Both integral and peripheral membrane proteins play an important role in vital processes due to their interaction with the biological membranes. With the exception of lipid-soluble molecules, membrane proteins are indispensable for the communication between the cell and its environment.
What are five major functions of membrane protein?
The functions of a membrane protein include cell cohesion, relaying signals between the inside and outside of a cell and transporting proteins across the membrane. A membrane protein is a protein that is attached to a cell and interacts with biological membranes. Each type of membrane protein has a different function.
What functions does a protein in a cell membrane have?
What are the functions of membrane proteins?
- 6 Functions of Membrane Proteins. Transport.
- Transport. Hydrophilic channel.
- Enzymatic activity. Sequential steps in metabolic pathway.
- Signal transduction. relay chemical messages.
- Intercellular Joining. Various Cell Junctions.
- Cell-cell recognition.
- Attachment to the cytoskeleton and the ECM.
What are the four functions of a cell membrane?
What are the six functions of the plasma membrane?
- A Physical Barrier. ...
- Selective Permeability. ...
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis. ...
- Cell Signaling. ...
- Phospholipids. ...
- Proteins. ...
- Carbohydrates. ...
- Fluid Mosaic Model.
What is the difference between peripheral and integral proteins?
Peripheral proteins are embedded on the membrane. While integral proteins pass across the membrane. While integral protein are a part of lipid bilayer. Peripheral proteins are usually globular structure. While integral proteins are usually receptors are transfer proteins, having trans membrane spanning regions.

What is the function of peripheral protein in the cell membrane?
Peripheral proteins form temporary bonds with the cell membrane, allowing them to detach and reattach at specific times, with specific signals. This allows cells to coordinate and communicate using networks of proteins and reactions.
What are the functions of integral and peripheral proteins and where are they located?
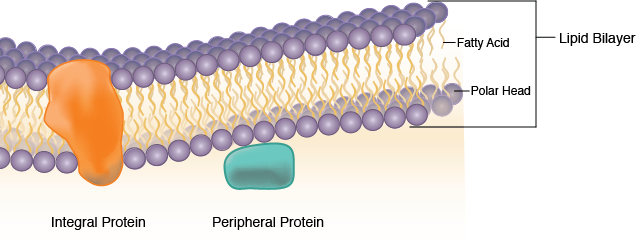
Integral and peripheral proteins are two types of membrane proteins in the phospholipid bilayer. Integral proteins penetrate the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer while peripheral proteins are attached to the intracellular or extracellular surface of the lipid bilayer.
What are the two functions of integral membrane proteins?
They are the entry and exit routes for many ions, nutrients, waste products, hormones, drugs and large molecules such as proteins and DNA. They are also responsible for much of the communication between cells and their environment.
What is the major function of integral proteins?
Integral membrane proteins reside within the bilayer membranes that surround cells and organelles, playing critical roles in movement of molecules across them and the transduction of energy and signals.
What is the main difference between integral and peripheral membrane proteins?
The peripheral proteins (also known as extrinsic proteins) are soluble and readily dissociate from the membrane, whereas the integral proteins (also known as intrinsic proteins) are relatively insoluble and dissociate with difficulty.
What is the function of peripheral proteins quizlet?
Peripheral: Provides the framework for the plasma membrane and is attached to integral protein.
What are the 3 functions of membrane proteins?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
What is an example of a peripheral protein?
Examples of peripheral membrane proteins are proteins involved in electron transport chains, such as cytochrome c, cupredoxins, high potential iron protein, adrenodoxin reductase, some flavoproteins, and others.
Where are peripheral proteins found?
Peripheral proteins are attached to the surface of the bimolecular lipid layer, probably by electrostatic interactions, whereas integral proteins are integrated into the lipid bilayer in whole or part (Fig. 5.3A).
What are the 6 major functions of membrane proteins?
Membrane protein functionsEnzymatic functions. All enzymes are a type of protein. ... Transportation. Membrane proteins can allow hydrophilic molecules to pass through the cell membrane. ... Signal transduction. Some membrane proteins can feature a binding site. ... Cell recognition. ... Intercellular joining. ... Attachment.
What are integral proteins also called?
Integral proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, and also called transmembrane proteins.
What is an integral membrane protein quizlet?
Membrane proteins. integral proteins (structural channels or pores, carrier proteins, enzymes, receptors) and peripheral proteins (attached to integral proteins, function as enzymes or controllers of transport through membrane pores)
Where are peripheral proteins located?
These enzymes have been described as peripheral membrane proteins, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane facing the cytosol, or in the cellular membranes of bacteria.
Where are peripheral proteins located head or tail?
Peripheral membrane proteins are found on the outside and inside surfaces of membranes, attached either to integral proteins or to phospholipids.
What are two functions of integral membrane proteins quizlet?
The five functions of integral membrane proteins includes signal transduction, transport, enzymatic activity, intracellular binding, and cell recognition.
What is the difference between integral and peripheral proteins?
Integral and peripheral membrane proteins are not the same. Integral proteins are permanently embedded within the cell membrane, whereas peripheral...
What is an example of a peripheral membrane protein?
An example of a peripheral membrane protein is cytochrome C. It is mostly found at the location of the mitochondrial membrane, where it functions a...
Where are peripheral membrane proteins?
Peripheral membrane proteins are closely associated with the cell membrane. They attach to the surface of the cell membrane but are able to attach...
What is the function of the peripheral membrane?
Peripheral membranes allow many molecules to be carried around the cell. Some peripheral membrane proteins carry molecules between other proteins. As shown in Figure 3 (see video), the function of cytochrome c is to carry electrons from one protein to the next. If cytochrome c was not present, the proteins that aid in generating energy would not ...
What Are Peripheral Proteins?
Most molecules cannot cross cell membranes alone because it is impenetrable to them. The role of the plasma membrane is to form a barrier and protect the cell from the environment. The problem is, the cell membrane is a bit overzealous at its job. If it were up to the cell membrane, hardly anything would get in or out of the cell. This is counterproductive if the cell is going to stay alive since the cell membrane blocks vital molecules from crossing. Think of the plasma membrane as a dumb dictator whom you cannot reason with. For this reason, the cell membrane is full of proteins that help keep the plasma membrane and other membranes in the cell in check.
Why are peripheral membranes important?
Even though peripheral membranes don't form entryways to the cell since they don't penetrate the membrane, they're really vital to the function of the cell. Think of them as the wingmen of the membrane proteins since they play vital roles for the cell. They do this by acting as partners with other proteins.
What are the two types of proteins that make up the cell membrane?
There are two types of membrane proteins: integral and peripheral. Think of proteins as diplomats who can reason with cell membranes and form ways to bring molecules into the cell.
Why are peripheral proteins called peripheral proteins?
They're called 'peripheral proteins' because they sit on the outside of the membrane and do not integrate into the membrane. {"error":true,"iframe":true}.
What would happen if the cell membrane was up to the cell membrane?
If it were up to the cell membrane, hardly anything would get in or out of the cell. This is counterproductive if the cell is going to stay alive since the cell membrane blocks vital molecules from crossing. Think of the plasma membrane as a dumb dictator whom you cannot reason with.
Is cytochrome C a peripheral protein?
In some cancer cells, this does not happen, and cells with damaged DNA are allowed to grow out of control and form tumors. So cytochrome c is a peripheral protein, that is essential for life and for health, but we never even think about it.
What are membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins that extend from a cell’s external surface often carry carbohydrate chains, forming glycoproteins. Some glycoproteins facilitate cell-cell recognition by functioning as “ID tags” that can be recognized by membrane proteins of other cells. Vinothkumar, Kutti R., and Richard Henderson.
Do integral proteins cross the membrane?
Integral proteins insert partially or fully through the membrane, or in some cases, are bound very tightly to another integral protein. Peripheral proteins do not cross the membrane, but are instead linked to the membrane by weaker interactions with integral proteins. Integral proteins are usually amphipathic molecules.
What is the difference between integral and peripheral proteins?
The main difference between integral and peripheral proteins is that integral proteins are embedded in the whole bilayer whereas peripheral proteins are located on the inner or outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer.
What is integral protein?
Integral proteins are proteins that are permanently attached to the plasma membrane. They penetrate through the phospholipid bilayer. Therefore, these proteins are attached to the lipid bilayer through hydrophobic, electrostatic or non-covalent interactions. On that account, detergents should be used to remove integral proteins from the lipid bilayer. This will destroy the hydrophobic interactions of the whole lipid bilayer. Transmembrane proteins, which completely penetrate the lipid bilayer, are integral proteins. All transmembrane proteins are integral proteins, but all integral proteins are not transmembrane proteins. This means some integral proteins can partially penetrate the lipid bilayer.
What are the two types of membrane proteins in the phospholipid bilayer?
Conclusion. Integral and peripheral proteins are two types of membrane proteins in the phospholipid bilayer. Integral proteins penetrate the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer while peripheral proteins are attached to the intracellular or extracellular surface of the lipid bilayer. Transmembrane proteins are a type of integral proteins.
What are the proteins that are permanently attached to the plasma membrane?
Integral Proteins : Integral proteins are proteins that are permanently attached to the plasma membrane. Peripheral Proteins: Peripheral proteins are proteins that are temporarily attached to the plasma membrane.
What is the membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment?
Plasma membrane is the biological membrane which separates the contents of the cell from the outside environment. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Plasma membrane serves as a selectively permeable barrier which only allows certain molecules to pass through the membrane. Different types of proteins are embedded in the plasma membrane as well.
What should be used to remove integral proteins from the plasma membrane?
Integral Proteins: Detergents should be used to remove integral proteins from the plasma membrane.
What are the types of interactions between lipids?
Types of Interactions with Lipid Bilayer. Integral Proteins: Integral proteins bind to the lipid bilayer by hydrophobic, electrostatic or non-covalent interactions . Peripheral Proteins: Peripheral proteins on the inner surface of the lipid bilayer are held by the cytoskeleton.
What is the function of integral proteins?
Integral Protein Function. The basic function of at least one part of every integral protein is to attach the protein to a plasma membrane. This membrane may be the plasma membrane surrounding the mitochondria, or the inner membrane of the mitochondria. They are present on the outermost cell wall, as well as the nuclear envelope, ...
What is the difference between integral and peripheral proteins?
A peripheral protein is often attached to the plasma membrane, but only to the heads of the phospholipid molecules. Most can detach easily, and are not really bound within the membrane. An integral protein, because of the chemistry of the environment around it, can never leave the plasma membrane. Sometimes a peripheral protein ...
What is a lipid anchor?
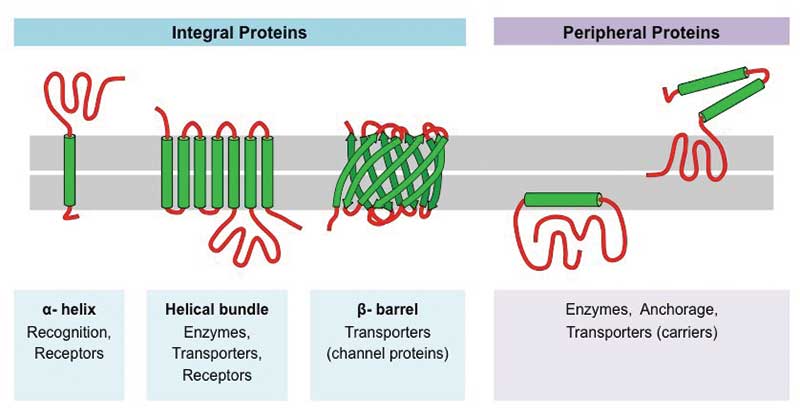
A lipid anchor is a non-polar, hydrophobic attachment to some proteins which allows it to be embedded within the plasma membrane. Instead of being coded into the genetic code of the protein, the protein itself is modified through a different process. Through a biochemical reaction, a fatty acid or other lipid is covalently bonded to the protein itself, usually at one end. The lipid is then used in the constitution of the plasma membrane, where it becomes trapped by its nature with the other lipids of the tail regions of the phospholipids. An integral protein with a lipid anchor is not picture in the above image.
What are the three themes of binding to the plasma membrane?
The first two involve the sequence of amino acids which makes up the protein, and the third involves a modification to the protein after it is created which gives it a lipid -based anchor within the plasma membrane.
How many alpha helices are there in an integral protein?
An integral protein may only have one region of alpha helix, as shown in the far left of the image below. Many other proteins employ several alpha helices, which span the membrane. This allows for the creation of a protein channel, or a hole in the plasma membrane which allows various substances to pass.
What is an integral protein?
An integral protein, sometimes referred to as an integral membrane protein, is any protein which has a special functional region for the purpose of securing its position within the cellular membrane. In other words, an integral protein locks itself into the cellular membrane. It does so with regions of specific amino acids which are attracted ...
Why do proteins need to be bound to the plasma membrane?
Instead, these integral proteins may need to be bound to a membrane so that their product is easy to expel. Some of the proteins responsible for producing neurotransmitters operate in this way.