
What are the four phosphate groups? Phosphate group Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Phosphoproteins.
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
- Phosphoproteins.
- Adenosine triphosphate.
- Dihydrogen phosphate.
What are examples of a phosphate group?
What are phosphate groups Examples?
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
- Phosphoproteins.
- Adenosine triphosphate.
- Dihydrogen phosphate.
What are the three phosphate groups in ATP?
Why do ATP three phosphate groups labeled Alpha Beta and Gamma? The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma. The two bonds between the phosphates are equal high-energy bonds (phosphoanhydride bonds) that, when broken, release sufficient energy to power a variety of cellular reactions and processes.
What chemical group does phosphate belong to?
Phospholipids belong to the lipid family of biological polymers.A phospholipid is composed of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, a phosphate group, and a polar molecule. The polar head region in the phosphate group of the molecule is hydrophillic (attracted to water), while the fatty acid tail is hydrophobic (repelled by wate
How many phosphate groups are attached in AMP?
All Nucleotides have a common structure. (a) Chemical structure of adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP), a nucleotide that is present in RNA. All nucleotides are composed of a phosphate moiety, containing up to three phosphate groups, linked to the (more)
How many oxygen atoms are in a phosphate group?
What is Phosphate?
What is the relationship between a phosphate and a nucleotide?
What is the chemical link between phosphate and carbon?
Why are phosphates important?
What is the compound formed when two phosphate groups are bonded to one another?
What are the building blocks of DNA?
See 4 more
About this website
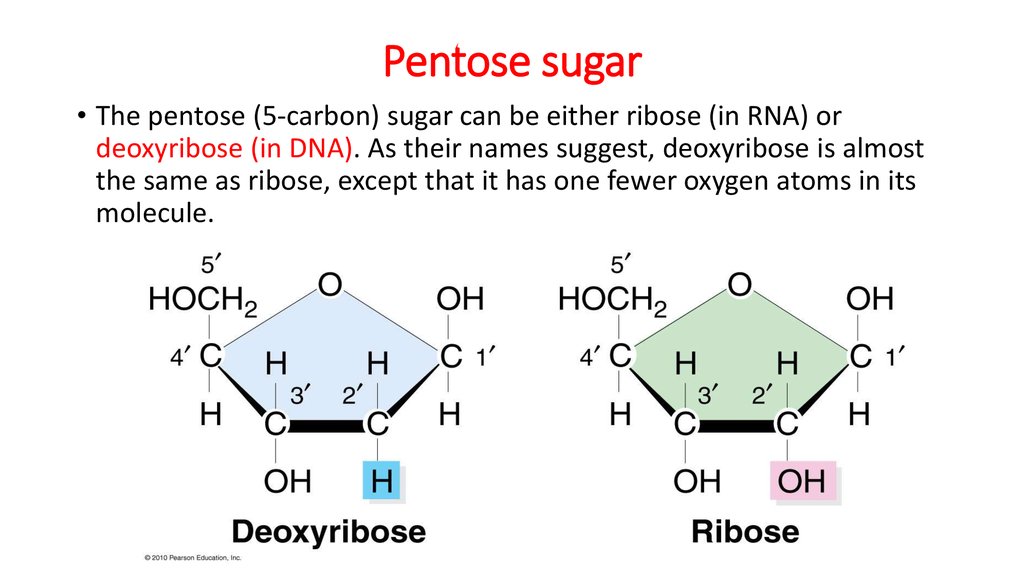
What are the 4 phosphate groups?
Phosphate Backbone Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T).
How many phosphate groups are there?
three phosphatesThe three phosphates are designated by Greek letters a, b, and g, with the a phosphate being the one closest to the ribose. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP) are also important players in the reactions of this chapter.
What are the types of phosphates?
Different Types of PhosphatesOrganic Phosphates.Inorganic Phosphates. Orthophosphates. Condensed Phosphates. Polyphosphate. Metaphosphate. Other variations of inorganic phosphates.
What are phosphate groups in DNA?
Phosphate backbone. Explanation: The phosphate backbone of DNA is negatively charged due to the bonds created between the phosphorous atoms and the oxygen atoms. Each phosphate group contains one negatively charged oxygen atom, therefore the entire strand of DNA is negatively charged due to repeated phosphate groups.
What are the 3 phosphate groups in ATP?
The three phosphoryl groups are labeled as alpha (α), beta (β), and, for the terminal phosphate, gamma (γ).
How many phosphate groups are in ATP?
three phosphate groupsATP is a nucleotide consisting of an adenine base attached to a ribose sugar, which is attached to three phosphate groups. These three phosphate groups are linked to one another by two high-energy bonds called phosphoanhydride bonds.
What is primary phosphate?
…can be grouped as: (1) primary phosphates that have crystallized from a liquid; (2) secondary phosphates formed by the alteration of primary phosphates; and (3) fine-grained rock phosphates formed at low temperatures from phosphorus-bearing organic material, primarily underwater.
Is phosphate and phosphorus the same?
Phosphorus is a mineral that combines with other substances to form organic and inorganic phosphate compounds. The terms phosphorus and phosphate are often used interchangeably when talking about testing, but it is the amount of inorganic phosphate in the blood that is measured with a serum phosphorus/phosphate test.
What is the difference between phosphate and phosphorus?
Phosphate is an electrically charged particle that contains the mineral phosphorus. Phosphorus works together with the mineral calcium to build strong bones and teeth.
How many phosphate groups are there in DNA?
A free, unincorporated nucleotide usually exists in a triphosphate form; that is, it contains a chain of three phosphates. In DNA, however, it loses two of these phosphate groups, so that only one phosphate is incorporated into a strand of DNA.
What is an example of a phosphate group?
Organic phosphates are often abbreviated using 'OP' and 'OPP' for mono- and diphosphates, respectively. For example, glucose-6-phosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate are often depicted as shown below.
What elements make up phosphate group?
Phosphate, chemical formula PO43-, is a chemical compound made up of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms. When it is attached to a molecule containing carbon, it is called a phosphate group.
Is phosphate and phosphorus the same?
Phosphorus is a mineral that combines with other substances to form organic and inorganic phosphate compounds. The terms phosphorus and phosphate are often used interchangeably when talking about testing, but it is the amount of inorganic phosphate in the blood that is measured with a serum phosphorus/phosphate test.
Are phosphate groups Basic?
Since amino groups can remove H+ from solution, they are considered basic. Charged, ionizes to release H+. Since phosphate groups can release H+ ions into solution, they are considered acidic.
What is the name of po4 3 ion?
PhosphatePO43- is a chemical derivative of phosphoric acid with a chemical name Phosphate. Phosphate is also called Phosphate ion or Orthophosphate. It is a trivalent inorganic anion and a conjugate base of hydrogen phosphate.
What is phosphate group in biology?
Definition. noun, plural: phosphate groups. (biochemistry) A functional group or radical comprised of phosphorus attached to four oxygen, and with a net negative charge, thus represented as PO4–
What is the phosphate group in DNA made of?
The sugar-phosphate groups form the backbone of the single strand of DNA. The four oxygen atoms in the phosphate groups are linked to the phosphoru...
Where is the phosphate group in DNA?
The phosphate group present in the nucleotide creates a covalent bond with the sugar molecule of the adjacent nucleotide to form a long chain of th...
What is phosphate used for?
Phosphates are used for the activation of proteins to make them perform specific functions. One phosphate group combines with another phosphate gro...
How do you identify a phosphate group?
The conjugate base of phosphoric acid that is deprotonated is called a phosphate ion or inorganic phosphate. The four oxygen atoms in the phosphate...
Phosphate Group: Definition, Characteristic, and Examples
A negative-charged functional group or radical composed primarily of phosphorus connected to four oxygen atoms. The sign PO 4– is used to represent it.. The phosphate group plays a variety of roles in living organisms.
Phosphate Group - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The phosphate group of phospholipids shows a strong P O stretching band at 1350–1250 cm −l, which is sometimes a doublet and may be shifted to lower frequencies with an increase in intensity.Vibration of the P–OH group gives rise to absorption at 2700–2560 cm −l.Differences occur in the P–O stretching frequency between phosphatidylethanolamine (1227 cm −l) and phosphatidylserine ...
Learn About Phosphate Functional Groups | Chegg.com
The set of atoms that is present in a molecule is important for the molecule’s particular characteristics or properties. These functional groups exhibit specific consistent reactions and characteristics without being dependent on the molecule they are present.
What are the functions of phosphate groups?
These are all functions of phosphate groups. Phosphates provide energy to cells in the form of ATP, activate proteins through phosphorylation, and limit the growth of life when they are too abundant in an ecosystem. 2.
How many oxygen atoms are in a phosphate?
A phosphate is made up of one phosphorus atom attached to four oxygen atoms. When a molecule of phosphate is attached to a carbon-containing molecule, it is then known as a phosphate group. 3.
What is the atomic number of phosphorus?
Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and is represented by the letter P. Nucleotide – the building block of DNA and RNA; consists of a phosphate group attached to a 5-carbon sugar and nitrogenous base. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the main energy molecule of cells, made up of an adenosine molecule attached to three phosphate groups.
How is ATP formed?
When these bonds are broken, energy is released. ATP is formed when the molecule ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is phosphorylated.
What is the chemical formula for phosphorus?
Phosphate, chemical formula PO 43- , is a chemical compound made up of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms. When it is attached to a molecule containing carbon, it is called a phosphate group. It is found in the genetic material DNA and RNA, and is also in molecules such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) that provide energy to cells.
What is phosphorylation in biology?
C is correct. Phosphorylation is when a phosphate group is added to a molecule. Phosphate groups can activate proteins through phosphorylation.
Why are phosphate groups important?
Phosphate groups are important in activating proteins so that the proteins can perform particular functions in cells. Proteins are activated through phosphorylation, which is the addition of a phosphate group. Protein phosphorylation occurs in all forms of life. Dephosphorylation, the removal of a phosphate group, deactivates proteins.
What is a phosphate group?
Phosphate Group Definition. A phosphate group, in the context of biology, is a molecule composed of a phosphorous atom and four oxygen atoms. A phosphate group is part of many important biological molecules. A phosphate group functions as part of energy-storing molecules, has an important role in the regulation of cellular metabolism, ...
How many oxygens are in a phosphate group?
Phosphate Group Structure. In its free state, a phosphate group is centered around the phosphate atom, with 4 oxygens surrounding it. These molecules are bound via covalent bonds, meaning they share electrons. The negativity of the oxygen atoms repels each other, pushing the oxygen molecules as far away from each other as possible.
What happens when you add a phosphate group to a molecule of adenosine?
When a phosphate group is added to a molecule of adenosine, it becomes adenosine monophosphate, or AMP. This molecule is used in a number of biochemical reactions, and is heavily involved in both storing energy and as a second messenger in cellular signaling. When you add another phosphate group, you get adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
What happens when you add another phosphate group?
This molecule has an additional phosphate group bound to the first, and stores energy in this bond. This ADP molecule can accept another phosphate group, and become adenosine triphosphate. Commonly called ATP, this molecule can transfer the third phosphate group ...
What is the molecule that can transfer phosphate groups to enzymes?
Commonly called ATP, this molecule can transfer the third phosphate group to a number of enzymes, activating them or imbuing energy to some process. You can see the recycling of phosphate groups between ADP and ATP in the diagram below. Phosphate groups are one of the most important cellular components. Unfortunately for organisms, it is primarily ...
What is the name of the bond between adenosine and phosphate?
This stores energy in the bonds between the phosphate groups, known as phosphodiester bonds. Phosphodiester bonds also make up the backbone of DNA and RNA, and the.
Why are phosphorus groups important?
Phosphate groups are one of the most important cellular components. Unfortunately for organisms, it is primarily based on a source of phosphorous atoms. This is the reason phosphorous is commonly a limiting nutrient. It is commonly a component of fertilizer for agricultural crops, which allows both the plants and the microorganisms in ...
What is the phosphate functional group?
The phosphate which is made up of single phosphorus along with 4 atoms of oxygen connects with the macromolecule which is contained with carbon to form the phosphate functional group. This exists in RNA, DNA, ATP, and so on. It is important for phospholipid formation, The atoms of oxygen are comparatively more electronegative than the atom of phosphorus which results in the covalent bond of polar molecules. This group also includes the negative charge for involving in bonds of ions.
What are functional groups?
The functional groups are the specific set of atoms present in the molecules which is crucial for the molecule's particular characteristics or properties. The compound which comprises 1 phosphorus and 4 oxygen atoms get connected to the carbon molecule, which leads to the creation of the phosphate group.
What is the energy molecule of ATP?
Energy molecule: ATP bonds are broken to provide energy to the different cells. This ATP is comprised of 1 adenosine and 3 phosphate functional group. Further, this functional group does exist in certain other less familiar energy molecules such as GTP, CTP, and UTP in which molecule adenosine is replaced by Guanine, Cytosine, and Uridine respectively.
What are the parts of DNA and RNA?
Nucleic acid Part: The RNA and DNA, both are made up of a five-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base, and the phosphate group. These three parts combined to create the genetic material of the organisms. The nucleotide’s phosphate group along with the 5-carbon sugar creates the DNA’s or RNA’s backbone.
How is ATP derived from ADP?
In the same way, the function group is removed by the dephosphorylation to deactivate the proteins. ATP is also derived from ADP by the phosphorylation reaction.
Is phosphate a buffer?
Buffer solution: Phosphate also exists as a buffer solution in the phosphate-buffered saline form which is made up of water, salt, and a phosphate group. This is used in several studies in biology.
What are the two types of phosphates?
Phosphates can be grouped into primary and secondary phosphates. The primary phosphate is the first in a series of phosphates that end with a different substance.
How many phosphate groups are in triphosphates?
They have three phosphate groups bonded with each other. Triphosphates are very rare in nature and are only found as nucleoside diphosphates like NADP.
Why are phosphate groups important?
Phosphate groupings can be used to build coenzymes and nucleic acids. These are important in cellular metabolism, even if they are not phosphates. The bonds that are formed between phosphates and carbon-containing groups help to hold the molecules together.
What is DNA made of?
DNA is composed of nucleotides made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. The DNA’s phosphate group connects the nucleotides and helps them form their helical shape or structure.
How do phosphates in DNA link?
The phosphate groups in DNA link to each other and adenine and thymine (or cytosine in RNA) via hydrogen bonds. The three hydrogen bonds hold the phosphate groups in place.
What is the chemical formula for phosphate?
The other end is a positive ion, phosphate, with the chemical formula PO43.
Which group of DNA binds to one of the four nucleotides?
The phosphate group is attached to the deoxyribose sugar in the DNA, and it usually binds to one of four nucleotides.
Which two molecules are identical in DNA?
c. The amounts of adenine and thymine are identical in a DNA molecule
How many copies of DNA are produced in replication?
In DNA replication, two copies of a DNA molecule are produces. In each copy, one strand is new and the other is parental. This result is referred to as...
How many oxygen atoms are in a phosphate group?
The four oxygen atoms in the phosphate groups are linked to the phosphorus atom forming a tetrahedral geometry. There are a total of five bonds to phosphorus. There are four s bonds and one is a localized pi bond. The oxygen atoms in phosphate groups are denoted as connecting atoms or non-connecting atoms based on their position. An inorganic diphosphate consists of two bridging oxygens and five non-bridging oxygens. A single phosphate that is linked to two organic groups is known as a phosphate di-ester. The backbone of DNA has phosphate di-esters. The organic phosphate has oxygen atoms associated with it as well as the negative charges. Net negative charges prevail on organic monophosphates, diphosphates, and triphosphates, and they are protonated at the physiological pH. By convention, they normally exist in a fully deprotonated state.
What is Phosphate?
When an electrically charged molecule is combined with mineral phosphorus, it is considered part of the phosphate group. Four oxygen atoms are bonded to the central phosphorus mineral atom in a tetrahedral geometry to form a phosphate group. Phosphorus with mineral calcium builds strong bones and teeth. It also plays a major role as phosphate in biology.
What is the relationship between a phosphate and a nucleotide?
The phosphate group present in the nucleotide creates a covalent bond with the sugar molecule of the adjacent nucleotide to form a long chain of the nucleotide monomers. The sugar-phosphate groups form the backbone in the single strand of DNA. The nucleotides protrude out from the backbone. The atoms in the five-carbon sugar are numbered as 1’, 2’, 3’, 4’ and 5’ starting clockwise from oxygen. The phosphate group is attached to the 5’ carbon of a nucleotide and 3’ carbon of the adjacent nucleotide. In its natural state, DNA consists of two single strands attached to one another by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The base pairing takes place between purines and pyrimidines. An adenine base links with a thymine base and a cytosine base links with a guanine base. Chargaff’s rule indicates that the percent of adenine is same as that of thymine and the percent of guanine is same as that of cytosine due to the complementarity nature of the two strands.
What is the chemical link between phosphate and carbon?
The chemical link between phosphate and carbon atoms is phosphate ester. Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) has a single phosphate ester bond. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) has one phosphate ester bond and two phosphate anhydride bonds. Hydrolysis by ATP is a process where the phosphate group is removed to release energy. ATP synthase is an enzyme that makes use of the energy from food to attach the phosphate to a molecule. Phosphorylation is when a phosphate group attaches to a molecule. This process is carried out by the group of enzymes called kinases.
Why are phosphates important?
Phosphates are used for the activation of proteins to make them perform specific functions. One phosphate group combines with another phosphate group and an organic molecule to form an energy molecule. Phosphate acts as a buffer. In about 85% of the human body, phosphorus exists in the form of phosphate. Phosphates are part of phospholipids in the cell membrane. The presence of excess phosphates in freshwaters reduces the amount of oxygen available for the survival of the aquatic animals. Phosphate forms diester bonds in the DNA backbone.
What is the compound formed when two phosphate groups are bonded to one another?
When two phosphate groups are bonded to one another, the bond is called ‘phosphate anhydride’ and the compound formed is ‘inorganic pyrophosphate’.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is made up of the building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide comprises of three components such as a phosphate group, a nitrogenous base, and a deoxyribose. DNA comprises of four types of nitrogenous bases. Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) are purines with two rings. Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T) are smaller pyrimidines with a single ring structure. The name of the nucleotide is set according to the type of nitrogenous base present in it.
Phosphate Group Definition
Functions of Phosphate Groups
- Part of Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA, the genetic material of all living things, are nucleic acids. They are made up of nucleotides, which in turn are made up of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. The 5-carbon sugar and the phosphate group of each nucleotide attaches to form the ba… - Activating Proteins
Phosphate groups are important in activating proteins so that the proteins can perform particular functions in cells. Proteins are activated through phosphorylation, which is the addition of a phosphate group. Protein phosphorylation occurs in all forms of life. Dephosphorylation, the rem…
Related Biology Terms
- Phosphorus– a chemical element that, with oxygen, forms the molecule phosphate. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and is represented by the letter P.
- Nucleotide– the building block of DNA and RNA; consists of a phosphate group attached to a 5-carbon sugar and nitrogenous base.
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)– the main energy molecule of cells, made up of an adenosine …
- Phosphorus– a chemical element that, with oxygen, forms the molecule phosphate. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and is represented by the letter P.
- Nucleotide– the building block of DNA and RNA; consists of a phosphate group attached to a 5-carbon sugar and nitrogenous base.
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)– the main energy molecule of cells, made up of an adenosine molecule attached to three phosphate groups.
- Phospholipid– the main component of cell membranes, consisting of a lipid attached to a phosphate group.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these activities involves phosphate groups? A. Providing energy to cells B. Activating proteins to perform certain functions in cells C. Limiting the growth of plants and animals in ecosystems D.All of the above 2. Phosphate consists of phosphorus bonded to what other element? A. Oxygen B. Fluorine C. Hydrogen D.Sulfur 3. What is phosphorylation? A. The saturati…
Phosphate Group Structure
- The phosphate group is a chemical structure that consists of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms. It can be represented by the symbol PO4. The phosphate group is found in many places, including DNA, ATP, phospholipids, and other biomolecules. One phosphate group in the structure is a chemical formula of phosphorus with four oxygen atoms. The PO43-...
Nucleic Acids Structure and The Function of The Phosphate Group
- Nucleic acidsare essential to life as we know them. They are the genetic material of our cells, and they dictate how our body is built and repaired. Nucleic acid structures can be divided into two categories: DNA and RNA. The difference between these two types of nucleic acid is that DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, whereas RNA contains ribose sugar. This distinction has a huge im…
Nucleic Acids Structures
- Nucleic acids are built from nucleotides. A nucleotide is a molecule that is composed of three components: sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugars in DNA are always deoxyribose, whereas the sugars in RNA can be either ribose or deoxyribose so long as there is one more oxygen atom than carbon atoms; otherwise, the sugar is considered deoxyribose. DNA…
The Roles of The Phosphate Group in The DNA
- DNA is composed of nucleotides made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. The DNA’s phosphate group connects the nucleotides and helps them form their helical shape or structure. The phosphate group is attached to the deoxyribose sugar in the DNA, and it usually binds to one of four nucleotides. The phosphate group in DNA is crucial to it…
Nucleotides Polymerization to Create Nucleic Acids
- Nucleic acids are made from nucleotides, and each nucleotide has a phosphate group linked to a pentose sugar by phosphodiester bonds. This fact makes the nucleotide a polymer. The structure of DNA and RNA is similar but not identical, even though they are created from the same set of nucleotides. The structure of DNA is a double helix, while the structure of RNA is less complex a…
Phosphate Groupings
- Phosphates can be grouped into primary and secondary phosphates. The primary phosphate is the first in a series of phosphates that end with a different substance. In DNA, the last phosphate group in a polyanion is called a primary phosphate. Polyanion is the most reactive form of phosphates because it has a high charge density and less steric hindrance. The most common …
Phosphate Bonding
- The five-oxygen group of phosphate can form a bond with carbon. When it does so, it forms an ester called a phosphate diester. In nature, phosphates are connected to other molecules by this type of bond. Phosphoesters are oxygen-containing esters. This type of bond can be found in carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and coenzymes. One phosphate diester that is important is ADP. T…
Phosphate Linkage
- Enzymes move phosphate groups from high-energy compounds to ADP, a process called substrate-level phosphorylation. It was discovered that cells used a different mechanism for this process, and it is now known as ATP synthesis. Phosphate groupings can be used to build coenzymes and nucleic acids. These are important in cellular metabolism, even if they are not p…
Different Natures of Phosphorus Compounds
- Monophosphates
These are phosphoric acid, -P(=O)(OH)2, and salts. Phosphorus is found in the center of monophosphate, which is an ester of phosphoric acid. Hydrogen atoms are bonded to the oxygen and phosphorus atoms of the phosphate group. This is the inorganic form of phosphates. One e… - Diphosphates
They have two phosphate groups bonded to one or more organic compounds. They are found in nucleotides like ATP and GTP. The bond that holds the phosphate groups together is stronger than a monophosphate bond because it’s a double bond. An example of diphosphates is Adenos…
Other Places Where The Phosphate Group Is Found
- The Phosphate Group in the ATP molecule
The phosphate group in the ATP molecule is found on the fifth carbon atom of ribose. The phosphoryl group, which has a negative charge, is on the third carbon atom of adenosine. The arrangement allows for a reaction to take place between these two pieces, which are called nucl… - The Phosphate Group in Phospholipids
Phosphate groups are found in phospholipids and can be seen as one of the main parts. Phospholipids carry a phosphate group that connects the glycerol to a fatty acid. Phosphate groups in phospholipids are one of the main parts. They are found as a link between glycerol an…