Types of intermolecular forces
- Dipole-dipole forces
- Ion-dipole interaction
- Ion-induced dipole interaction
- Van der Waal forces (Keesom forces, Debye forces, London dispersion)
- Hydrogen bonding
How to tell which intermolecular forces?
How to determine intermolecular forces? Intermolecular forces are determined based on the nature of the interacting molecule. For example, a non-polar molecule may be polarised by the presence of an ion near it, i.e., it becomes an induced dipole. The interaction between them is called ion-induced dipole interactions.
What are the different intermolecular forces?
Van der Waals Forces
- Keesom Interactions. These interactions occur between permanent dipoles, which can be either molecular ions, dipoles (polar molecules) or quadrupoles (e.g. ...
- Debye Force. These interactions occur between permanent dipoles and induced dipoles. ...
- London Dispersion Force. ...
- Examples of Intermolecular Forces. ...
What are some examples of intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular Forces are the forces that exist between the molecules of a compound. Intermolecular forces are much weaker than intramolecular forces. The forces help to determine the physical properties of a molecule such as melting point, boiling point, density, etc. ... Some examples of a hydrogen bond are water (H 2 ...
What are five types of forces?
some types of contact forces are given in the list below:
- Applied force
- Normal force
- Frictional force
- Tension force
- Air resistance force
- Spring force
What are the main types of intermolecular forces?
There are three types of intermolecular forces: London dispersion forces (LDF), dipole- dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding.
What are the 4 intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest?
Intermolecular forces In the order of weakest to strongest:dispersion force.Dipole-dipole force.Hydrogen bond.Ion-dipole force.
What are the 5 types of intermolecular forces?
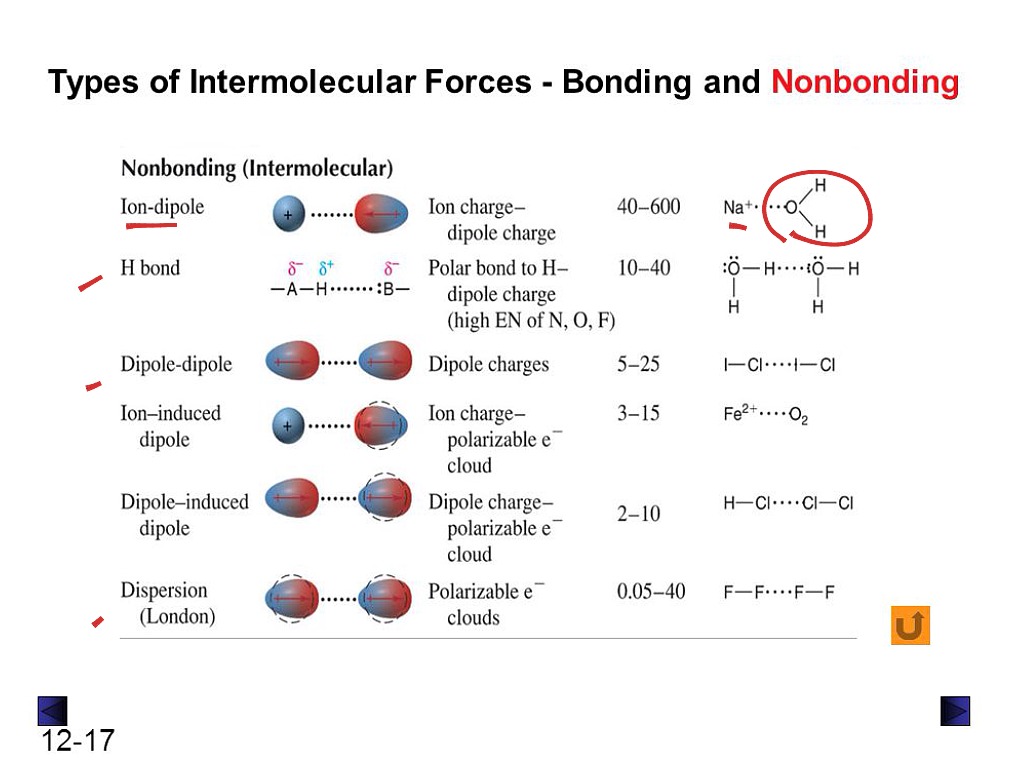
There are five types of intermolecular forces: ion-dipole forces, ion-induced-dipole forces, dipole-dipole forces, dipole-induced dipole forces and induced dipole forces. Ion-dipole forces exist between ions and polar (dipole) molecules.
Which of the 4 intermolecular forces is the strongest?
Dipole-dipole interactions are the strongest intermolecular force of attraction.
Which intermolecular bonds are the strongest?
Hydrogen bonds are a special case of dipole-dipole interactions. H-bonds are the strongest intermolecular force. (They are worth ca. 5 kJ•mol-1).
Which is strongest among the types of intermolecular forces explain your answer?
The strongest intermolecular forces are dipole-dipole interactions. A dipole-dipole force is when the positive side of a polar molecule attracts the negative side of another polar molecule. For this kind of bond to work, the molecules need to be very close to each other as they are in a liquid.
What are the 6 intermolecular forces?
The intermolecular forces depend on the following interactions:Dipole-Dipole Interactions.Ion-Dipole Interactions.Ion Induced Dipole Interactions.Dipole Induced Dipole Interaction.Dispersion Forces or London Forces.
How do you identify the types of intermolecular forces?
0:325:36How to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf a compound is nonpolar. Then it will have london dispersion forces. Only if a compound is polarMoreIf a compound is nonpolar. Then it will have london dispersion forces. Only if a compound is polar it will have lung dispersion.
What is intermolecular forces in chemistry?
Intermolecular forces are the forces that are between molecules. And so that's different from an intramolecular force, which is the force within a molecule. So a force within a molecule would be something like the covalent bond. And an intermolecular force would be the force that are between molecules.
Which among the intermolecular forces is the weakest?
London dispersion forces are the weakest of the intermolecular forces and exists between all types of molecules, whether ionic or covalent or polar or nonpolar. The more electrons a molecule has, the stronger the London dispersion force.
What are the three types of intramolecular bonds?
Covalent Bonds The three types of intramolecular forces are covalent, ionic, and metallic bonding. Covalent bonds occur between two nonmetals. In this type of bond, the atoms share electrons.
Why is dipole-dipole the strongest?
It's the strongest intermolecular force, and is only present in compounds with H−F , H−O , or H−N bonds. So, if dipole-dipole forces are being compared to intermolecular forces like London dispersion forces, they would be stronger.
Which intermolecular forces are the weakest?
London dispersion forces are the weakest of the intermolecular forces and exists between all types of molecules, whether ionic or covalent or polar or nonpolar.
What bonds are strongest to weakest?
The ranking from strongest to weakest bonds is: Covalent bond > ionic bond > hydrogen bond > Van der Waals forces.
How do you find the weakest intermolecular force?
6:3512:22How to Determine the Strength of Intermolecular Forces (IMFs) and ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipGo by what has most electrons.MoreGo by what has most electrons.
How to determine intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are determined based on the nature of the interacting molecule. For example, a non-polar molecule may be polarised by the pre...
How do intermolecular forces of attraction affect boiling point?
The higher the boiling point, the greater the magnitude of the intermolecular forces.
Which are the strongest intermolecular forces?
Ion-dipole interaction is the strongest intermolecular force.
What are the types of intermolecular forces?
The different types of intermolecular forces are dipole-dipole interactions, dipole-induced dipole interactions, ion-dipole interactions, ion-induc...
How to describe intermolecular forces?
We can describe intermolecular forces graphically by considering the molecules spherically symmetrical. The figure shows how the potential energy of two molecules and the force between them changes with their separation. Here we can imagine one molecule to be fixed at O.The force at any point is found from F =-dU/dr, where U is the potential energy. Two forces act between the molecules:
Which molecule induces the creation of the apolar molecule in a polar molecule?
In this case, the polar molecule induces the creation of the apolar molecule in a polar molecule.
What type of union occurs when both molecules have positive and negative charges?
This type of union occurs when both molecules have positive and negative charges, that is, they are polar molecules or that have polarity, attracting each other electrostatically and forming the union.
Why do molecules repel each other?
Thus these forces are short-range forces. The molecules repel each other because there is no way for a molecule to rearrange itself internally to prevent repulsion of the adjacent external electrons.
How to tell if a molecule is completely separated from its neighbor?
For a molecule to be completely separated from its neighbor it must gain an amount of energy F, represented by CM on the diagram. The latent heat of vaporization for the two molecules is CM when there is no residual attractive force. This length also represents the latent heat of vaporization for the whole material. In a solid, the distance OM is some 2-3 ×10 -10 m and you can see that around this point the force between the molecules varies approximately linearly with distance.
What is the separation distance between two molecules at which the mutual potential energy is zero?
The separation distance between the two molecules at which the mutual potential energy is zero is called the distance of the closest approach. Any disturbance from this position would produce a force tending the return of the molecule to M.The force of attraction between the molecules increases as the molecules are separated from M to B. The breaking point is at B since beyond this point the force of attraction decreases with increasing separation.
Do molecules interact with each other?
These molecules are electrically neutral in the sense that the negative charge of the electron is equal and opposite charge to the positive charge of the nuclei. This does not mean, however, that the molecules do not interact electrically.
What are the three forms of intermolecular force?
Intermolecular Forces: Water exists in all three forms, i.e., ice, water, and water vapour . Molecules are arranged tightly in ice, less tightly in water, and free in water vapour. That is, an intermolecular force of attraction decreases as the distance between the molecules increases. In this article, let us explore more about intermolecular force ...
What are the 6 Intermolecular Forces?
The intermolecular forces come into existence due to the following types of interactions:
What is Ion-Dipole Interaction?
The ion-dipole interaction involves the attraction between an ion (either a cation or an anion) and a polar molecule. The strength of ion-dipole interaction depends on the charge and size of the ion and also on the magnitude of dipole moment and size of the polar molecule. Since the charge density on cations is higher as compared to that on anion, cation attracts a dipole more strongly than an anion having the same charge but bigger size.
How Intermolecular Forces Affect Boiling Point?
The intermolecular forces are electrostatic and much weaker than the chemical forces. They exist in all the states of matter and play an important role in deciding several structural features and physical properties of matter.
Why do molecules have dispersion forces?
The existence of dispersion forces in such molecules is due to the development of an instantaneous or temporary dipole moment in them. Atoms and molecules are electrically symmetrical and, as such, do not possess any dipole moment.
What are attractive forces?
The attractive forces come into existence due to instantaneous dipoles created in non-polar molecules like hydrogen ( H 2), oxygen ( O 2), chlorin ( C l 2), iodine ( I 2), etc., and monatomic noble gases such as helium ( H e), neon ( N e), argon ( A r), xenon ( X e), etc., are called dispersion force or London force. It is also called instantaneous dipole interactions.
What is the term for a polar molecule that destroys a nonpolar molecule?
A polar molecule having a permanent dipole destroys a normal non-polar molecule and induces a dipole moment in it. This is known as dipole-induced dipole interactions. The force is developed due to interaction between a dipole, and the induced dipole is called Debye forces.
Types of intermolecular forces
Mainly, intermolecular forces are divided into three types; dipole to dipole interactions, van der Waals forces (Londen Dispersion forces), and Hydrogen bonding. But the term induced dipoles, referring to Londen dispersion forces (LDF) is divided into further types. This makes five types of intermolecular forces.
1. Dipole-dipole interaction
Dipole to dipole interaction is due to the partially positive and negative poles across molecules. The negative poles of molecules attract the positive poles of other molecules and result in the establishment of electrostatic forces of attraction between molecules known as dipole-dipole interaction.
2. Ion-dipole interaction
Ion to dipole interactions occur when ions and polar molecules interact and an interactive force is established between them.
3. Ion-induced dipole interaction
Ions are responsible for ion-induced interactions. When an ion comes near a nonpolar molecule, it induces partial positive and negative poles generation on that molecule, converting it into a dipolar structure. In other words, an ion induces a dipole moment on nonpolar molecules and converts them into polar molecules.
4. Van der Waals forces
Named after Dutch physicist, Johannes Diderik van der Waals, these interactions are the attractive forces between all atoms and molecules. These forces quickly vanish upon increase in the distance between individual atoms or molecules and the threshold distance for such forces is called van der Waals contact distance.
5. Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a type of dipole-dipole interaction but it is placed separately as another type of intermolecular force due to its extremely strong nature. The hydrogen bond is the only intermolecular force to have the word “bond” in its name because it resembles intramolecular forces’ strength.
Effects of intermolecular forces on chemical compounds
Intermolecular forces deal with the physical effects in chemical substances like boiling and melting point, etc. The stronger these forces are, The more energy is required there, to break the bonds. They considerably increase the melting and boiling point of the compounds.