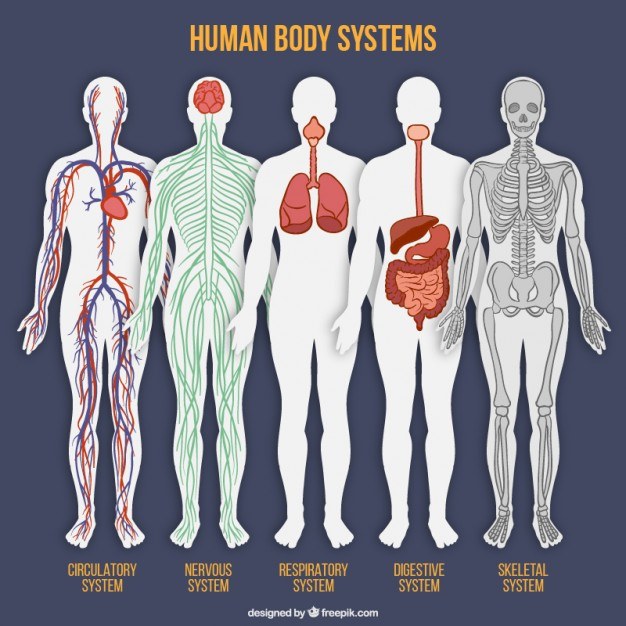
Key facts about the human body systemsTable quiz
| System of organs | A group of organs that work together to ... |
| Musculoskeletal system | Mechanical support, posture and locomoti ... |
| Cardiovascular system | Transportation of oxygen, nutrients and ... |
| Respiratory system | Exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide be ... |
| Nervous system | Initiation and regulation of vital body ... |
| Body System | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Reproductive | Reproduction |
| Nervous/Sensory | Communication between and coordination of all the body systems |
| Integumentary | Protects against damage |
| Muscular/Skeletal | Provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body |
What are the 11 major organ systems and their functions?
jmmaple. Major Organ Systems Functions of the Human Body"MURDERS LINC"Muscular,Urinary,Reproductive,Digestive,Endocrine,Respiratory,Skeletal, Lympathic,integumentary,nervous,circulatory. Terms in this set (11) Circulatory System. Transports nutrients, wastes, hormones, and gases. Digestive System.
What are the 9 systems of the body?
Your body's major organ systems are as follows:
- Circulatory system: heart, blood, blood vessels, and lymphatics.
- Digestive system: esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon.
- Endocrine system: pituitary, thyroid, ovaries, and testes.
- Immune system: organs (including lymphatics and spleen), special.
What are the main organ systems and their functions?
System Function Diagram Major Organs Interactions- Working with Other Systems Excretory 1. removes waste products from cellular metabolism (urea, water, CO 2) 2. filters blood Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra Lungs Skin – sweat glands Liver (produces urea) 1. w/circulatory – filters waste out of blood 2. w/lungs – removes
What are the 12 major body systems?
The 12 Major Meridians of the Body
- Lung
- Large intestine
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Heart
- Small intestine
- Bladder
- Kidney
- Pericardium
- Triple Warmer
What are the functions of all the body systems?
Human body systemsSystem of organsA group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body.Reproductive systemProduction of reproductive cells and contribution towards the reproduction process.Integumentary systemPhysical protection of the body surface, sensory reception, vitamin synthesis.8 more rows
What are the functions of the 11 body systems?
11 Cards in this SetIntegumentary SystemInsulates, protects, temperature and water regulationSkeletal SystemProvides support for bodyMuscular SystemCreates and limites movement, moves food along the digestive tract and circulates blood.Nervous SystemControls and regulates all systems of the body7 more rows
What are the 10 main body systems responsible for the body's function?
Ten major systems include the skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and the reproductive system. Body functions are the physiological or psychological functions of body systems.
What are the 12 main systems of the human body?
They are Integumentary System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Nervous System, Endocrine System, Cardiovascular System, Lymphatic System, Respiratory System, Digestive System, Urinary System, and Reproductive System (Female and Male).
What are the 11 major organ systems and their main functions quizlet?
Terms in this set (11)Circulatory System. Transports nutrients, wastes, hormones, and gases.Digestive System. Extracts and absorbs nutrients from food, removes wastes, maintains water and chemical balances.Endocrine System. ... Urinary System/Excretory. ... Lymphatic. ... Integumentary System. ... Muscular System. ... Nervous System.More items...
What are the 3 most important body systems?
Body Systems Lesson For Kids | Circulatory, Digestive & Respiratory.
What are the functions of the 12 body systems?
Body Systems, Functions, and OrgansBody SystemPrimary FunctionRespiratoryBreathingCardiovascular/CirculatoryBlood circulationDigestiveProcessing foodEndocrineHormone production6 more rows
What are the 7 vital organs?
Scientific viewThe brain. The brain is the control centre of the nervous system and is located within the skull. ... The lungs. The lungs are two sponge-like, cone-shaped structures that fill most of the chest cavity. ... The liver. ... The bladder. ... The kidneys. ... The heart. ... The stomach. ... The intestines.
How many systems are there in a human body?
The nine major organ systems in the human body are the integumentary system, the musculoskeletal system, the respiratory system, the circulatory system, the digestive system, the excretory system, the nervous system, the endocrine system, and the reproductive system.
Which of the 11 organ systems is the most important in humans?
While your heart is a vital organ, the brain (and the nervous system that attaches to the brain) make up the most critical organ system in the human body. The human nervous system is responsible for coordinating every movement and action your body makes.
How do you remember the 11 body systems?
MR DICE RUNSM-Muscular.R-Respiratory.D-Digestive.I-Integumentary.C-Circulatory.E-Endocrine.R-Reproductive.U-Urinary.More items...
What are the 11 organ systems quizlet?
Terms in this set (11)Skeletal System. function: provides support and strucutre, stores calcium, minerals, fats, marrow. ... Integumentary System. function: provides protection regulates body temp, prevents water loss. ... Muscle System. ... Nervous System. ... Endocrine System. ... Circulatory System. ... Lymphatic System. ... Digestive System.More items...
Which body system is based on the function of the body part they support?
Elements of the skeletal system are adjusted to the function of the body part they support. Thus, the anatomy of bones, joints and ligaments is studied topographically, as the bones of the; head and neck, thorax, abdomen, upper and lower limbs .
Which system controls the activities of the body?
Central nervous system . The central nervous system definition is that it receives information from the body’s environment and generates instructions, thereby controlling all the activities of the human body. This two-way information flow into, and out of, the CNS is conveyed by the peripheral nervous system.
What is the digestive system?
Digestive system - anterior view. The human body is a biological machine made of body systems; groups of organs that work together to produce and sustain life. Sometimes we get lost while studying about cells and molecules and can’t see the forest for the trees.
What is the circulatory system?
They all comprise a continuous network of vessels which act to carry blood around the body. Blood leaves the heart via arteries, these progressively reduce in size to continue as smaller arterial vessels called arterioles. Arterioles end in a web of even smaller vessels called capillaries. The exchange of gases and nutrients occurs through the capillary walls.
What is the cardiovascular system?
The cardiovascular system is comprised of the heart and the circulatory system of blood vessels. The heart is composed of four chambers; two atria and two ventricles. Blood enters the heart through the upper chambers of the left and right atria and exits via the left and right ventricles.
How many circuits are there in the circulatory system?
There are three separate circuits to the circulatory system.
What are the respiratory organs?
The respiratory system consists of a series of organs; the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs ( alveoli ). The nasal cavity and pharynx are together called the upper respiratory system, while the remainder of the organs comprise the lower respiratory system.
Why is skin important to the body?
Skin is our body’s first line of defense against pathogens, harmful substances, injuries, and more. It also controls how much heat and water our body loses to the environment, allowing us to sweat. Even goosebumps are part of our skin’s regulation system; the tightening of the skin raises our fine hairs upright, trapping warm air close to our skin.
What are the functions of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system allows the body to respond to environmental changes, and to other types of survival changes, such as the need to reproduce. Some examples of messages sent by the endocrine system are: 1 Fight or flight response – When a threat appears in the environment, the adrenal glands secrete a flood of adrenaline. In response to this chemical message, the heart pumps blood faster, breathing deepens to take in more oxygen, and the nervous system sharpens perception and memory formation. Other changes also occur to make the body ready to fight or flee from a potential threat. 2 Reproductive signals – When the body is ready to reproduce, the ovaries or testes send chemical messages that influence other organs, including the brain. In the female reproductive system, preparing the uterus for pregnancy involves a complex cascade of chemical messages that repeat on a monthly cycle – the menstrual cycle. 3 Hungry or full – When the body is hungry, your stomach releases a hormone (called ghrelin) that tells the brain and other organ systems to start seeking food. When the body is full, on the other hand, another set of hormone messengers (including a hormone called leptin) are released to tell your body to stop eating.
How does the liver help the body digest food?
The liver helps the process of digestion by releasing substances that assist the stomach and intestines in breaking down food, and by breaking down toxic substances in the blood. Once the nutrients have been extracted from foods, they are distributed to the body’s cells by the circulatory system.
Why do cells die in a heart attack?
Without oxygen to fuel cellular respiration, cells begin to die within minutes. This is the primary reason that heart attacks are deadly. Although the heart is part of the circulatory system, not the respiratory system, it is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to our cells.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system consists of a number of tissues that send out chemical messages – called ‘hormones’ – to the rest of the body. Each of these messages has its own unique purpose, to which the body’s other systems respond accordingly.
How long does it take for blood to circulate?
The body’s entire blood volume takes about a minute to circulate – making this a truly high-speed expressway for distributing oxygen, nutrients, messages, and removing waste. The heart is the central pump of the circulatory system, sending blood throughout the body at very high speeds.
What are the components of the cardiovascular system?
These substances include oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. The cardiovascular system includes the heart, the blood, and the blood vessels. The cardiovascular system is a highly efficient system for moving substances around the body.
What is the function of the body?
Body Functions. Body functions are the physiological or psychological functions of body systems. The body's functions are ultimately its cells' functions. Survival is the body's most important business. Survival depends on the body's maintaining or restoring homeostasis, a state of relative constancy, of its internal environment.
When does the body perform its functions?
In general, the body performs its functions least well at both ends of life - in infancy and in old age. During childhood, body functions gradually become more and more efficient and effective. During late maturity and old age the opposite is true.
What is homeostasis in biology?
In his words, homeostasis "means a condition that may vary, but which is relatively constant.". Homeostasis depends on the body's ceaselessly carrying on many activities. Its major activities or functions are responding to changes in the body's environment, exchanging materials between the environment and cells, metabolizing foods, ...
What is the term for the chemical reactions that occur in the body?
Metabolism . Metabolism is a broad term that includes all the chemical reactions that occur in the body. One phase of metabolism is catabolism in which complex substances are broken down into simpler building blocks and energy is released.
What is the act of sensing a stimulus and responding to it?
Responsiveness or irritability is concerned with detecting changes in the internal or external environments and reacting to that change. It is the act of sensing a stimulus and responding to it.
What is the ability of muscle fibers to shorten and thus to produce movement called?
The diaphragm moves with every breath. The ability of muscle fibers to shorten and thus to produce movement is called contractility.
What is the function of the body in isolation?
All function together, in fine-tuned balance, for the well being of the individual and to maintain life. Disease such as cancer and death represent a disruption of the balance in these processes. The following are a brief description of the life process:
What are the functions of the body?
Let’s see their functions and parts. Function: The digestive system takes nutrients from the food and turns it into energy. Mouth.
What is the function of the circulatory system?
Function: The circulatory system transports blood and oxygen from the lungs to all body’s cells. Parts. Heart. The heart pumps the blood to the different parts of the body. Arteries. The arteries carry oxygenated blood to organs and cells in the body.
What organs move food into small pieces?
Parts. Mouth. The mouth chews and breaks the food down into small pieces to be digested. Teeth. The teeth chop the food into small pieces. Tongue. The tongue rolls and moves the food in the mouth. Salivary glands. The saliva moistens and lubricates the food.
What is the function of the gallbladder?
Gallbladder. The gallbladder stores and recycles excess bile.
Which organs exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen?
Alveolus. The alveolus exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen. Diaphragm. The diaphragm contracts and relaxes the thoracic cavity in order to let the air moves into and out of the lungs. Circulatory system. Function: The circulatory system transports blood and oxygen from the lungs to all body’s cells. Parts. Heart.
What part of the body prevents food from being aspirated?
Larynx. The larynx prevents food or drinks from being aspirated in the respiratory tract.
Which organ absorbs nutrients from food?
The small intestine absorbs the nutrients from the food. Pancreas. The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine. Liver. The liver processes the nutrients from the small intestine and secretes the bile for the digestive process. It also filters toxins from the blood.
How many systems are there in the human body?
The body is made up of 11 systems that work together.
Which system is responsible for transporting oxygen-rich blood to all of the body's organs and tissues?
The cardiovascular system with its heart-pump and network of arteries and veins shuttles oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to all of the body's organs and tissues. Cells throughout the body take their fill of oxygen and nutrients and dispose of carbon dioxide and waste products, which eventually flow back to the heart's right-sided chambers; then on to the lungs to exchange carbon dioxide with oxygen. Inhaled air passes through your nasal passages, throat and lung airways reaching tiny alveoli, the site of gas exchange. The newly oxygen-rich blood travels back from the lungs to the heart's left-sided chambers, where it gets pumped out at great pressure via arteries to reach the needy tissues once again. And so the cycle continues. Other organ systems, such as the endocrine and nervous system, directly and indirectly regulate the cardiovascular system.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system largely governs many processes related to reproduction and sexual maturity, as well. Advertisement. The immune system is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to attack pathogens that try to invade your body. Bacteria, parasites and fungi that may cause infection meet a system of immune soldiers, ...
What cells are immune soldiers?
Bacteria, parasites and fungi that may cause infection meet a system of immune soldiers, including T-lymphocytes, macrophages and neutrophils. With time, the immune system's B-lymphocytes can produce antibodies against a new unknown invader.
Where do fibers travel?
Fibers, undigestible material, bile and loads of bacteria travel through the large intestines and out through the colon and rectum. The kidneys filter out wastes from the blood to form urine, which flows down the ureters and enters the urinary bladder.
Which organ collects urine and releases urine when full?
The bladder collects the urine and releases when full, out through a the urethra. Both digestive and excretory systems are regulated with input from the nervous system and endocrine system, and the cardiovascular system is inextricably linked with bowel and kidney function on multiple levels.
Which system produces hormones?
The endocrine system system uses hormones, or chemical messengers across distances to effect target organs and tissues. Hormones are typically produced by a gland such as the pituitary, thyroid or gonads, and released into the bloodstream.
What is the body system?
Definition of Body Systems. We can define body systems as groups of organs and tissues that work together to perform important jobs for the body. There are some organs in our body which are part of more than one body system as they serve more than one function. Apart from these, other organs and tissues serve only one purpose in the body system.
Which system moves materials between body systems?
Also, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can all be used by our cells as sources of the energy that they need to stay alive. 3. Cardiovascular or Circulatory System. This system moves materials between body systems, including oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. It includes the heart, arteries, and veins.
What is the purpose of the digestive system?
2. Digestive System or Excretory System. This system intakes food, breaks it down into usable nutrients and excretes solid waste products. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and intestines. One of the most important purposes of food is to serve as cellular fuel.
How does the respiratory system work?
The lungs accomplish this function by passing large amounts of blood over gas exchange membranes; the body’s whole blood volume passes over these membranes about once per minute. Without oxygen to fuel cellular respiration, cells begin to die within minutes. Thus, the respiratory system is one of the body’s most important system.
What is the reproductive system?
The reproductive system is not essential to individual survival, but it is essential for the survival of the species.
What is the skeletal system of animals?
The skeletal system of animals consists of either an endoskeleton, like mammals, or an exoskeleton, seen in insects. With the help of endo and exoskeletons, the muscles attach directly to the skeleton, through tendons and other connective tissues.
What system allows the body to move on command?
7. Musculoskeletal System. It allows the body to move on command. The system of muscles throughout an organism operates to move the organism and stimulate the internal organs. There are several main types of muscles in a mammal: smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscle.
What are the body systems?
12 Body Systems. 1. Cardiovascular System. Consists of blood, heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins. Functions: Pumps blood to and from the heart to supply oxygen to the body. 2. Digestive System. Organs include mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small and large intestine, appendix and rectum.
Which system helps the body fight pathogens and maintain fluid balance?
Lymphatic system. Lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus, spleen, a secondary circulatory system that helps the body fight pathogens and maintain its fluid balance. 7. Musculoskeletal System. Muscles, Bones, Joints, Tendons and ligaments. Provides structure, support for other tissues and allows motion of the body.
What organs are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood?
Consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Function: Filters waste products from the blood and removes wastes from the blood and helps to maintain water and electrolyte balance.
Which system excretes waste products from the body?
And excretes waste products from the body. 3. Endocrine System. Produces chemical messengers and hormones into the blood, which direct the activities of different organ systems, regulate growth, development, and homeostasis.
Which organ system provides sensory information and regulates body temperature?
Organ system that includes hair, skin and the underlying structures of connective tissue, including fat, glands, and blood vessels and nails. Skin provides barrier protection between the inside of the body and the external environment. And provides sensory information and regulates body temperature.
Which system is responsible for breathing?
Respiratory System. Responsible for breathing. Parts: Lungs, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and diaphragm. Adds oxygen to the blood (and removes carbon dioxide from the blood).
What is the body's speedy, electrochemical communication system?
Brain, Nerves, Spinal Cord, the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Enables thinking, self-awareness, and emotions.
Which system controls all other organ systems?
Nervous system. This is a master system that controls all other organ systems of the body. It regulates the whole-body physiology. It comprises the brain, spinal cord, sympathetic nervous system, and also the parasympathetic nervous system. It stimulates the release of hormones when needed.
How many organ systems are there in the human body?
The human body has different organs located in various parts of the body. These organs work together to form 11 organ systems that play a vital role in body physiology.
What are the bones in the body made of?
This system consists of bones in the body. These bones are made of bone cells and cartilage cells , which are hardened. They provide the body a proper shape, frame, and support to other organs. In places, the bony compartment, like the skull and thorax, also protects the essential organs like the brain, heart, lungs.
What happens when one organ is disturbed?
If one of the organs is disturbed, then the whole function of digestion is in trouble. So these organs are perfectly interlinked and connected. In most cases, every organ in the organ system has only one specific physiologic function. But some organs may be a part of one or more organ systems.
What is the anatomical structure of the body called?
This anatomical structure is called an organ. The tissues in the organ are made up of different types of cells. A set of organs is referred to as an organ system due to its distinct physiological goals in the body.
Where does the blood flow to in the urinary system?
This is transported by the blood to the kidneys of the urinary system. There the blood flows through the glomerulus of the nephron and gets filtered to lose those wastes. The load on the kidney is reduced as other organs like the skin, lungs, and saliva also participate in the excretion of waste from the body. 11.
What system helps to absorb atmospheric oxygen from the air and supply it to the body?
The respiratory system helps to absorb the atmospheric oxygen from the air and supply it to the body.

Organization
- At all levels of the organizational scheme, there is a division of labor. Each component has its own job to perform in cooperation with others. Even a single cell, if it loses its integrity or organization, will die.
Metabolism
- Metabolism is a broad term that includes all the chemical reactions that occur in the body. One phase of metabolism is catabolism in which complex substances are broken down into simpler building blocks and energyis released.
Responsiveness
- Responsiveness or irritability is concerned with detecting changes in the internal or externalenvironments and reacting to that change. It is the act of sensing a stimulus and responding to it.
Movement
- There are many types of movement within the body. On the cellular level, molecules move from one place to another. Blood moves from one part of the body to another. The diaphragm moves with every breath. The ability of muscle fibersto shorten and thus to produce movement is called contractility.
Reproduction
- For most people, reproduction refers to the formation of a new person, the birth of a baby. In this way, life is transmitted from one generation to the next through reproduction of the organism. In a broader sense, reproduction also refers to the formation of new cells for the replacement and repair of old cells as well as for growth. This is cellular reproduction. Both are essential to the su…
Growth
- Growth refers to an increase in size either through an increase in the number of cells or through an increase in the size of each individual cell. In order for growth to occur, anabolic processes must occur at a faster ratethan catabolic processes.
Differentiation
- Differentiation is a developmental process by which unspecialized cells change into specialized cells with distinctive structural and functional characteristics. Through differentiation, cells develop into tissues and organs.
Respiration
- Respiration refers to all the processes involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the cells and the external environment. It includes ventilation, the diffusionof oxygen and carbon dioxide, and the transport of the gases in the blood. Cellular respiration deals with the cell's utilization of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide in its metabolism.
Digestion
- Digestion is the process of breaking down complex ingested foods into simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood and utilized by the body.
Excretion
- Excretion is the process that removes the waste products of digestion and metabolism from the body. It gets rid of by-products that the body is unable to use, many of which are toxicand incompatible with life. The ten life processes described above are not enough to ensure the survival of the individual. In addition to these processes, life depends on certain physical factor…