietnam, featuring variations in heights from 1,500 to 3,000 feet.
What is the result of a barren land with jagged terrain and chance caves?
Resulting is a barren land with jagged terrain and chance caves, all of which allows for more water to seep in. A karst river, such as Ljubljanica in Slovenia, disappearing underground and resurfacing in numerous places under other names, leads to the formation of underground cave systems or underground stream channels.
Where is karst topography found?
Karst topography generally develops in those areas where thick beds of massive limestones lie just below the layer of surficial materials. Besides, karst topography also develops on dolomite, dolomitic limestones and chalks. Besides typical karst region of earstwhile Yugoslavia, karst topography has well developed in Causes Region of southern France; Spanish Andalusia; northern Puertorico; western Cuba; Jamaica; southern Indiana, west-central Kerntucky, Virginia, Tennessee and central Florida of the USA.
Why does the surface of the Karst Plain look like a sieve?
The surface of the karst plain looks like a sieve because of development of closely spaced numerous sink holes. These sink holes act as funnels because surface water disappears to go underground through these holes.
What is the limestone topography of Yugoslavia?
Numerous caves and stalagmites and stalactites have been formed below the surface. Thus, the limestone topography all over the world having characteristic features similar to the karst region of earstwhile Yugoslavia is universally called karst topography.
What are the landforms produced by chemical weathering or chemical erosion of carbonate rocks?
Landforms produced by chemical weathering or chemical erosion of carbonate rocks mainly calcium carbonate (CaCO 3, limestones) and magnesium carbonate (dolomites) by surface and subsurface water (groundwater) are called karst topography which refers to characteristic landforms produced by chemical erosion on crystalline jointed limestones of Karst region of earstwhile Yugoslavia situated along the eastern margin of Adriatic Sea.
How is a karst window formed?
Karst window is formed due to collapse of upper surface of sink holes or dolines. These windows enable the investigators to observe sub-surface drainage and other features formed below the ground surface. Extensive depressions are called uvalas which are upto one kilometre across.
What is the process that dissolves limestones and other carbonate rocks along their joints?
Chemically active rainwater (charged with atmospheric carbon dioxide) dissolves limestones and other carbonate rocks along their joints and thus numerous types of solution holes (e.g. sink holes, dolines etcr) are developed at the ground surface when limestones are directly exposed to the atmospheric processes.
Why should limestones not be porous?
ADVERTISEMENTS: (2) Limestones should not be porous wherein permeability is largely controlled by joints and not by the mass of rocks because if limestones are porous, the water may pass through the rock mass and thus whole rock mass will become weak and will collapse.
What are the characteristics of a karst?
Common geological characteristics of karst regions that influence human use of its land and water resources include ground subsidence, sinkhole collapse, groundwater contamination, and unpredictable water supply.
What are some examples of karst landscapes?
Examples include the sinkhole plains and caves of central Kentucky, the large crystal-clear springs of Florida, and the complex, beautifully decorated caves of New Mexico.
Why is karst important?
And why is it important? Karst is a special type of landscape that is formed by the dissolution of soluble rocks, including limestone and dolomite. Karst regions contain aquifers that are capable of providing large supplies of water. More than 25 percent of the world’s population either lives on or obtains its water from karst aquifers.
What percentage of the US is karst?
In the United States, approximately 20 percent of the land surface is karst and roughly 20 percent of all groundwater withdrawals in the year 2000 came from karst aquifers ( Maupin and Barber, 2005 ). Natural features of the landscape such as caves and springs are typical of karst regions.
Early Study
Common Features
- Most caves are formed when a rather narrow range of physio-geographic conditions have been met, and, therefore, when one discovers a cave, they can almost be certain that they are in one of the karst areas of the world. They will also find themselves in the presence of other common physical characteristics of such areas, including lapiés, natural bridges, and pepino hills. Anothe…
How Karst Forms
- In general, the features of Karst Topography are the effects of the underground water that excavates the soluble limestone composition of the Earth's surface. All types of Karst topography, from simple crevices to projecting bluffs and hollow caves, require three main components in their creation. The most grandiose Karst topographical features are...
Where Karst Can Be Found?
- Karst is not specific to a certain geographic area on Earth, but scattered throughout, to be found on all continents but Antarctica, in over 60 countries of the world. Some examples are Europe's gorged plateaus of south-western France, called the Causses, including the "Ares de l'Anie" in the Barétous valley, the Burren karst hills on the west coast of Ireland, and China's Kwangsi area or t…
Effects on Human Life
- Although there are a few ways in which Karst Topography is useful to humans aside from creating marvellous landscapes and other natural wonders, it often poses an impediment to human activities, such as farming. In Karst regions where limestone is predominant, the soils are unable to hold on to water, even being fertile and receiving abundant rainfall. Farmers in karst areas mu…
Karst Ecosystem
- Although trees are sparser here, a large variety of low-growing plants can grow in Karst ecosystems, having adopted highly developed root systems. By entering the cracks and anchoring themselves to the ground, they absorb water according to their needs. Karst ecosystems present suitable living conditions for animals such rabbits, foxes, reptiles and other invertebrates, bats, a…