
Tight junctions contain proteins called claudins while gap junctions contain proteins called connexins
Connexin
Connexins, or gap junction proteins, are a family of structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions (an entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, form gap junctions in invertebrates). Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, or co…
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.
How do gap junctions work?
How do gap junctions work? Gap junction. Gap junctions are a specialized intercellular connection between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulated gate between cells.
What is an example of a gap junction?
Gap junctions are common in the muscle tissue of animals' hearts, for example, as they allow ions to pass rapidly from cell to cell to coordinate cardiac muscle contraction. Plasmodesmata connect plant cells to one another in the same way, and they enable rapid transport and communication between adjacent cells.
What does gap junction mean?
Gap junction: An organized collections of protein channels in cell membranes that allows ions and small molecules to pass between adjacent cells. The protein channels that make up gap junctions consist of two connexons. One connexon resides in the membrane of one cell.
What is the definition of gap junction?
Gap junctions are a type of cell junction in which adjacent cells are connected through protein channels. These channels connect the cytoplasm of each cell and allow molecules, ions, and electrical signals to pass between them.
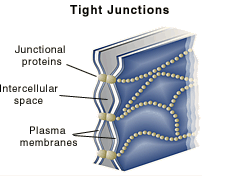
What is the role of tight and gap junctions?
The purpose of tight junctions is to keep liquid from escaping between cells, allowing a layer of cells (for instance, those lining an organ) to act as an impermeable barrier. For example, the tight junctions between the epithelial cells lining your bladder prevent urine from leaking out into the extracellular space.
What are the functions of gap junctions?
Gap junctions are channels that physically connect adjacent cells, mediating the rapid exchange of small molecules, and playing an essential role in a wide range of physiological processes in nearly every system in the body, including the nervous system.
What is the functional difference between tight junction and gap junction?
Tight junction refers to a specialized connection of two adjacent animal cell membranes, such that, space usually lying between them is absent while a gap junction refers to a linkage of two adjacent cells consisting of a system of channels extending across a gap from one cell to the other, allowing the passage.
What is the function of the gap function?
Gap junctions allow the exchange of ions, second messengers, and small metabolites between adjacent cells and are formed by two unrelated protein families, the pannexins and connexins. Mutations in connexin genes cause a variety of genetic disorders, implicating a critical role in tissue homeostasis.
What do gap junctions function most like?
The main function of gap junctions is to connect cells together so that molecules may pass from one cell to the other. This allows for cell-to-cell communication, and makes it so that molecules can directly enter neighboring cells without having to go through the extracellular fluid surrounding the cells.
What is the function of gap junctions quizlet?
Gap junctions allow cellular communication via passage of electrical and chemical signals between adjacent cells.
What type of cell junction is a tight junction?
Occluding junctions The borders of two cells are fused together, often around the whole perimeter of each cell, forming a continuous belt like junction known as a tight junction or zonula occludens (zonula = latin for belt).
Which of the following best describes tight junctions?
Which of the following describes tight junctions? In a tight junction, a series of integral protein molecules (including occludins and claudins) in the plasma membranes of adjacent cells fuse together, forming an impermeable junction that encircles the cell.
What is a tight junction?
Tight junctions are intercellular adhesion complexes in epithelia and endothelia that control paracellular permeability. This paracellular diffusion barrier is semipermeable: it is size- and charge-selective. Paracellular ion permeability at tight junctions is largely determined by their claudin composition.
Where are the tight junction?
Tight junctions, or zonula occludens (ZO), are characteristic of epithelial and endothelial cells (Figure 1). Located at the border between apical and lateral membranes, tight junctions regulate the passage of proteins and liquids across the cell monolayer.
What is a tight junction in anatomy?
Tight junctions form leakproof seals by fusing the plasma membranes of adjacent cells, creating a continuous barrier through which molecules cannot pass. The membranes are fused by tight associations of two types of specialized integral membrane proteins, in turn repelling large water-soluble molecules.
What is the main purpose of gap junctions Mcq?
Correct answer: Gap junctions prevent molecules and ions from traveling between cells in the extracellular space.
What do gap junctions do in animals quizlet?
Gap junctions are found in plant cells and plasmodesmata are found in animal cells. Gap junctions are capable of dilation whereas plasmodesmata are rigid. Gap junctions are found in animal cells and plasmodesmata are found in plant cells. Animal cells can share some metabolites, such as ATP and coenzymes.
Why are gap junctions important in cardiac muscle?
Abstract. In the heart, individual cardiac muscle cells are linked by gap junctions. These junctions form low resistance pathways along which the electrical impulse flows rapidly and repeatedly between all the cells of the myocardium, ensuring their synchronous contraction.
What are the three types of cell junctions and the function of each?
Cell junctions fall into three functional classes: occluding junctions, anchoring junctions, and communicating junctions. Tight junctions are occluding junctions that are crucial in maintaining the concentration differences of small hydrophilic molecules across epithelial cell sheets.
Why are gap junctions important?
The main function of gap junctions is to connect cells together so that molecules may pass from one cell to the other. This allows for cell-to-cell communication, and makes it so that molecules can directly enter neighboring cells without having to go through the extracellular fluid surrounding the cells. Gap junctions are especially important during embryonic development, a time when neighboring cells must communicate with each other in order for them to develop in the right place at the right time. If gap junctions are blocked, embryos cannot develop normally.
What is a gap junction?
Gap junctions are a type of cell junction in which adjacent cells are connected through protein channels. These channels connect the cytoplasm of each cell and allow molecules, ions, and electrical signals to pass between them. Gap junctions are found in between the vast majority of cells within the body because they are found between all cells that are directly touching other cells. Exceptions include cells that move around and do not usually come into close contact with other cells, such as sperm cells and red blood cells. Gap junctions are only found in animal cells; plant cells are connected by channels called plasmodesmata instead.
Why are plasmodesmata different from gap junctions?
Plasmodesmata are structured differently than gap junctions due to plant cells having thick cell walls, their function is essentially the same. Plant cells can regulate the passage of small molecules and communicate with each other through their plasmodesmata.
How many connexins are in a gap junction?
Groups of six connexins form a connexon, and two connexons are put together to form a channel that molecules can pass through. Other channels in gap junctions are made up of pannexin proteins. Relatively less is known about pannexins; they were originally thought only to form channels within a cell, not between cells.
What is the anchoring junction?
Anchoring junction – A type of cell junction in which cells are connected by a mass of proteins. Tight junction – A type of cell junction where cells are tightly bonded to form a barrier. Plasmodesmata – Channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells. Connexin – A family of proteins that makes up gap junctions.
What happens when gap junctions are blocked?
If gap junctions are blocked, embryos cannot develop normally. Gap junctions make cells chemically or electrically coupled. This means that the cells are linked together and can transfer molecules to each other for use in reactions.
Where are anchoring junctions found?
Tight junctions are areas where cells are bound very closely together to form a barrier, and they are often found in epithelial cells, which are cells found on the surface of the body and lining organs. Plant cells do not have gap junctions, ...
Why are tight junctions important?
Their most important functions are to help cells form a barrier that prevents molecules from getting through, and to stop proteins in the cell membrane from moving around. Tight junctions are often found at epithelial cells, which are cells that line the surface of the body and line body cavities. Not only do epithelial cells separate the body from the surrounding environment, they also separate surfaces within the body. Therefore, it is very important that the permeability of molecules through layers of epithelial cells is tightly controlled.
What is a tight junction?
Tight Junctions Definition. Tight junctions are areas where the membranes of two adjacent cells join together to form a barrier. The cell membranes are connected by strands of transmembrane proteins such as claudins and occludins. Tight junctions bind cells together, prevent molecules from passing in between the cells, ...
What are the two proteins that regulate the cell membrane?
Regulation proteins regulate what proteins are brought to the cell membrane in vesicles. Claudins and occludins are the two main types of proteins present at tight junctions, and they are both transmembrane proteins. Claudins are important in forming tight junctions, while occludins play more of a role in keeping the tight junction stable ...
What is the function of tight junctions in exocytosis?
Exocytosis also relies on specific proteins in order to work correctly. Tight junctions keep the correct proteins on the correct sides of the cell in order for these functions to occur. This also helps maintain the polarity of cells. Another function of tight junctions is simply to hold cells together. The branching protein strands of tight ...
How do molecules pass through the cell?
They could pass through special proteins in the cell membrane, or be engulfed by the cell through endocytosis. Using these methods, the cell has greater control over what materials it takes in and allows to pass through. However, in endothelial cells, certain proteins must be kept on certain sides of the cell. The apical, or outside layer, of the sheet of cells contains proteins that only let certain substances pass through. The basal, or inside layer, is where cells let molecules pass through them by expelling them from their membrane in a process called exocytosis. Exocytosis also relies on specific proteins in order to work correctly. Tight junctions keep the correct proteins on the correct sides of the cell in order for these functions to occur. This also helps maintain the polarity of cells.
What are the two types of junctions in vertebrate cells?
Tight junctions are one of three main types of junctions in vertebrate cells. The other two types are gap junctions and anchoring junctions. Gap junctions , also known as communicating junctions, are channels in cells that let adjacent cells communicate with one another without having to send molecules through the extracellular fluid surrounding ...
Which proteins are involved in tight junctions?
Scaffolding proteins organize transmembrane proteins, which are the main proteins involved in tight junctions. Claudins and occludins are the two main proteins in tight junctions, and they are both transmembrane proteins.
Definition of Gap Junction
Gap junction is known for bridging gaps between the adjacent cell and creates a direct path between the cytoplasm of the two cells. In plants, these linkages are known as plasmodesmata.
Definition of Tight Junction
In the body of the vertebrates, more than 60% of the cells types are epithelial.
Similarities
Both gap junctions and tight junctions have a specialized channel known as connexons.
Conclusion
In this article we have studied about the gap junction and tight junction, in the Gap junction allows the rapid diffusion of micro-molecules and water-soluble molecules whereas tight junction seals the diffusion of proteins and lipids in the linings of the plasma membrane.
What are Tight Junctions?
These are also known as occluding junctions or zonulae occludentes. These junctions form the closest contacts as compared to the other cell junctions and can therefore form a barrier that is virtually impermeable to fluids. These are the most apical structures of the apical complex, and they form the demarcation between the apical and the basolateral membranes of the domains.
What is the role of tight junctions in the body?
Tight junctions are required for cell adhesion in various tissues of the body. These structures are seen to be present on the epithelium cells that form the internal lining of the body. These are usually of one or two layers of cells. Recent studies have also highlighted their role in barrier function in the skin as well.
What is the Structure of Tight Junctions?
Tight junctions are usually made of trans-membrane proteins that are linked to a cytoplasmic plaque. Trans-membrane proteins are usually of two types: tetra-span and single-span trans-membrane proteins. Tetraspan proteins contain four membrane spanning domains, these include proteins like occludins, claudins, and tricellulins.
Where are Tight Junctions Found in the Body?
Tight junctions are required for cell adhesion in various tissues of the body. These structures are seen to be present on the epithelium cells that form the internal lining of the body. These are usually of one or two layers of cells. Recent studies have also highlighted their role in barrier function in the skin as well.
What enzymes interact with the epithelial barrier?
Proteolytic enzymes from pollen, many viruses, dust mites, and enterotoxins from bacteria, like ,. Clostridium perfringens, interact with these junctions to bring about the loss of the epithelial barrier function.
Why are occludins needed in tight junctions?
Occludins present in tight junctions are required for suppression of cell proliferation, and the absence of these proteins may lead to uncontrolled cancerous growth of cells. Certain biochemical studies indicate that tight junctions are required for the maintenance of apico-basal polarity. Proteins that are required for cell polarization usually ...
What are the three types of cell junctions?
There are three basic types of cell junctions: anchoring junction, communicating or GAP junctions , and tight junctions. Anchoring junctions are protein complexes that are used to anchor the cells of a tissue either to each other or to the extra cellular matrix. Communicating jun ctions bring about direct chemical communication between adjacent cells.
What is a cell junction?
3. A cell junction is a type of structure that exist within the tissue of some multicellular organisms. Or Cell junction are complex structure of protein exist in between cells or between cells and matrix. They connect cell to other cells, they often occur in epithelial tissue. What is a cell junction?
Do all tight junctions have the same permeability?
9. Not all the tight junctions exhibit the same permeability . Only those with several parallel strand tend to form better seals than junctions with one or a couple of strands. Some tight junctions are to specific ions or solutes to which other tight junctions are impermeable. Eg :- ascending limb of kidney are permeable to magnesium ions. Properties

Gap Junction Definition
Function of Gap Junctions
- The main function of gap junctions is to connect cells together so that molecules may pass from one cell to the other. This allows for cell-to-cell communication, and makes it so that molecules can directly enter neighboring cells without having to go through the extracellular fluidsurrounding the cells. Gap junctions are especially important durin...
Gap Junction Structure
- In vertebratecells, gap junctions are made up of connexin proteins. (The cells of invertebrates have gap junctions that are composed of innexin proteins, which are not related to connexin proteins but perform a similar function.) Groups of six connexins form a connexon, and two connexons are put together to form a channel that molecules can pass through. Other channels …
Other Cell Junctions
- The two other types of cell junctions in vertebrates are anchoring junctions and tight junctions. Anchoring junctions adhere cells through proteins that are connected to the cell’s cytoskeleton. Tight junctions are areas where cells are bound very closely together to form a barrier, and they are often found in epithelial cells, which are cells found on the surface of the body and lining org…
Related Biology Terms
- Anchoring junction– A type of cell junction in which cells are connected by a mass of proteins.
- Tight junction– A type of cell junction where cells are tightly bonded to form a barrier.
- Plasmodesmata– Channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells.
- Connexin– A family of proteins that makes up gap junctions.
Quiz
- 1. How many connexins are found in one gap junction channel? A. 6 B. 4 C. 12 D.2 2. What is the “bystander effect” in relation to gap junctions? A. Molecules can enter neighboring cells without passing through extracellular fluid. B. Cells next to a cell that is undergoing cell death can also die. C. Cells can transmit therapeutic compounds to one another. D.Gap junctions are only found in c…
References
- Alberts, Bruce, et al. (1994). Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd. ed.Ch. 1. Garland Science: New York. ISBN: 978-0815316206.
- Davidson, Michael W. (2015-11-13). “Plasmodesmata”. Molecular Expressions Cell Biology.Retrieved 2017-04-13 from https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/.
- Evans, W.H. and Martin, P.E. (2002). “Gap junctions: structure and function (Review)”. Mol. M…
- Alberts, Bruce, et al. (1994). Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd. ed.Ch. 1. Garland Science: New York. ISBN: 978-0815316206.
- Davidson, Michael W. (2015-11-13). “Plasmodesmata”. Molecular Expressions Cell Biology.Retrieved 2017-04-13 from https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/.
- Evans, W.H. and Martin, P.E. (2002). “Gap junctions: structure and function (Review)”. Mol. Membr. Biol.19 (2): 121–36.
- Kimball, John W. (2015-03-02). “Junctions Between Cells”. Kimball’s Biology Pages.Retrieved 2017-04-12 from http://www.biology-pages.info/.