What are the 5 components of reading?
English Language Learners and the Five Essential Components of Reading InstructionPhonemic awareness. Phonemes are the smallest units making up spoken language. ... Phonics. ... Vocabulary development. ... Reading fluency, including oral reading skills. ... Reading comprehension strategies.
What are the different areas of reading?
The Five Components of ReadingPhonics. Phonics is the process of mapping the sounds in words to written letters. ... Phonemic awareness. Children develop phonemic awareness by learning about sounds (phonemes), syllables and words. ... Vocabulary. ... Fluency. ... Reading comprehension.
What are the 5 reading strategies?
There are 5 separate strategies that together form the High 5 Reading Strategy.Activating background knowledge. Research has shown that better comprehension occurs when students are engaged in activities that bridge their old knowledge with the new. ... Questioning. ... Analyzing text structure. ... Visualization. ... Summarizing.
What are 5 characteristics of a good reading study area?
Effective instructional programs and materials emphasize the five essential components of effective reading instruction: phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension.
What are the 7 types of reading?
7 Reading Techniques or Styles are the following:Scanning.Skimming.Active Reading.Detailed.Speed.Structure-Proposition-Evaluation.Survey-Question-Read-Recite-Review.
What are the 5 benefits of reading?
5 Benefits of ReadingReduces stress and helps you relax. ... Improves your concentration and memory. ... Vocabulary expansion and strengthens your writing abilities. ... Enhances your knowledge. ... Increases your imagination and creativity.
What are the 4 types of reading?
Four Reading Skills—From Skimming and Scanning to Intensive and Extensive ReadingSkimming.Scanning.Intensive.Extensive.
What are the basic skills of reading?
Basic Reading SkillsDecoding. Decoding or sounding out words is the first step in reading. ... Vocabulary. Good readers increase their vocabulary every time they read and are able to recall these words when they see them again. ... Fluency. ... Comprehension.
What are the 4 strategies of reading?
To improve students' reading comprehension, teachers should introduce the seven cognitive strategies of effective readers: activating, inferring, monitoring-clarifying, questioning, searching-selecting, summarizing, and visualizing-organizing.
What are the 5 stages of literacy development?
The five stages of literacy development are emergent literacy, alphabetic fluency, words and patterns, intermediate reading, and advanced reading.
What are the different stages of reading?
These three phases are pre-reading, while-reading and after-reading phases. Each of them has its own important role. They are all necessary parts of a reading activity. In language classrooms, these phases have to be put in consideration in order to achieve to develop students' reading skills.
What are the 5 language skills?
You should not be surprised to learn that these five categories are Reading, Listening, Speaking, Writing, and Grammar.
What are the 4 different levels of reading?
There are four levels of reading....The 4 Levels of ReadingElementary Reading. The first level of reading is elementary reading, which is what we learned to do in elementary school. ... Inspectional Reading. ... Analytical Reading. ... Syntopical Reading.
What are the 4 levels of reading comprehension?
4 Levels of Reading Comprehension.Level 1: Right There – the answer is in front of you.Level 2: Think and Search – the answer is in front of you, but you need. to look for it.Level 3: “The Author and You – the answer is not in front of you, use. ... Level 4: “In you Head – the answer is not in the book – it is your own.
What are three types of reading required in the content areas?
During this process he is (hopefully) making meaning on three different levels: literal (understanding the information written on the page), inferential (reading 'between the lines') and evaluation (making judgments and conclusions about the information).
What is reading in the content area?
Content area reading is most simply, reading to learn. It encompasses all the skills and abilities required for a student to read the complex, informational text found typically in Social Studies, Science, and Math.
What are the components of Read Naturally?
In accordance with our commitment to deliver reading programs based on research-based instructional strategies, Read Naturally’s programs develop and support the five (5) components of reading identified by the National Reading Panel —phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. Phonological and phonemic awareness, phonics and decoding, fluency, and print concepts are widely recognized as foundational reading skills.
What is fluency in reading?
Fluency is the ability to read as well as we speak and to make sense of the text without having to stop and decode each word.
What is phonemic awareness?
Phonemic awareness refers to the student’s ability to focus on and manipulate these phonemes in spoken syllables and words. According to the National Reading Panel, teaching phonemic awareness to children significantly improves their ...
How is vocabulary related to comprehension?
Vocabulary development is closely connected to comprehension. The larger the reader’s vocabulary (either oral or print), the easier it is to make sense of the text. According to the National Reading Panel, vocabulary can be learned incidentally through storybook reading or listening to others, and vocabulary should be taught both directly and indirectly. Students should be actively engaged in instruction that includes learning words before reading, repetition and multiple exposures, learning in rich contexts, incidental learning, and use of computer technology.#N#Learn more about vocabulary
What is the relationship between letters in written language and the individual sounds in spoken language?
Phonics. Phonics is the relationship between the letters (or letter combinations) in written language and the individual sounds in spoken language. Phonics instruction teaches students how to use these relationships to read and spell words.
How do young readers develop text comprehension?
The National Reading Panel determined that young readers develop text comprehension through a variety of techniques, including answering questions (quizzes) and summarization (retelling the story). Learn more about comprehension.
What is the impact of guided reading?
The National Reading Panel’s research findings concluded that guided oral reading and repeated oral reading had a significant and positive impact on word recognition, reading fluency, and comprehension in students of all ages. Learn more about fluency.
What are the five pillars of reading?
The building blocks of reading, as defined by the National Reading Panel, include phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension . Together, these five pillars make up the components of successful reading instruction by shaping learners' brains one step at a time, to learn to read and understand the written English language.
Why do independent readers need to be read aloud?
Why it matters: Even before children become independent readers, they can begin practicing and developing comprehension skills when books are read aloud to them. Students who comprehend what they read are both purposeful and active readers. They use metacognitive strategies to think about the purpose of what they’re reading and monitor their own understanding as they read. This allows these students to isolate and verbalize where they have a lack of understanding, which, in turn, opens doors for them to apply specific strategies to attain that understanding.
What does comprehension mean in reading?
What it means: Students with developed reading comprehension abilities can predict, infer, make connections, and analyze what is being read. If you want to think of reading like a watering can, then the four preceding pillars are the different parts that make up the watering can, like the handle, spout, and body of the can itself. Comprehension is the water. Without it, you still have a watering can, but an empty watering can won’t help your flowers grow. Comprehension allows the flowers of literacy to bloom as it gives meaning and purpose to what is being read.
What is phonemic awareness?
What it means: Teaching phonemic awareness means instructing students to identify and manipulate the approximately 44 phonemes in the English language. It doesn’t require students to be able to read or even see printed letters to grasp this concept; it’s all about the sounds that word parts make. Essentially, students begin by learning individual phonemes, then joining phonemes, and finally, building words.
What is the ability to hear, identify, manipulate, and substitute phonemes?
What it is: The ability to hear, identify, manipulate, and substitute phonemes—the smallest units of sound that can differentiate meaning—in spoken words. What it means: Teaching phonemic awareness means instructing students to identify and manipulate the approximately 44 phonemes in the English language.
Why is phonemic awareness important?
Why it matters: Phonemic awareness is a strong predictor of long-term reading and spelling success. By using effective teaching strategies, phonemic awareness can be successfully taught during your literacy block. As you’re planning instruction, it’s also important to recognize that phonemic awareness development must be quickly followed by the introduction of phonics. Research shows that teaching sounds along with letters of the alphabet helps students better understand how phonemic awareness relates to their reading and writing.
Why is fluency important in reading?
Why it matters: Developing fluency is critical to a student’s motivation to read. When students struggle to sound out letters and words, reading can become a laborious and exhausting task, and students may begin to perceive reading as a negative activity. As students begin to acquire words more easily, they should also practice dividing text into meaningful chunks, knowing when to pause and change intonation and tone. With regular guidance and feedback, students begin to recognize these cues during reading and develop deeper comprehension.
What is the first phase of reading development?
During the initial phase of the reading development process children sample and learn from a full range of multiple sounds, words, concepts, images, stories, exposure to print, literacy materials, and just plain talk during the first five years of life.
What is the second phase of reading?
During the second phase of the reading development process children are learning the relationships between letters and sounds and amongst printed and spoken words. The child begins to read stories with high-frequency words and phonically regular words and uses emerging skills and insights to “sound out” new one-syllable words.
How to teach fluency in reading?
Two instructional approaches have typically been used to teach reading fluency. One, guided repeated oral reading, encourages students to read passages out loud with systematic and explicit guidance and feedback from their teacher. The other, independent silent reading, encourages students to read silently on their own, inside and outside the classroom, with little guidance or feedback from their teachers.
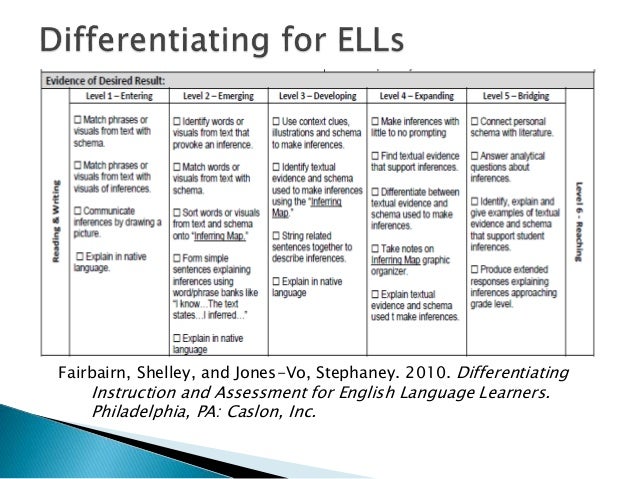
How can teachers enable phonemic awareness in English for ELLs?
Teachers can enable phonemic awareness in English for ELLs by understanding the linguistic characteristics of students' native language, including the phonemes that exist and do not exist in the native language.
Why is it important for ELLs to understand phonemes?
Some phonemes may not be present in ELLs' native language and, therefore, may be difficult for a student to pronounce and distinguish auditorily, as well as to place into a meaningful context. For ELLs, as with all students, it is important that instruction have meaning, so that the words and sounds students are manipulating are familiar. It is therefore necessary for ELLs to have knowledge of the English vocabulary words within which they are to understand phonemes. Teachers can teach phonemic awareness while also explicitly teaching vocabulary words, their meaning, and their pronunciation to ELLs.
What are some activities that ELLs can do?
Scientifically-based research suggests that ELLs respond well to meaningful activities such as language games and word walls, especially when the activities are consistent and focus on particular sounds and letters. Songs and poems, with their rhythm and repetition, are easily memorized and can be used to teach phonemic awareness and print concepts to ELLs (Hiebert, et al., 1998). These rhymes exist in every language and teachers can ask students or their parents to share these culturally relevant and teachable rhymes with the class, and build phonemic awareness activities around them.
How many phonemes are there in English?
English consists of about 41 phonemes. Phonemes combine to form syllables and words. For example, the word stop has four phonemes (s-t-o-p), while shop has three phonemes (sh-o-p). Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to identify and manipulate these phonemes in spoken words.
What do letters represent in writing?
Students may have learned to read and write in a native language in which the letters correspond to different sounds than they do in English, or they may have learned to read and write in a language with characters that correspond to words or portions of words. For example, "alphabetic writing systems such as the three different ones used for English, Greek, and Russian represent speech sounds or phonemes with letters or letter sequences. In contrast, in logographic writing systems, such as Chinese, each written character represents a meaning unit or morpheme; while in syllabic writing systems, such as kana in Japanese and Sequoyah's Cherokee syllabify, each written symbol represents a syllable (Peregoy & Boyle, 2000, p. 241)."
What is the NRC in literacy?
The NRC complements CIERA's recommendations about initial literacy in the native language. The NRC asserts that learning to speak English first contributes to children's eventual fluency in English reading, as oral proficiency provides a foundation to support subsequent learning about the alphabetic principle through an understanding of the structure of spoken English words and of the language and content of the material they are reading (Snow, Burns, & Griffin, 1998). This reinforces the recommendation for vocabulary development in ELLs: that in addition to reading instruction, ESL or ELD instruction must be an integral part of curriculum for ELLs.
What are the Big 5 in Reading?
Here’s a video you can watch for a visual overview of each of these Big 5 Reading Skills.
What is the Big 5 Reading Instruction Strategy?
The Big 5 Reading Instruction Strategy #1: If possible, have mini lessons for each area. You don’t need a huge long lesson for each area, each day. In fact, The National Reading Panel even reported that extensive, long lessons could even be detrimental to reading development.
What is reading skills?
Reading Skills Definition. Reading skills are the tools and strategies that students develop to become successful readers. There are more components to reading than people realize. Reading is so much more than just sounding out words.
Why is it important to integrate reading skills?
Integrating gives you more time to teach all of the reading skills, and gives them practice putting them together.
Do you need a long lesson for each area?
You don’t need a huge long lesson for each area, each day. In fact, The National Reading Panel even reported that extensive, long lessons could even be detrimental to reading development. The most effective lessons were brief, but focused.
Do you need to backtrack on phonics?
The exception to this is students who are already proficient in the lower skills (phonemic awareness, phonics, and sometimes fluency). You do not need to back track and spend time on skills that students have already mastered.
Do lower students need more support in phonemic awareness?
Sometimes our students need more help in one area than the others. For example, lower students may need more support in phonemic awareness at the beginning, while your higher students do not need much practice in it. When doing tier 2 reading interventions or small group reading, customize your reading instruction to that group’s needs. Choose the biggest area of need and focus on that, but still include the other areas as much as possible.
When was the National Reading Panel established?
Congress appointed a National Reading Panel (NPR) in 1997 to review reading research and determine the most effective methods for teaching reading. The NRP reviewed over 100,000 studies and analyzed them to see what techniques actually worked in teaching children to read. The group only looked at quantitative studies, ...
What are the techniques used in phonics?
1. Explicit instruction in Phonemic Awareness. 2. Systematic Phonics Instruction. 3. Techniques to improve Fluency. These include guided oral reading practices where the student reads aloud and the teacher makes corrections when the student mispronounces a word. A teacher can also model fluent reading to the student.
What is comprehension skills?
Comprehension skills are the strategies a reader can use to better comprehend a text. This is the foundation of reading, but it is also the foundation of education generally. Every subject is dependent on reading, and mastery of these subjects depends on developing a strong foundation in these early literacy skills.
What is phonemic awareness?
Phonemic awareness is the understanding that all spoken words are made up using a subset of about 44 individual sounds, called phonemes. Mastery of the skill of phonemic awareness has to be to the point of automaticity in order for fluency to be developed. On top of this comes systematic Phonics.