
Characteristics of underground water that make it particularly desirable for industry are its uniform temperature and uniform quality at a given source.
Full Answer
What are the characteristics of groundwater?
Often. Increased by high temperatures Some of the most typical characteristics of groundwater are weak turbidity, a constant temperature and chemical composition and almost overall absence of oxygen. Circulating groundwater can have extreme variation in the composition with the appearance of pollutants and various contaminants.
What is underground water made of?
Underground water includes all water that occurs below the earth's surface, occupying interstices or voids of pervious rocks and soil; like surface water, it is derived principally from precipitation that falls upon the earth's surface and percolates downward under gravity.
How is the quality of underground water affected by the environment?
Although all underground water contains mineral matter derived principally from soil and rocks through which it moves, its quality and temperature will generally remain constant at a given locality unless it is contaminated by human activities.
How much of Texas'water comes from underground?
More than half of all municipal water in Texas comes from underground water. The largest single use of underground water in Texas is for irrigation. In 1990, 6 million acres in Texas was irrigated, and about 70 percent of all irrigation water came from underground sources.
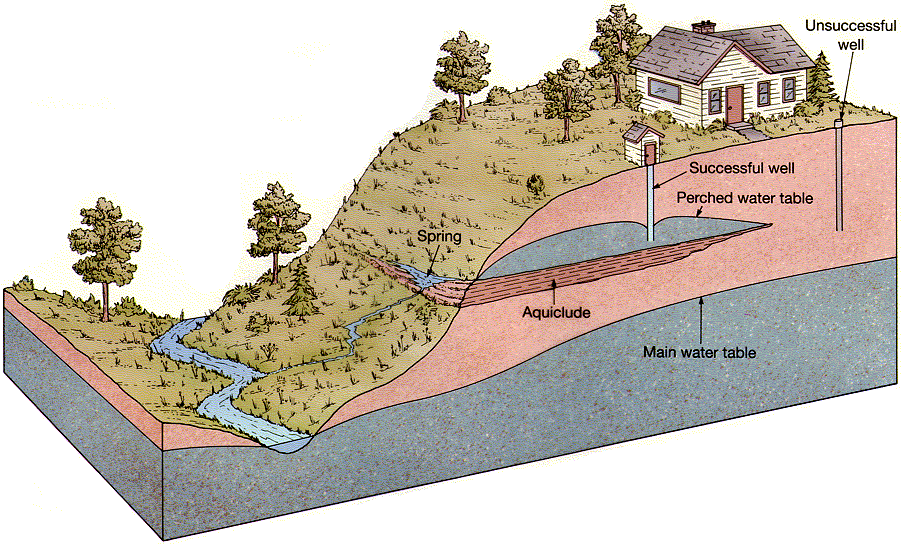
How many major aquifers are there in Texas?
In all, Texas has seven major and sixteen minor aquifers. They underlie approximately 76 percent of the area of Texas. The massive Ogallala aquifer accounts for 90 percent of the total water in all the Texas aquifers. In the mid-to-late 1980s 11 million acre-feet a year was being withdrawn from aquifers in the state of Texas.
How much water was withdrawn from the Texas aquifer in the 1980s?
In the mid-to-late 1980s 11 million acre-feet a year was being withdrawn from aquifers in the state of Texas. However, only 5.3 million acre-feet a year replenished the aquifers. Underground water is a principal water resource in Texas, and its importance as a source of supply for municipal, industrial, and irrigation uses, ...
What is underground water?
Underground water includes all water that occurs below the earth's surface, occupying interstices or voids of pervious rocks and soil; like surface water, it is derived principally from precipitation that falls upon the earth's surface and percolates downward under gravity. Underground water in the zone of saturation may occur in ...
What is the largest use of underground water in Texas?
The largest single use of underground water in Texas is for irrigation. In 1990, 6 million acres in Texas was irrigated, and about 70 percent of all irrigation water came from underground sources. More underground water is used for irrigation in Texas than for all other uses combined.
What is the main source of water in Texas?
Underground water is a principal water resource in Texas, and its importance as a source of supply for municipal, industrial, and irrigation uses, as well as domestic and livestock purposes, is immeasurable. In 1990 more than half of the water used in Texas was underground water; about 71 percent was for agricultural use and 21 percent for municipal use, with the remainder going to industrial needs. Many large cities and most of the smaller cities and communities in Texas supply their water needs from municipally-owned wells or from a combination of surface and underground water sources. More than half of all municipal water in Texas comes from underground water. The largest single use of underground water in Texas is for irrigation. In 1990, 6 million acres in Texas was irrigated, and about 70 percent of all irrigation water came from underground sources. More underground water is used for irrigation in Texas than for all other uses combined. Heavily irrigated areas using underground water are the High Plains region, the Winter Garden Region, Pecos-Coyanosa, and the Salt Basin areas in the Trans-Pecos. Of all water pumped for irrigation purposes in Texas, 68 percent is produced in the Southern High Plains.
Why is underground water important?
Characteristics of underground water that make it particularly desirable for industry are its uniform temperature and uniform quality at a given source.
How long has Texas history been recorded?
From Cabeza de Vaca’s ship-wreck in 1528 through the Texas Revolution to present day… almost 500 years of recorded history … a myriad of significant events in Texas history have occurred (political, cultural, sporting, meteorological, criminal, tragic and amusing). These events are arranged by day of the year to allow the reader to see ‘into ]
How many people rely on groundwater for drinking water?
The quality of our Nation's waters: Water quality in principal aquifers of the United States, 1991-2010. About 130 million people in the United States rely on groundwater for drinking water, and the need for high-quality drinking-water supplies becomes more urgent as our population grows.
What is the purpose of the USGS?
USGS scientist tests groundwater samples for water quality. The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling.
How long does groundwater stay in an aquifer?
As a result, water could remain in an aquifer for hundreds or thousands of years. Groundwater is the source of about 40 percent of water used for public supplies and about 39 percent of water used for agriculture in the United States.
What is the USGS?
The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling. The latest results from five regional aquifers are now available.
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. The upper surface of the saturated zone is called the water table. Contrary to popular belief, groundwater does not form underground rivers. It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock, ...
How much groundwater was withdrawn in 2015?
In 2015, about 84,600 million gallons per day (Mgal/d) of groundwater were withdrawn in the United States for various uses including public supply, self-supplied domestic, industrial, mining, thermoelectric power, aquaculture, livestock, and irrigation.
How often do precipitation events occur?
Large precipitation events that occur about every 10 years are a critical source of recharge for replenishing groundwater resources, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey and the Bureau of Reclamation.
What are the properties of groundwater?
Composition: The geological nature of the soil determines the chemical composition of the groundwater. Water is constantly in contact with the ground in which it stagnates or circulates, so equilibrium develops between the composition of the soil and that of the water: i.e.
Why is water under pressure?
The water held in these spaces is under pressure because of the weight of water in the portion of the aquifer above it. If a well is drilled from the land surface through the overlying impervious layer into the aquifer, this pressure will cause the water to rise in the well.
What determines the rate of groundwater flow?
The rate of groundwater flow is controlled by two properties of the rock: porosity and permeability. Porosityis the percentage of the volume of the rock that is open space (pore space). This determines the amount of water that a rock can contain. In sediments or sedimentary rocks the porosity depends on grain size, grain shapes, the degree of sorting, and the degree of cementation. Permeabilityis a measure of the degree to which the pore spaces are interconnected, and the size of the interconnections. Low porosity usually results in low permeability, but high porosity does not necessarily imply high permeability. It is possible to have a highly porous rock with little or no interconnections between pores. A good example of a rock with high porosity and low permeability is a vesicular volcanic rock, where the bubbles that once contained gas give the rock a high porosity, but since these holes are not connected to one another the rock has low permeability [2].
Why does groundwater move upwards?
First groundwater moves downward due to the pull of gravity. But it can also move upwards because it will flow from higher-pressure areas to lower pressure areas.
Is artesian water cold?
Water from an artesian well or spring is usually cold and free of organic contaminants, making it desirable for drinking .
Groundwater Management and Resources
1. Choose citation style Select style Vancouver APA Harvard IEEE MLA Chicago
Abstract
Groundwater system is very vital to humanity and the ecosystem. Aquifers are determined based on the absence or presence of water table positioning, that is, confined, unconfined, leaky aquifers and fractured aquifers.
1. Introduction
Groundwater (GW) belongs to all subsurface water, including saturated and unsaturated zones. More than 1.5 billion inhabitants around the globe depend on the groundwater for agriculture usage and industrialization consumption. However, pollutions were identified as one of the major challenges in hampering GW withdrawal ( Figure 1) [ 1 ].
2. Groundwater distribution and aquifer characteristics
The distribution of groundwater is classified into two zones based on the water table, namely, unsaturation zone and saturation zone.
3. Groundwater and surface water interaction
Groundwater moves across flow paths arranged in space and develop a flow system. GW flow system is classified into local, intermediate, and regional flow systems ( Figure 3) [ 17 ]. Water travels to the adjacent discharge area in a local flow system.
4. Different types of SW-GW interactions
There are several types of interactions between GW and SW. A losing river does not lose water as it flows downstream by percolation, but it can also lose water through evaporation, use of plants, and consumption of human activities.
5. Methods
The methods for the investigation of aquifer systems such as remote sensing (RS) and geographic information system (GIS), resistivity test, and pumping tests will be discussed.
