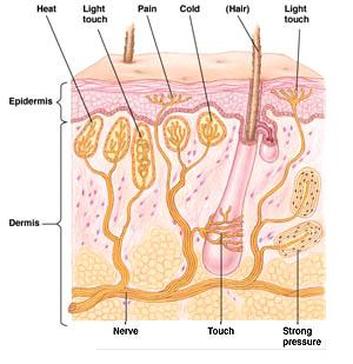
There are four main types of Touch receptors, which are located in the skin and deeper tissues. They include Pacinian corpuscles, Ruffini corpuscles The Bulbous corpuscle or Ruffini ending or Ruffini corpuscle is a slowly adapting mechanoreceptor found in the cutaneous tissue of humans. It is named after Angelo Ruffini. Ruffini corpuscles are enlarged dendritic endings with elongated capsules.Bulbous corpuscle
What are the different types of touch receptors in the skin?
Each type of skin receptor is attuned to a different physical sensation, which is then transmitted to the brain. So what kinds of touch receptors are found in the skin? Let’s get started! The main categories of touch receptor are called thermoreceptors, chemoreceptors, and mechanoreceptors.
What are the 4 types of receptors in the body?
There are four basic types of receptors like. Ligand-gated ion channel receptors. G-protein coupled receptors. Kinase-linked receptors. Nuclear receptors. These receptors are located in the cells, tissues and help to control all most all the body organs.
What is an example of a receptor?
These receptors coordinate body responses like a reflex action, sense of pain, touch, movements. Examples: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, GABA A receptors. G-protein coupled receptors. This is the largest class of receptors. They are also called metabotropic receptors.
Where are the receptors in the skin for sense of motion?
These receptors are located in hairy skin. They are more sensitive to stretch, so become stimulated during stretching of the skin. An example is stretching during motion and for the direction of force detection, along with muscle spindle for hand shape and finger position perception, etc.
What are the 4 stimuli for the sense of touch?
We have a range of different nerve endings embedded in the skin, combinations of which respond to the four basic sensations of pressure, hot, cold, and pain. But only the sensation of pressure has its own specialized receptors. Proprioception is our ability to sense the positions and movements of our body parts.
What do the 4 receptors of touch detect?
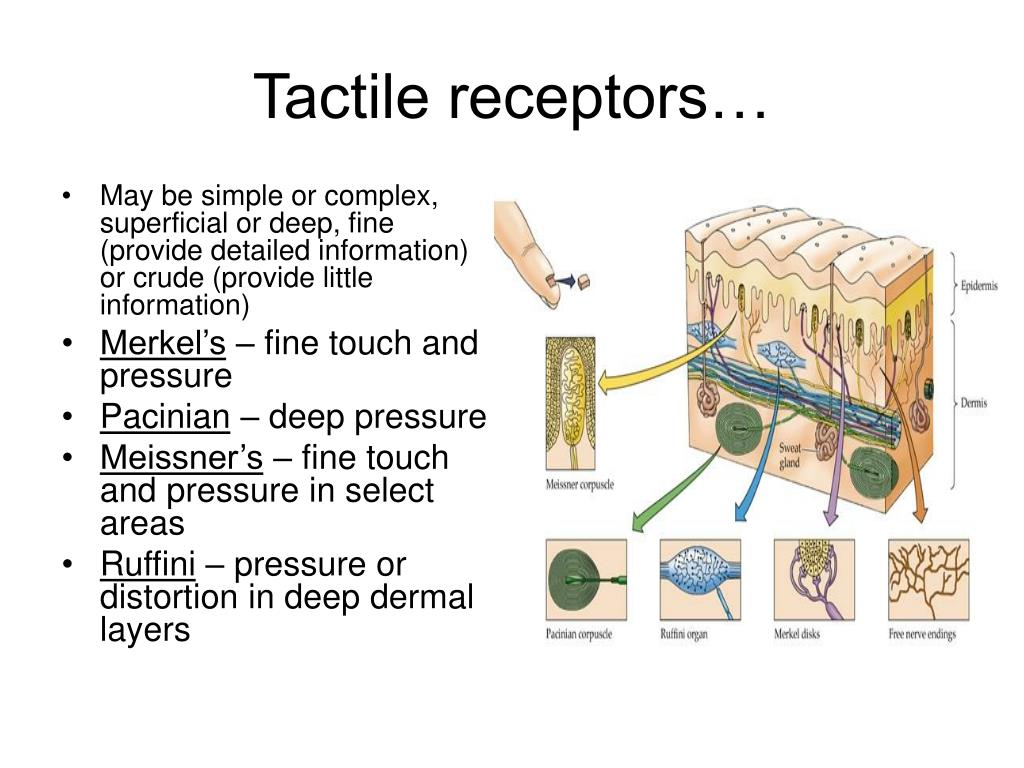
Mechanoreceptors: These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure, vibrations, and texture. There are four known types of mechanoreceptors whose only function is to perceive indentions and vibrations of the skin: Merkel's disks, Meissner's corpuscles, Ruffini's corpuscles, and Pacinian corpuscles.
What are the receptors for touch?
Touch receptors are a subtype of sensory neuron that are located in the skin and possess specialized endings that respond to mechanical stimulation. As part of the somatosensory system, touch receptors therefore transmit information regarding tactile stimuli to the central nervous system.
How many touch receptors are in the human body?
These produce a slow, burning pain; the faster the neurons fire, the more intense the pain. The tongue, lips, and fingertips are the most touch- sensitive parts of the body, the trunk the least. Each fingertip has more than 3,000 touch receptors, many of which respond primarily to pressure.
What are the 5 sensory receptors in your skin?
The hypodermis, which holds about 50 percent of the body's fat, attaches the dermis to the bone and muscle, and supplies nerves and blood vessels to the dermis. Sensory receptors are classified into five categories: mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, proprioceptors, pain receptors, and chemoreceptors.
Where are touch receptors mostly found?
The receptors in our skin are not distributed in a uniform way around our bodies. Some places, such as our fingers and lips, have more touch receptors than other parts of our body, such as our backs. That is one reason why we are more sensitive to touch on our fingers and face than on our backs.
Why are the touch receptors important?
Receptors are small in size, but they collect very accurate information when touched. They may sense pain, temperature, pressure, friction, or stretch. Unique receptors respond to each kind of information. This helps provide the body with a full picture of what is touching the skin.
What kind of touch do Pacinian corpuscles detect?
Meissner's corpuscles respond to touch and low-frequency vibration. Ruffini endings detect stretch, deformation within joints, and warmth. Pacinian corpuscles detect transient pressure and high-frequency vibration.
Which type of receptor detects light touch?
mechanoreceptorsOur somatosensory system has three basic types of sensory receptors that detect different types of external stimuli. These include mechanoreceptors that detect light touch, vibration, pressure, and texture; nociceptors that detect pain; and thermoreceptors that detect temperature.
What types of sensations do sensory receptors detect?
These receptors include those for tactile sensations, such as touch, pain, and temperature, as well as those for vision, hearing, smell, and taste. Interoceptors (visceroceptors) respond to stimuli occurring in the body from visceral organs and blood vessels.
Why are the touch receptors important?
Receptors are small in size, but they collect very accurate information when touched. They may sense pain, temperature, pressure, friction, or stretch. Unique receptors respond to each kind of information. This helps provide the body with a full picture of what is touching the skin.
What are the main categories of touch receptors?
The main categories of touch receptor are called thermoreceptors, chemoreceptors, and mechanoreceptors.
What are touch receptors?
Touch receptors are a group of specialized neurons directly beneath the skin that are largely responsible for our ability to interact with the physical world around us. So it is probably unsurprising that they come in a lot of different shapes and forms. Each type of skin receptor is attuned to a different physical sensation, which is then transmitted to the brain. So what kinds of touch receptors are found in the skin? Let’s get started!
What are the touch receptors found in the skin that respond to mechanical stimulation?
Mechanoreceptors3 are the touch receptors found in the skin that respond to mechanical stimulation – for example, physical sensations like holding a ball or pencil.
What do Merkel nerve endings tell you?
Merkel nerve endings3 work best to tell you about the pressure and location of objects you interact with; for example, you can discover that a particular rock is both solid and sharp because of these activated endings.
Where are chemoreceptors found?
Chemoreceptors2 cover chemical changes in the body, and are often found in unusual places – for example, chemoreceptors can be specialized to exist in your mouth and contribute to your ability to taste.
Which corpuscles are sensitive to vibrations?
Pacinian corpuscles3 are highly sensitive to vibrations, and allow your brain to tell the difference between smooth surfaces and rough ones.
What is the function of the Bulbous corpuscle3?
Bulbous corpuscle3, or Ruffini corpuscle, is a specialized mechanoreceptor that activates when you stretch your skin, allowing you to interpret and process actions like flexing your fingers or moving your arms.
How are receptors classified?
Receptors get classified based on the type of stimulus activating them. The following are common types of receptors
What is the distinguishing characteristic of each receptor?
One distinguishing characteristic of each receptor is the degree of adaptation.
How do sensory receptors become activated?
Sensory receptors become activated by stimuli in the environment by receiving signals. The transmission of any message in the neurons of our body requires it to be in the form of an action potential; the sensation must undergo conversion into electrical signals. The structures which convert mechanical signals into electrical signals are receptors.
Which type of receptor is the most sensitive?
Distributed throughout the palm and finger, the Pacinian corpuscle is the most sensitive receptor type. These are large, onion-like layered structures enclosing a single nerve ending. Pacinian corpuscles function as a mechanical filter to protect from very large, low-frequency stress during manual labor.
Why is it important to have a working knowledge of the structure and operation of the sensory system?
While the system is complex, it is vital to have a working knowledge of the structure and operation of the sensory system, to optimize patient care of all kinds.
What is the baseline firing rate of the skin receptors?
These receptors have some baseline firing rates. Cold receptors are sensitive between 10 and 32 degrees C. Firing at a baseline rate during 30 to 35 degrees C , firing rate increases in cold while it decreases when the temperature increases. In the same way, warm receptors have baseline firing around 38 degrees C and increase with an increase in temperature. [4]
Where are warm and cold receptors located?
Located in the skin and include cold and warm receptors. These are present in the skin.