Some Importances and Functions of Cell Parts Cells provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food substances and later on convert those nutrients into energy in order to carryout specialised functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and they can also replicate themselves.
What are the parts of cell and its functions?
Cell Parts and Function Notes . 1) Cell Membrane -Surrounds the cell and controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. -Made up of phospholipid molecules . 2) Cytoplasm -The jelly- like material that fills the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It contains all of the organelles . and many reactions occur here.
What are the basic components of a cell?
What are the basic components of cells?
- PLASMA MEMBRANE / CELL MEMBRANE. Structure- a bilipid membraneous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates.
- CYTOPLASM.
- NUCLEUS.
- 1. "
- RIBOSOMES.
- GOLGI BODY / APPARATUS.
- LYSOSOMES.
- MITOCHONDRIA.
What are the four main cell components?
What are the 5 cell structures?
- cell walls.
- mitochondria.
- chloroplasts.
- cell membrane.
- vacuole.
- nucleus.
- ribosomes.
- plasmids.
What parts of the cell and its function?
- Gatekeepers: Some receptors allow certain molecules through and stop others.
- Markers: These receptors act as name badges, informing the immune system that they are part of the organism and not a foreign invader.
- Communicators: Some receptors help the cell communicate with other cells and the environment.
What are the function of cell components?
Cells provide structure and support to the body of an organism. The cell interior is organised into different individual organelles surrounded by a separate membrane. The nucleus (major organelle) holds genetic information necessary for reproduction and cell growth.
What are the cells components?
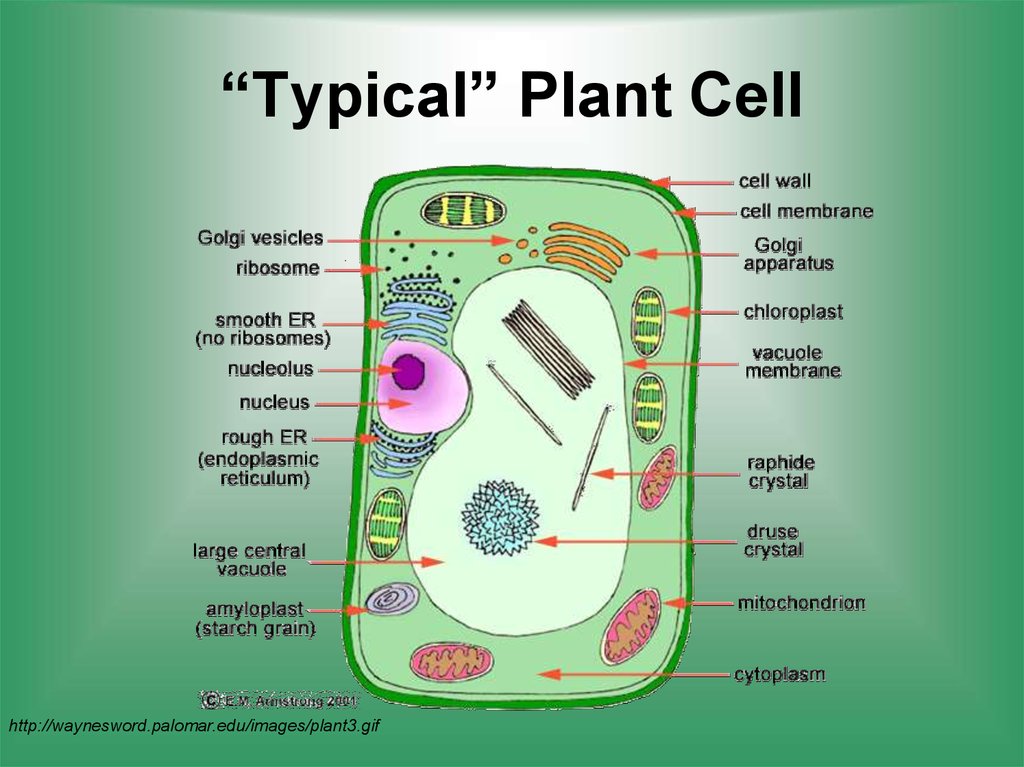
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
What are the 4 components of all cells what are their main functions?
All cells share four common components: (1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; (2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; (3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and (4) ...
What are the 5 main components of cells?
Although cells come in diverse shapes, all cells have certain parts in common. These parts include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cytoskeleton, and DNA.
What are the four components of cells?
All cells share four common components: 1) a plasma membrane, an outer covering that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment; 2) cytoplasm, consisting of a jelly-like region within the cell in which other cellular components are found; 3) DNA, the genetic material of the cell; and 4) ribosomes, ...
What are the three main components of a cell?
A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm.
Which is the most important component of a living cell?
Nucleus is an important component of the living cell. It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the animal cell and at the periphery of plant cells. It can be stained and seen easily with the help of a microscope. Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane.
What are major components of living cells?
Living organisms, however, are made of only a small selection of these elements, four of which—carbon (C), hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O)—make up 96.5% of an organism's weight.
What are the living components of cell?
Protoplasm is called the living substance of the cell. The entire content of a living cell is known as protoplasm. It includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
What are the 7 functions of a cell?
The cell wall has the following functions:Protects the cell from physical injury.Gives the cell a sense of organisation.Keeps osmotic bursting at bay.It maintains the shape of the cell.Regulates the flow of information between cells.It regulates the expansion of cells.Provides protection against pathogens.
What is cell and its functions?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions.
What is the function of cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is responsible for holding the components of the cell and protects them from damage. It stores the molecules required for cellular processes and is also responsible for giving the cell its shape.
Which is the major component of cell?
The cell is composed of three main parts; Cytoplasm, Nucleus, and cell membrane.
What are the main components of a cell free system?
All cell-free protein expression systems contain at least these three parts.Translational machinery. ... Energy. ... A messenger RNA to be translated.
What are the 7 functions of a cell?
The cell wall has the following functions:Protects the cell from physical injury.Gives the cell a sense of organisation.Keeps osmotic bursting at bay.It maintains the shape of the cell.Regulates the flow of information between cells.It regulates the expansion of cells.Provides protection against pathogens.
What are the two major components of cell membranes?
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments.
Who discovered the Golgi Apparatus?
Golgi Apparatus was discovered in 1898 by Camillo Golgi.
Who discovered Nucleus?
Robert Brown was responsible for discovering the nucleus of a cell in 1831
Who discovered Plastids?
The term, “Plastid” was first coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Who discovered Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Endoplasmic Reticulum was discovered by Keith R. Porter in 1954.
Why is Cell Membrane called selectively permeable?
It allows the transport of selective substances into and out of the cell, but not all substances. This is why it is known as ‘selectively permeable’.
1. Cell membrane (Plasma membrane)
It is made of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972). The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components —including phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates—that gives the membrane a fluid character.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum
Discovered by Keith R. Porter in 1954. It is absent in Human RBCs, Blue-Green Algae, Bacteria.
4. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm of a cell, and also on the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
5. Golgi Apparatus
Its function is to store and transport proteins & lipids that have been synthesized.
10. Nucleus
Robert Brown was responsible for discovering the nucleus of a cell in 1831
Functions cytoplasm
i.All living substances including nucleus are suspended in the semi-fluid cytoplasm
CELL WALL
The cell wall is the non-living outer boundary of the cell made of cellulose. It has tiny pores or its pits through which nutrient pass from one cell to another. Cell wall is absent in animal cell
CELL MEMBRANE
The cell membrane is a thin and flexible living later that surrounds the entire cytoplasm and separates the cell from neighboring cells.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of canals found abundantly in the cytoplasm. It ribosome are attached to it in rough ER and if no ribosome are attached it is called smooth ER.
Ribosome
These are minute and spherical organelles found in large number attached to endoplasmic reticulum or suspended in the cytoplasm
MITOCHONDRION
These are tiny red-shaped bodies or granules in the cytoplasm. They are more concentrated in very active cells such as liver cells.
Lysosomes
These are minute and rounded bodies containing enzymes found in animal cells
Why do cells have special structures?
Because some cells perform specific functions, they have special modified structures. For example, red blood cells are the oxygen carriers in the body. They lack a nucleus to make more space for ...
How do cells get nutrients?
Cells import nutrients to use in the various chemical processes that go on inside them. These processes produce waste which a cell needs to get rid of. Small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and ethanol get across the cell membrane through the process of simple diffusion.
What is the goal of sciencing?
Our goal is to make science relevant and fun for everyone. Whether you need help solving quadratic equations, inspiration for the upcoming science fair or the latest update on a major storm, Sciencing is here to help.
How do cells grow in mitosis?
Facilitate Growth Through Mitosis. In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. This takes place through the process of mitosis in which the parent cell breaks down to form two daughter cells identical to it.
Why is reproduction important?
Reproduction is vital for the survival of a species. A cell helps in reproduction through the processes of mitosis(in more evolved organisms) and meiosis. In mitosis cells simply divide to form new cells. This is termed asexual reproduction.
How do complex organisms grow?
In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. This takes place through the process of mitosis in which the parent cell breaks down to form two daughter cells identical to it. Mitosis is also the process through which simpler organisms reproduce and give rise to new organisms.
How many organ systems are there in the human body?
Five Major Organ Systems of the Body
What is the power house of the cell?
It is termed as the power house of the Cell. Plays an major part in the terminal stages of Aerobic Respiration. Synthesizes ATP – hence called the power house of cell as ATP is the primary source of Energy. Manufactures Polysaccharides.
Which membrane serves as a transport channel for DNA and RNA?
Nuclear Membrane : Pores in the membrane serve as Transport Channels Site of Synthesis of RNA and DNA
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is also termed as a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances, found between the cell membrane and nucleus. They are mainly composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell. There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell as they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in several organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, sausage-shaped organelle, found in almost all eukaryotic cells.
Plastids
Plastids are large, membrane-bound organelles which contain pigments. Based on the type of pigments, plastids are of three types:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein.