
What are the forces that change the shape of the Earth?
The Earth's surface is constantly changing through forces in nature. The daily processes of precipitation, wind and land movement result in changes to landforms over a long period of time. Driving forces include erosion, volcanoes and earthquakes. People also contribute to changes in the appearance of land.
What is the driving force that most changes the Earth?
Dec 05, 2021 · How Do Forces Inside The Earth Affect Its Surface?Wind, water, and ice erode and shape the land. Volcanic activity and earthquakes alter the landscape in a dramatic and often violent manner. And on a much longer timescale, the movement of earth's plates slowly reconfigures oceans and continents. Ea
How does water change the earth's surface?
Moving water is the driving force that most changes the Earth. Water has slowly changed the surface of the earth through weathering and erosion . The Colorado River formed the Grand Canyon through weathering and erosion. Weathering and erosion play an important part in changing rocks and changing the shape of Earth.
How do internal forces affect the earth's surface?
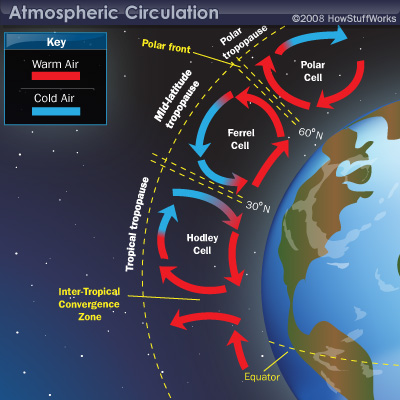
How has water changed the Earth's surface?
Water has slowly changed the surface of the earth through weathering and erosion . The Colorado River formed the Grand Canyon through weathering and erosion. Weathering and erosion play an important part in changing rocks and changing the shape of Earth.
What is the process of breaking down rocks?
Weathering is a process that breaks down rocks, from large boulders to form small gravel and soil. Erosion is the removal and carrying off of these materials from one place to another. The Grand Canyon was shaped by water from the Colorado River breaking down, and carrying away, rock particles.

Formation
Environment
- Coastal erosion has become a major issue in recent years in the Arctic, with Alaskas North Slope losing as much as 30 meters (100 feet) per year! Climate change is thought to be the underlying cause. As the climate warms and sea ice melts, more of the suns energy is absorbed by ocean water. As this heat is transferred to the land, the permafrost (frozen soil) thaws, making the coa…
Records
- Katabatic winds in Antarctica and Greenland are intensely cold and fast, often reaching hurricane speed. You can hear these fierce winds in this YouTube video
Contents
- The theory of plate tectonics describes the motions of earths lithosphere, or outermost layer of hard, solid rock, over geologic time. Plate tectonics provides scientists with a great deal of information about the polar regions past.
Geology
- Earths lithosphere is broken into seven major and many minor tectonic plates. These plates move in relation to each other, slowly changing the location of earths continents and oceans. Geological evidence from Antarctica supports the theory that North America and Antarctica were connected approximately one billion years ago in the global supercontinent Rodinia. The continents eventu…
Composition
- Volcanic eruptions may be explosive (violent) or effusive (passive), depending on the lava chemistry (amounts of silica and dissolved gases). Silica is a mineral found in nature as sand or quartz. High levels of silica mean very viscous (thick) lava, and low levels mean more fluid lava. Dissolved gases build up inside the volcano, much like a can of soda or other carbonated bevera…
Causes
- Seismic activity (earthquakes) is most often associated with tectonic plate boundaries. As plates slowly move, their jagged edges stick and suddenly slip, causing an earthquake.
Publications
- Copyright December 2008 The Ohio State University. This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0733024. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. This work is licensed under an …