A Brief Summary on Cell Organelles
| Cell Organelles | Structure | Functions |
| Cell membrane | A double membrane composed of lipids and ... | Provides shape, protects the inner organ ... |
| Centrosomes | Composed of centrioles and found only in ... | It plays a major role in organizing the ... |
| Chloroplasts | Present only in plant cells and contains ... | Sites of photosynthesis. |
| Cytoplasm | A jelly-like substance, which consists o ... | Responsible for the cell’s metabolic act ... |
What does an organelle have to do with a cell?
Organelles have a wide range of responsibilities that include everything from generating energy for a cell to controlling the cell's growth and reproduction. Organelles are structures within a cell that perform specific functions like controlling cell growth and producing energy. Plant and animal cells can contain similar types of organelles.
What are the functions of the organs in a cell?
Cells build tissues, which form organs; and organs work together to keep the organism alive. ... Muscle cells are important for a huge range of functions, including movement, support, and internal ...
What are the parts and functions of a cell?
Inside the cell
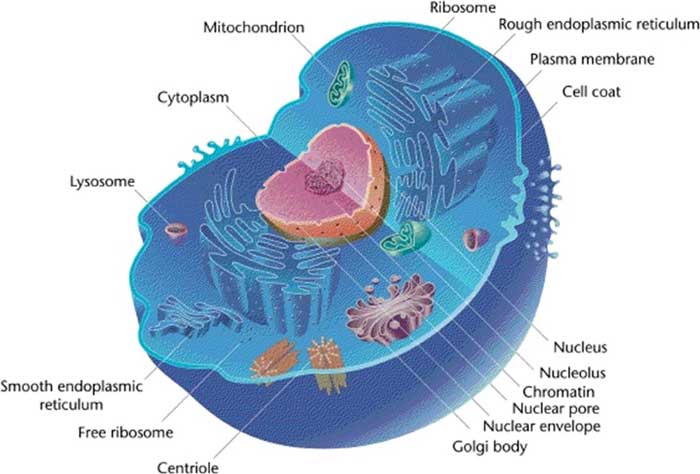
- Nucleus. The nucleus can be thought of as the cell’s headquarters. ...
- Plasma membrane. To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane.
- Cytoplasm. ...
- Lysosomes and peroxisomes. ...
- Cytoskeleton. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
- Golgi apparatus. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
- Ribosomes. ...
What are some important functions of cells?
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells are characterised by a true nucleus.
- The size of the cells ranges between 10–100 µm in diameter.
- This broad category involves plants, fungi, protozoans, and animals.
- The plasma membrane is responsible for monitoring the transport of nutrients and electrolytes in and out of the cells. ...
- They reproduce sexually as well as asexually.

What are the responsibilities of organelles?
Organelles have a wide range of responsibilities, from generating energy for a cell to controlling its growth and reproduction. From this point of view, you can also think of organelles as different teams within the factory.
What is an organelle?
What is organelle? An organelle is a tiny cellular structure that performs specific functions within a cell. You can think of organelles as a cell’s internal organs. For example, the nucleus is the cell’s brain, and the mitochondria are the cell’s hearts.
What organelle produces energy for plants?
Chloroplasts are organelles that conduct photosynthesis and produce energy for the plant cells. Chloroplasts convert the light energy of the Sun into sugars (a process called “ photosynthesis ”) that can be used by cells. At the same time, the reaction produces oxygen (O 2) and consumes carbon dioxide (CO 2 ).
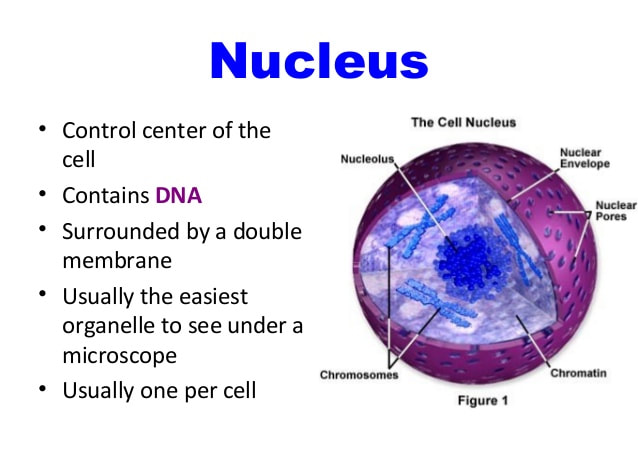
What is the nucleus?
Nucleus. The nucleus (plural: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle that stores most of our genetic information (genome). The key feature that separates eukaryotic cells (animals, plants, and fungi) from prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea) is the presence of a nucleus.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is a rod-shaped organelle that is considered the power generators of the cell. Mitochondrion performs cellular respiration, which converts glucose and oxygen to adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the biochemical energy “currency” of the cell for all activities.
Which organelle generates ATP?
Mitochondrion generates ATP like a hydraulic dam. It happens via the electron transport chain across the IMM. Mitochondria (in plant cells, chloroplasts, too) are the only organelles that have their own DNA other than the nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is circular and encoded only 13 genes.
Which organelle contains fluid?
Vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that contains a mass of fluid.
What are the functions of organelles?
Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions, destroying toxins, and responding to external signals. Organelles are considered either membranous or non-membranous.
What are non-membrane organelles?
Most non-membranous organelles are part of the cytoskeleton, the major support structure of the cell. These include: filaments, microtubules , and centrioles.
How do ribosomes synthesize proteins?
Ribosomes, either free in the cytosol or associated with rER, synthesize proteins as polypeptide chains. This occurs through the translation of RNA. Specifically, ribosomes bind to messenger RNA, abbreviated mRNA. The ribosome reads a series of nucleotide bases in groups of three called codons. The first codon read is the start codon. Each codon following the start codon represents a specific amino acid that is then brought to the ribosome by transfer RNA, abbreviated tRNA. The tRNA carrying the amino acid is bound into the A site of the ribosome. Here the amino acid is linked to the amino acid that precedes it, in the P site. The bond between two amino acids in a polypeptide chain is referred to as a peptide bond. After the peptide bond is created the ribosome translocates to the next three nucleotide bases on the mRNA strand and repeats the process until a stop codon is reached.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membranes responsible for the production of proteins, metabolism and transportation of lipids, and detoxification of poisons. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum with separate functions: smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. The presence or absence of ribosomes in the ER’s plasma membrane determines whether it is classified as smooth or rough ER.
What is the function of transport vesicles?
Transport vesicles are used to move proteins around the cell and to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic space.
What is the function of peroxisomes?
Peroxisomes are single membrane compartments that contain enzym es used to remove hydrogen atoms from substrates. The free hydrogen atoms then bind to oxygen and create hydrogen peroxide.
What is the function of a ser?
Its functions vary among cell types. For example, sER in cells of the liver have detoxifying functions while sER in cells of the endocrine system mainly produce steroid hormones. Detoxification occurs through enzymes associated with the sER membrane and usually involves adding hydroxyl groups to molecules.
Which organelle is responsible for controlling all the metabolic activity of the cell?
Cytoplasm is responsible for controlling all the metabolic activity of the cell.
What are the functional structures inside a cell?
Organelles are the functional structures contained inside the cell. Every single species is composed of cells including both single celled and multicellular organisms. Apart from providing shape and structure to an organism, the cell performs different functions in order to keep the entire system active. So, the functional structures called organelles inside the cell are responsible to keep the entire system active.
What are the organelles without membranes?
Organelles without membrane: include cell wall, ribosomes and cytoskeleton. These organelles are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What is the largest organelle in eukaryotic cells?
Nucleus is a double membraned and the largest organelle present in all eukaryotic cells. It acts as the storehouse of the cell`s DNA and functions as the control centre of the cellular activities. This round nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and is dark in colour. The nuclear membrane is a porous membrane and forms a wall between cytoplasm and nucleus. Nucleus contains tiny spherical bodies called nucleolus. It also carries other essential structure called chromosomes. Chromosomes are a thread like structures which carry other important component called gene.
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance found between cell membrane and nucleus. All the cell organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. It is composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. Cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell that is present in both plant and animal cells. Cytoplasm functions by controlling all the metabolic activities taking place within the cell and most of the chemical reactions are carried within it.
What is the cell wall of fungi?
Cell wall is a non-living structure forming the outer covering for the plasma membrane of fungi and plants. Cell wall gives shape to the cell and protects the cell from damage and infection. It also helps in cell-to-cell interaction and provides a barrier to undesirable macromolecules. The cell wall of algae is composed of cellulose, galactans, mannans and minerals like calcium carbonate. And the cell wall of plants has a composition of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin and proteins. The cell wall of young plants is capable of growth which is gradually diminished while the cell matures and then forms the secondary wall on the inner side of the cell. The middle lamella layer mainly consists of calcium pectate which holds different neighbouring cells together. The cell wall and middle lamellae may be traversed by plasmodesmata connecting the cytoplasm of neighbouring cells.
Which organelle stores food or different nutrients?
Ans. Vacuoles are the cell organelles that store food or different nutrients required for the cell.
Which organelle is responsible for locomotion?
Flagella: These are the organelles of locomotion. They are found in a few cells like protozoans and human cells sperms. Cilia:These are the organelles that help in the movement of a particle near the membrane on the outer surface. Genetic material: This compromises DNA, chromosomes which assist in cell multiplication.
Why is the cell wall important in plants?
Cell wall: Since plants are mostly non-motile, cell wall presence imparts rigidity, capacity to tolerate harsh conditions like wind, heat, wear and tear, etc. It imparts a definite shape to the cell.
What is the structure of the nucleus that extends in the cytoplasm?
Endoplasmic reticulum: This is also a sac-like structure attached to the nucleus and extends thereof like being suspended in the cytoplasm. It is of two types: rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Lysosome: Lysosomes are cell organelles found mostly bound to the cell membrane.
What are the pouches in the cell that store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates?
Vacuole: Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Where are lysosomes found?
Lysosome: Lysosomes are cell organelles found mostly bound to the cell membrane. This organelle is found in all the cells and contains hydrolytic enzymes.
Why do mitochondria multiply?
Hence mitochondria multiply within the cell even before a cell divides. This is because they are worn out during the process of respiration. So, they form new ones to carry out the function non-stop. Check for its structure Mitochondria structure.
Which layer of the cell is a lipid bilayer?
It is a lipid bilayer that encloses the entire cell and its organelles. It is a selectively permeable, flexible layer of the cell. It is one of the largest organelles in a cell structure. Mitochondria: These are sac-like organelles inside the cells. They have their own single-stranded DNA.
What is the function of cell organelles?
A cell having following Structure and Function of cell Organelles. 1.Cell Membrane- Cell membrane enclose the cell and regulates the in and out flow of substance. It is also known as plasma membrane which form the covering of animal cell. It is elastic, living, double layer and permeable membrane.
What is the most important organelle in a cell?
Nucleus- It is the most important organelle of a cell and usually lies in the center. It may lie in the periphery. Its basic function is cell division and multiplication. The nucleus has a double layered covering called nuclear membrane.
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Function- Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum helps in synthesizes and transports lipids and steroids. Some kinds of smooth E. R transport proteins from the rough E. R. And still other kinds break down energy rich glycogen and fats. Function- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) helps in the distribution of material.
What is the structure of ribosomes?
Ribosome- Discovered by Palade. Small granules like structure found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or in Free State. It is made up of ribonucleic acid (RNA).
What is the function of a cell?
A cell is a structural and functional unit of life. A microscope is required to study cell structure. Scientist Robert Hook First studied the cell structure in the year 1665 using a self designed microscope. A cell having following Structure and Function of cell Organelles.#N#Major Cell organelles are as follows#N#1.Cell Membrane- Cell membrane enclose the cell and regulates the in and out flow of substance. It is also known as plasma membrane which form the covering of animal cell. It is elastic, living, double layer and permeable membrane. It is made up of protein and lipid molecules.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Function- it helps in intercellular digestion. The enzyme found in lysosomes may digest the entire ell. Therefore lysosomes also known as the “suicide bags “ of a cell.
What is the outer layer of a plant cell?
2. Cell Wall – The outer layer in the plant cell is called cell wall. The cell wall lies outside the plasma membrane. The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose and chitin. Cellulose is a complex substance and provides structural strength to plant.
Which organelle has a membrane?
The simple answer here is that all of these organelles have a membrane, except for ribosomes. Nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cells as a whole have transmembrane proteins spanning the lipid bilayer, which can be used for transport or other purposes. Ribosomes are mostly comprised of rRNA and do not have membranes; thus, they will not bear transmembrane proteins.
Which organelle is involved in cellular respiration?
The mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles involved in the process of cellular respiration. Specifically, the Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and the electron transport chain takes place along the inner mitochondrial membrane. During aerobic respiration, oxygen is used as the final electron receptor of the electron transport chain and generates water as a byproduct. Without oxygen, the mitochondria cannot perform oxidative phosphorylation, and the cell must rely on glycolysis for energy.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for recognizing proteins based on their signal sequences and sending concentrations of similar proteins to various parts of the cell. It can also deliver proteins out of the cell using secretory vesicles. The membrane sacs of the Golgi apparatus are constantly used and regenerated to create vesicles of packaged proteins.
What is the function of the lysosome?
The lysosome is an organelle that is used to digest broken cellular machinery or foreign particles. It maintains an acidic environment inside by pumping hydrogen ions in, not out. This environment helps denature the things it needs to digest, and is the most effective pH for the digestive enzymes that are inside.
Where does cellular respiration occur?
Cellular respiration primarily occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane with the aid of membrane proteins. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis occur in the cytoplasm and are facilitated by proteins. Lipids are mostly stored in bones and adipose tissue. These processes do not require intervention from the cytoskeleton or microtubules that compose the centrioles.
How many organelles are there in an animal cell?
The animal cell has 13 different types of organelles ¹ with specialized functions. Below you can find a list will all of them ( animal cell organelles and their functions) with and image/diagram to help you visualize where they are and how they look within the cell. 2. ORGANELLES OF THE ANIMAL CELL AND THEIR FUNCTION.
Which organelle produces energy for the cell called ATP?
Mitochondria: Produces energy for the cell called ATP. Vacuole: Protection of the cell, collect waste products and maintain internal pH, among others. (*) Only in some animal cells. Lysosome: Cellular digestion.
What separates the cell from its environment?
Cell membrane: separates the cell from its environment; regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the function of a cell structure?
A cell structure that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell or for storage inside the cell.
Which organelle is responsible for producing energy?
Mitochondrion. An organelle containing enzymes responsible for producing energy. (Metabolism/respiration) Chloroplast. An organelle found in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy (photosynthesis). Cytoskeleton.
What is the cell wall?
Cell Wall. The structure outside of the cell membrane that is used to provide support and protection. Present in plants, algae, fungi, and many prokaryotes. Centriole. A cellular structure in an animal cell that helps to organize cell division. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... Cell Organelle Functions. 17 terms.
What is the hair-like projection on the cell surface that allows a cell to move?
Cilia. Hair-like projections on the cell surface usestructuresmotion or the movement of fluid over a cell. Flagellum. Most often a single whip-like projection on the cell surface that allows a cell to move.
Which cell structure forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the?
Ribosome. A small particle in the cell that can make proteins. Endoplasmic Reticulum. A cell structure that forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another. Golgi Apparatus.
What is the fluid between the cell membrane and the nucleus?
Cytoplasm. Fluid between the cell membrane and the nucleus. helps protect organelles. Nucleus. A part of the cell containing hereditary information and is responsible for growth and reproduction; the "command center" of the cell. Ribosome.