Six Main Cell Functions
- Provide Structure and Support Like a classroom is made of bricks, every organism is made of cells. ...
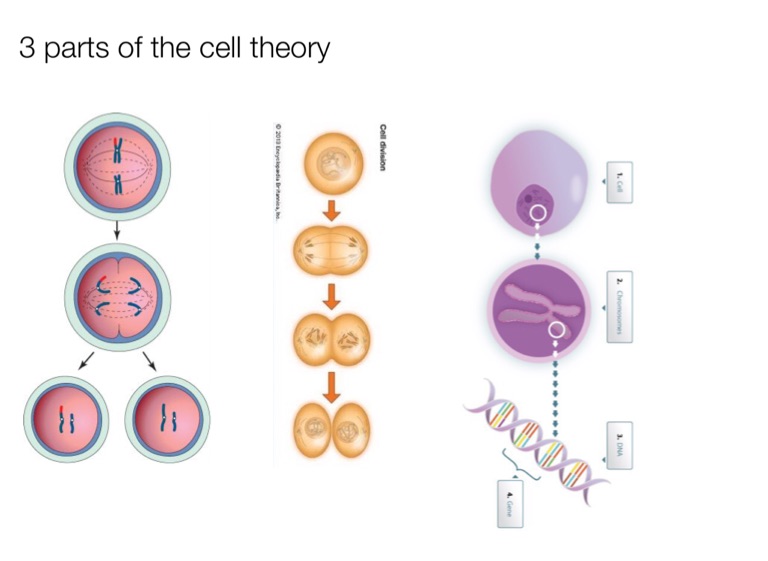
- Facilitate Growth Through Mitosis In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. ...
- Allow Passive and Active Transport Cells import nutrients to use in the various chemical processes that go on inside them. ...
- Produce Energy ...
- Create Metabolic Reactions ...
- Aids in Reproduction ...
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | DNA Storage |
| Mitochondrion | Energy production |
| Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) | Lipid production; Detoxification |
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) | Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell |
What are the cellular components called?
The cellular components are called cell organelles. These cell organelles include both membrane and non-membrane bound organelles, present within the cells and are distinct in their structures and functions. They coordinate and function efficiently for the normal functioning of the cell.
What is the function of the structure of a cell?
The various structures and organelles in a cell float in a liquid called the cytoplasm. Cells provide six main functions. They provide structure and support, facilitate growth through mitosis, allow passive and active transport, produce energy, create metabolic reactions and aid in reproduction.
What are the functions of cell organelles?
The cells provide shape, structure and carries out different types of functions to keep the entire system active. The cell contains different functional structures which are collectively called Organelles, and they are involved in various cellular functions. Let us learn more in detail about the different types and functions of Cell Organelles.
What are the parts of animal cell and their functions?
Animal Cell Parts And Their Functions 1 The Nucleus. ... 2 Ribosomes. ... 3 Mitochondria. ... 4 Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes inside a cell, and its main functions are to process and transport new materials. 5 Golgi Apparatus. ... 6 Lysosomes. ... 7 Cytoplasm. ... More items...
Who discovered the Golgi Apparatus?
Golgi Apparatus was discovered in 1898 by Camillo Golgi.
Who discovered Nucleus?
Robert Brown was responsible for discovering the nucleus of a cell in 1831
Who discovered Plastids?
The term, “Plastid” was first coined by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
Who discovered Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Endoplasmic Reticulum was discovered by Keith R. Porter in 1954.
Why is Cell Membrane called selectively permeable?
It allows the transport of selective substances into and out of the cell, but not all substances. This is why it is known as ‘selectively permeable’.
1. Cell membrane (Plasma membrane)
It is made of proteins and lipids. The fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicholson (1972). The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components —including phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates—that gives the membrane a fluid character.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum
Discovered by Keith R. Porter in 1954. It is absent in Human RBCs, Blue-Green Algae, Bacteria.
4. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm of a cell, and also on the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
5. Golgi Apparatus
Its function is to store and transport proteins & lipids that have been synthesized.
10. Nucleus
Robert Brown was responsible for discovering the nucleus of a cell in 1831
What is the power house of the cell?
It is termed as the power house of the Cell. Plays an major part in the terminal stages of Aerobic Respiration. Synthesizes ATP – hence called the power house of cell as ATP is the primary source of Energy. Manufactures Polysaccharides.
Which membrane serves as a transport channel for DNA and RNA?
Nuclear Membrane : Pores in the membrane serve as Transport Channels Site of Synthesis of RNA and DNA
Why do cells have special structures?
Because some cells perform specific functions, they have special modified structures. For example, red blood cells are the oxygen carriers in the body. They lack a nucleus to make more space for ...
How do cells get nutrients?
Cells import nutrients to use in the various chemical processes that go on inside them. These processes produce waste which a cell needs to get rid of. Small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and ethanol get across the cell membrane through the process of simple diffusion.
What is the goal of sciencing?
Our goal is to make science relevant and fun for everyone. Whether you need help solving quadratic equations, inspiration for the upcoming science fair or the latest update on a major storm, Sciencing is here to help.
How do cells grow in mitosis?
Facilitate Growth Through Mitosis. In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. This takes place through the process of mitosis in which the parent cell breaks down to form two daughter cells identical to it.
Why is reproduction important?
Reproduction is vital for the survival of a species. A cell helps in reproduction through the processes of mitosis(in more evolved organisms) and meiosis. In mitosis cells simply divide to form new cells. This is termed asexual reproduction.
How many organ systems are there in the human body?
Five Major Organ Systems of the Body
How do plants get energy?
For these reactions, cells require energy. Most plants get this energy through the process of photosynthesis, whereas animals get their energy through a mechanism called respiration.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. The study of cells from its basic structure to the functions of every cell organelle is called Cell Biology. Robert Hooke was the first Biologist who discovered cells.
Why are cells considered the structural and functional unit of life?
Meiosis causes the daughter cells to be genetically different from the parent cells. Thus, we can understand why cells are known as the structural and functional unit of life. This is because they are responsible for providing structure to the organisms and performs several functions necessary for carrying out life’s processes.
How is the cell interior organized?
The cell interior is organised into different individual organelles surrounded by a separate membrane.
Why is the discovery of cells important?
Discovery of cells is one of the remarkable advancements in the field of science. It helps us know that all the organisms are made up of cells, and these cells help in carrying out various life processes. The structure and functions of cells helped us to understand life in a better way.
What are the building blocks of life?
Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life . Each cell contains a fluid called the cytoplasm, which is enclosed by a membrane.
How big are cells?
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. They range in size from 0.0001 mm to nearly 150 mm across
Which cell type has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are characterised by a true nucleus.
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is also termed as a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances, found between the cell membrane and nucleus. They are mainly composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell. There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell as they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in several organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, sausage-shaped organelle, found in almost all eukaryotic cells.
Plastids
Plastids are large, membrane-bound organelles which contain pigments. Based on the type of pigments, plastids are of three types:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein.
