
...
Informal powers of the president.
| Power | Definition |
|---|---|
| Issuing signing statements | Giving the president's intended interpretation of bills passed by Congress |
What are informal powers does the US President have?
Along with the offices formal powers given by the Constitution, the President also has various informal powers including the ability to enact a legislative agenda, executive orders, sending out troops without a declaration of war, and conducting foreign policy initiatives. Simply so, what are some informal powers of the president?
What is the difference between formal and informal powers?
What Is The Difference Between Formal And Informal Power
- Difference Between Formal And Informal Imperialism. ...
- Leadership and Power. ...
- Land Mafia And The Land Mafia. ...
- Informal Government Powers. ...
- Leadership Behavior. ...
- Text For Thought : Employee Communications. ...
What are three informal requirements of a president?
Requirements to Become President of the United States
- The U.S. Constitution. ...
- Age Limits. In setting the minimum age of 35 for serving as president, compared to 30 for senators and 25 for representatives, the framers of the Constitution implemented their belief ...
- Residence. ...
- Citizenship. ...
What are the informal qualifications of the US President?
What are the informal qualifications for president of the United States?
- Experience in government or high military rank. Government experienced.
- Ability to raise large amounts of money. raise lots of money.
- Political beliefs- be a fit for a major party. beliefs.
- Personal characteristics- mental stability.
- Skill in debating and in fielding leading questions from reporters.
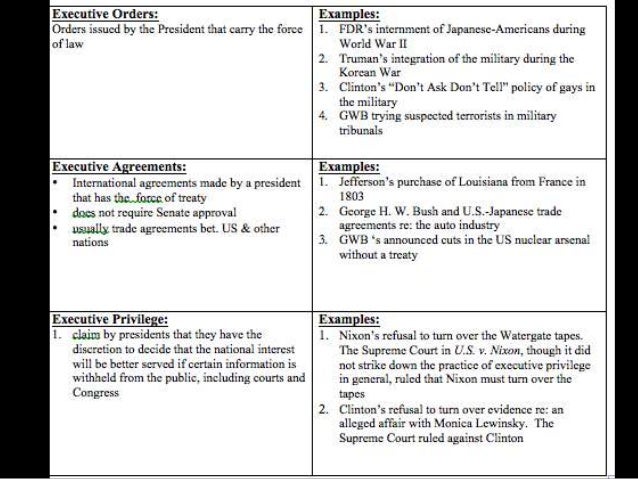
What are the formal powers of the president?
The Constitution explicitly assigns the president the power to sign or veto legislation, command the armed forces, ask for the written opinion of their Cabinet, convene or adjourn Congress, grant reprieves and pardons, and receive ambassadors.
What are the formal and informal powers of the president quizlet?
The President's listed powers: Power to appoint, power to convene congress, power to make treaties, veto power, power to preside over military as commander in chief, pardoning power. Informal powers: Public persuasion, establishing bureaucracy, issue executive orders, issue signing statements.
What are 2 formal powers of the president?
According to Article II of the Constitution the President has the following powers:Serve as commander in chief of the armed forces.Commission officers of the armed forces.Grant reprieves and pardons for federal offenses (except impeachment)Convene Congress in special sessions.Receive ambassadors.More items...
What are the president's informal implied powers?
What are the Presidents informal (implied) powers? Leading the armed forces when the nation is at war, he can command the Air Force, foreign policy, he can recommend laws, and he can impound the funds that Congress has appropriated for certain programs or projects if he doesn't want them implemented.
What is informal power?
Informal Power - power that is not tied to any position, often resulting from personal characteristics. This power allows the person/group to influence and/or represent a community without formal decision making.
What are the formal powers of the president quizlet?
The president has the following powers: To propose legislation to Congress. To submit the annual budget to Congress. To sign legislation passed by Congress. To veto legislation passed by Congress. To act as chief executive. To nominate executive branch officials. To nominate federal judges.More items...
Is veto formal or informal?
The president's formal role in lawmaking comes through the veto power, although Neustadt noted the informal power of persuasion through bargaining.
What are the 3 powers of the president?
veto bills and sign bills. represent our nation in talks with foreign countries. enforce the laws that Congress passes.
What are the informal powers of Congress?
Bargaining and persuasion - informal power that enables the presidents to secure congressional action. Executive orders - implied from the president's vested executive power, or from power delegated by Congress, executive orders are used by the president to manage the federal government.
What are the 6 informal powers of the president?
The power to go public, power of persuasion, make executive agreements, issue executive orders, issue signing statements, create & use bureaucracy, personality and leadership, and make legislative proposals. What is the primary job of the executive branch?
How does the president use formal and informal powers to accomplish a policy agenda?
The president can influence congress to implement a policy agenda. He does this through a "I scratch your back, you scratch mine" method. The formal powers are veto, signing laws into act, commander in chief. Informal powers are executive agreements, and signing statements.
Which of the following is an example of presidential use of informal powers?
A signing statement is when a bill is signed into law but interpreted by the president differently then originally intended by Congress. In this way the president controls the legislative process. These signing statements often go unchecked. Signing statements are another example of an informal power.
What powers does Congress have?
Congress has the power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts and excises; all duties, imposts and excises must be uniform throughout the United States. To borrow money. To coin money, set it’s value, and punish counterfeiting. To raise and support an army and navy and make rules for their governance. To declare war.
What are the formal and informal powers of the President?
Formal and Informal Powers of the President. The role and powers of the President of United States is outlined in Article II of the Constitution. Compared to the explicit powers of the Congress, the Constitution grants far fewer explicit powers to the President, the ambiguity and vagueness of Article II have made it possible for presidents ...
What is the role of Congress in the Constitution?
Under the Constitution, Congress is charged with carrying out the legislative functions of government. The framers of the Constitution wanted the lawmaking and national policy role to be in the hands of a representative body. The “formal powers”, structure, and procedures of the national legislature are outlined in considerable detail in Article I, ...
What is the formal power of the national legislature?
These powers are extensive, however as a means of “sharing” powers and functions between separate institutions, most of them are shared with the other two branches, particularly the executive.
What is the purpose of the post office?
To establish a post office. To establish rules for becoming a citizen and bankruptcy. To issue patents and copyrights to inventors and authors. To constitute tribunals inferior to the Supreme Court. To define and punish piracies, felonies on the high seas, and crimes against the law of nations.
How long can the President declare an emergency?
The President has the ability to declare a 90 day period of Emergency during which he can use the full force of the military without seeking permission from Congress either in the form of a declaration of war or through funding.
How many appointments does the President make?
The power of appointment; the President is responsible for making about 6,000 appointments – the most important of which are his cabinet and federal judges (most of these must be approved by the Senate).
What are the powers of the President?
The powers of the president outlined in Article II are known as formal powers, but over the years presidents have claimed other powers, known as informal powers. Presidents campaign for office based on their policy agendas: the things they promise voters that they will attempt to accomplish while in office.
What is the meaning of Article II of the Constitution?
Beyond the Constitution — Article II of the Constitution describes the formal powers of the president, but the president also has informal powers, which have grown over time. Because the president and Congress have interrelated powers, tension frequently erupts between the two branches.
What is the meaning of signing statements?
Issuing signing statements indicating the president's intentions for executing a law are an informal presidential power that has become more prevalent in the modern era. Here, President Ronald Reagan and Vice President George H. W. Bush examine legislation in the Oval Office in 1984. Image source: Wikipedia.
What is the meaning of executive order?
executive order. A presidential order to the executive branch that carries the force of law. The Supreme Court can rule executive orders unconstitutional. pocket veto. An indirect veto, which the president can use by neither signing or vetoing a bill passed by Congress fewer than 10 days before it adjourns.
What is the meaning of "negotiating executive agreements"?
Negotiating executive agreements. Agreements with heads of foreign governments that are not ratified by the Senate. Image of Ronald Reagan and George H. W. Bush in the Oval Office, looking at papers.
What is a presidential statement?
signing statement. A presidential statement upon signing a bill into law, which explains how a president’s administration intends to interpret the law. State of the Union address.
What is the term for a group of presidential advisers, including the heads of the executive departments, the attorney general
Term. Definition. cabinet . A group of presidential advisers, including the heads of the executive departments, the attorney general, and other officials chosen by the president. executive agreement. An international agreement between the president and another country, which does not require the consent of the Senate.
Why are informal powers important?
Unlike the formal powers, the informal powers are considered more critical due to the president’s right to manage the situation or event without Congress approval. However, informal powers are not applied regularly, as they might undertake conflict with Congress regarding sensitive issues or questions. The president’s informal powers are vital ...
What are informal powers?
Under the informal powers, the U.S. president can hide some information, force prohibitions, and intervene in legal processes. While Congress or Supreme Courts limit such intervention, as the application of the informal powers may cause severe damages and consequences for internal and external state affairs. Rate the answer:
What are the 4 powers of the President?
Here is the list of 4 major informal powers of the president: the ability to enact a legislative agenda; executive orders; sending out troops without a declaration of war; conducting foreign policy initiatives. The significant difference between these two powers of the U.S. president is that formal is defined in Constitution, ...
What powers does the President have to pardon?
The power to pardon is one of the least limited powers granted to the President in the Constitution. Executive agreements.
What are the most common inherent powers?
The most common inherent powers are Emergency Powers , exercised only in times of great need. Some emergency powers are limited in scope. The president can declare a place devastated by a storm a federal disaster area, making it eligible for federal aid. Other emergency powers are much vaster in scope.
What are the terms of the 30th Congress?
Terms in this set (30) Are powers that allow the president to form and maintain relationships with foreign countries. The president can veto any bill passed by Congress and, unless two-thirds in each house vote to override the veto, the bill does not become law.
What are the informal powers of the President?
The power to go public, power of persuasion, make executive agreements, issue executive orders, issue signing statements, create & use bureaucracy, personality and leadership, and make legislative proposals. Emergency Powers.
What is executive privilege?
Executive privilege. the right of executive officials to refuse to appear before, or to withhold information from, a legislative committee or the courts. Formal Powers of the President. Veto power, command armed forces, pardoning power, appointment powers, make treaties, convene Congress. Informal Powers of the President.
What happens if the Vice President and majority of the cabinet believe that the President is unfit?
If the Vice President and majority of the cabinet believe that the President is unfit, they can remove him from office (section 4) If this works, they need the vote of the house and the senate for final approval. How can Congress check the president. -Overriding a presidential veto with a 2/3 of both house vote.
What is the President's role in the legislative agenda?
Setting legislative agenda. President is the initiator, meaning that they can influence/recommend a law to Congress, but can' t start legislation. Executive orders. definition: a rule or regulation issued by the president that has the effect of law; they give administrative effect to provisions in the constitution, treaties and statues.
