
Explore
The outer ear. The outer ear is the external part of the ear. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and to direct them into the ear. Important parts of the outer ear are the pinna, the ear canal and the ear drum. Read more about the anatomy, the outer ear parts and the function of the outer ear.
What does your outer ear do?
- Transmit and transduce sound to the brain
- Maintain body balancing
- Act as a barrier which covers the internal sensitive structure
- Produces ear wax which acts as a lubricant and saves the inner ear from damages and bacterial infection.
What other function does the ear perform?
outer ear :the basic function is to concentrate and funnel sound waves to the eardrum middle ear :contains the ossicles which is responsible for the amplification of sound waves :contains small bones named for their shape- hammer, anvil, and stirrup inner ear :contains the cochlea- long coiled tube lined with sensory receptor hair cells
What is the basic function of the outer ear psychology?
How the Ear Functions . Home » How the Ear Functions. All vertebrates use the ear in the same way: to magnify waves of sound by transforming the waves into signals that the brain interprets. As a result, you are able to hear everything around you, from birds chirping to the voices of friends and family.
How exactly does the ear function?

What are the functions of the outer and inner ear?
While the external and middle ears are mainly concerned with the transmission of sound, the inner ear contains the cochlea – often called the organ of hearing – and also houses the body's organ of balance.
What is the function of the outer ear quizlet?
Responsible for gathering sounds from the acoustical environment and funneling them into the auditory mechanism.
What is function of middle ear?
The primary function of the middle ear is to offset the decrease in acoustic energy that would occur if the low impedance ear canal air directly contacted the high-impedance cochlear fluid.
What are three main functions of the external ear quizlet?
Terms in this set (44)Collects sound waves.Directs sound to the tympanic membrane.Converts compressed air pressure to vibration.
What is the outer part of the ear is called?
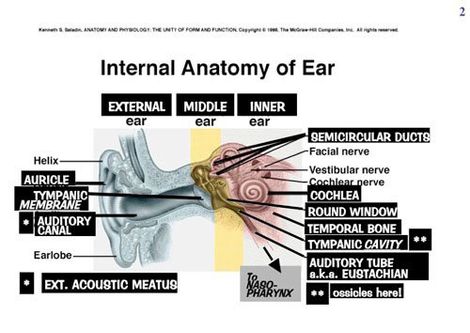
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The parts of the ear include: External or outer ear, consisting of: Pinna or auricle. This is the outside part of the ear.
What are the 3 parts of the ear?
Parts of the EarOuter Ear. The outer ear is made up of three parts; ... Middle Ear. The middle ear is made up of the eardrum and three small bones (ossicles) that send the movement of the eardrum to the inner ear.Inner Ear. The inner ear is made up of: ... The ear (auditory) Nerve.
What are the two 2 main functions of middle ear?
The main function of the middle ear is to carry sound waves from the outer ear to the inner ear, which contains the cochlea and where sound input can be communicated to the brain. Sound waves are funneled into the outer ear and strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate.
Is also known as the outer ear quizlet?
The pinna is the outer part of the outer ear. It is the most visible portion of the ear and acts like an antenna to pick up sound.
Is the eardrum part of the outer ear?
The outer ear includes: auricle (cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head) auditory canal (also called the ear canal) eardrum outer layer (also called the tympanic membrane)
Which tissue is located inside of the outer portion of the ear quizlet?
-The outer ear consists of the pinna, or auricle, and the ear canal (external auditory meatus). The pinna - the part of the "ear" that we see on each side of our heads - is made of cartilage and soft tissue so that it keeps a particular shape but is also flexible.
How does the ear work?
The outer ear is divided into several sections, but they all work together toward one purpose: The helix, antihelix, superior and inferior crus, the tragus and antitragus, the concha, and the external acoustic meatus all work together to funnel and direct sound waves from the world around you to the inner parts of your ears. Sound waves are carried from the outer ear and ear canal to the tympanic membrane, where vibrations are sent through the middle and inner ears and become electrical impulses (sound signals). These signals then give your brain information about both sound and the direction and balance of your body.
Where is the outer ear located?
Location. The outer ear lies directly next to the middle ear. Though mostly made of cartilage and skin, the outer ear arises from the temporal bone. Located on either side of the head, the ears are found directly over the temporal lobe of the brain.
What causes earwax buildup?
Cerumen impaction: Various skin cells and glands in the ear canal secrete waxy substances that protect the canal, but can also cause a buildup of earwax, or cerumen. Normally, cerumen can be removed as it builds, but in some cases it builds to the point that it obstructs the ear canal or eardrum.
What part of the ear is the most important for hearing?
The outer ear is the part of the ear that you can see and where sound waves enter the ear before traveling to the inner ear and brain. While the outer ear may not be as complex as its counterparts, it serves a vital function in your sense of hearing. AndreiDavid / Getty Images.
Which part of the ear is not supported by cartilage?
Tragus and antitragus: These two cartilage prominences border the concha at the top and bottom. Lobule: The lobule is the bottom-most part of the ear, often called the earlobe. It is the only part of the outer ear that is not supported by cartilage.
What nerves run through the ear?
The skin of the ear canal is thin and very sensitive, and branches of the facial and vagus nerves run under portions of the ear canal and other parts of the outer ear. 2 Other cranial nerves run through the ear as well, but have little to no known function. 3 . Hearing Loss and Deafness.
What is the ear canal called?
External acoustic meatus: This inch-long section is sometimes called the ear canal, and serves as the bridge between the outer and middle ear. It’s a hollow tube that curves slightly downward as it moves into the ear toward the tympanic membrane, or eardrum.
What is the outer ear?
The outer ear contains the ear canal, as well as several other major parts: 2 . Auricle: The outwardly visible part of the ear, this blend of skin and cartilage attaches to the skull. It has an outer (lateral) aspect as well as an inner (medial) one.
Where are the ears located?
Essential organs of human hearing and balance, the ears are located on either side of the head, at the level of the nose. Separated into an inner, middle, and outer ear, each ear is an intricate and complicated mixture of bones, nerves, and muscles. Naturally, these structures are at the heart of hearing loss problems as well as those affecting ...
Why does my ear ring?
Tinnitus: This persistent ringing in the ear can be subjective—likely occurring due to abnormal activity in the auditory nerve of the brain—or objective, in which a muscle spasm or other process in the middle ear is the cause . Tinnitus may be the result of age-related hearing loss, overexposure to loud noises, physical injury, Meniere’s disease (see below), or neurological disorders. Treatment may include correcting the hearing loss with hearing aids, modifying lifestyle, or cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
Why does my ear look buried?
Cryptotia: Due to malformation of ear cartilage, this variant gives off the appearance that the upper portion of the ear is buried inside the head.
What are the three parts of the ear?
In the broadest terms, the ear is divided into three portions: the outer ear (which includes the visible outer portion, as well as the ear canal), the middle ear, and the inner ear, representing the portion deepest in the skull. Each of these sections has a number of components. The outer ear contains the ear canal, ...
Which bone connects with the incus?
Stapes (stirrup): The last of these bones connects with the incus on the side via the incudostapedial joint, while, in its middle, it accesses the oval window as part of the mechanism that carries sound to the inner ear. This bone also has a head, which connects with the lenticular process, as well as two limbs that attach to the oval base, which connect with the oval window.
How is hearing loss tested?
Speech testing: Hearing loss can also be tested by having patients repeat certain words or phrases played at specific volumes.
Auricle
The Auricle (also known as the pinna) is the visible part of the ear. In fact, it is the only visible part of the whole ear system. The Auricle can typically be found on either side of the human head. Most humans have two Auricles.
Ear Canal
The Ear Canal (also known as the auditory canal) has one simple job. It has evolved to channel the soundwaves that have been collected by the Auricle through the eardrum and into the inner ear.
Eardrum
The Eardrum (also known as the tympanic membrane) is the most sensitive part of the outer ear. It is a membrane that can be found at the end of the ear canal. Once the sound passes through the eardrum it enters the middle ear.
What is the color of the outer ear?
Brown is outer ear. Red is middle ear. Purple is inner ear. The auricula. Lateral surface. The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal . It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum ( tympanic membrane ).
What is the visible part of the ear called?
The visible part is called the auricle, also known as the pinna, especially in other animals. It is composed of a thin plate of yellow elastic cartilage, covered with integument, and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles; and to the commencement of the ear canal by fibrous tissue.
What is the name of the disorder that characterizes the auditory canal?
Treacher Collins syndrome, characterised by dysplasia of the auricle, atresia of the bony part of the auditory canal, hypoplasia of the auditory ossicles and tympanic cavity, and 'mixed' deafness (both sensorineural and conductive), inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
What are the causes of external ear malformations?
Clinical significance. Malformations of the external ear can be a consequence of hereditary disease, or exposure to environmental factors such as radiation , infection. Such defects include: A preauricular fistula, which is a long narrow tube, usually near the tragus.
Why is the outer ear so sensitive to frequencies?
One consequence of the configuration of the outer ear is selectively to boost the sound pressure 30- to 100-fold for frequencies around 3 kHz. This amplification makes humans most sensitive to frequencies in this range — and also explains why they are particularly prone to acoustical injury and hearing loss near this frequency. Most human speech sounds are also distributed in the bandwidth around 3 kHz.
Where do sound waves travel from the pinna to the ear?
From the pinna, the sound waves move into the ear canal (also known as the external acoustic meatus) a simple tube running through to the middle ear. This tube leads inward from the bottom of the auricula and conducts the vibrations to the tympanic cavity and amplifies frequencies in the range 3 kHz to 12 kHz.
Can hearing aids prevent hearing loss?
If malformations are accompanied by hearing loss amenable to correction, then the early use of hearing aids may prevent complete hearing loss.
What is the outer ear?
This structure helps to give each of us our unique appearance. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna.
What are the three bones in the middle ear?
Three of the smallest bones of the body are found in the middle ear; they are called the malleus, the incus and the stapes . These bones are also known as the hammer, anvil and the stirrup. The medical term for all three bones together is the middle ear ossicles.
What is the ear drum?
The medical term for the ear drum is the tympanic membrane. The ear drum is a transparent gray membrane. Attached to the center part of the drum is the middle ear bone (the malleus). The space inside the ear drum is called the middle ear.
Where does the ear canal start?
The ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The canal is approximately an inch in length. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure. Under the skin the outer one third of the canal is cartilage and inner two thirds is bone. EAR DRUM.
What is the outer ear called?
It is also sometimes referred to as the auricle or the pinna. Although the outer ear is the least important part of the ear’s hearing function, it provides the necessary structure and protection. Its dish-like shape is also essential for collecting sound waves. This sound collection is the primary purpose of all of the parts ...
What is the human ear?
Ear Anatomy. The human ear is the highly advanced result of millions of years of evolutionary progress. Everyone knows that the ear is the organ used for hearing, but not many people are aware that it’s also necessary for balance. Most people also consider the ear just one part of the human body, but it’s a complex organ composed of many smaller, ...
What Are the 7 Main Parts of an Ear?
The ear can be further analyzed by seven content components, divided into the three ear categories listed above.
What Are the 6 Ear Bones?
Each ear contains three ossicles, or bones, in the middle ear: the malleus incus stapes. These ossicles transmit sound signals from the outer ear to the inner ear.
How to treat middle ear pressure imbalance?
This middle ear pressure imbalance can usually be alleviated by yawning or working the jaw, which exercises the mastoid bone and opens the eustachian tube. COVID 19 can occasionally enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. If you have been exposed to COVID 19, seek appropriate treatment or services.
What is the name of the two forks on the top of the ear called?
It is more rigid and provides more strength to the outer ear. It looks somewhat Y-shaped, and the two forks at the top of the ‘Y’ are called the superior crus and the inferior crus.
Where is the tympanic cavity?
The tympanic cavity is the small space in the middle ear between the tympanic membrane ear drum and the inner ear hearing organ. This space holds the ossicles and the Eustachian Tube. Ear infections can occur in the tympanic cavity.
What is the outer ear?
The outer ear includes: auricle (cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head) auditory canal (also called the ear canal) eardrum outer layer (also called the tympanic membrane) The outer part of the ear collects sound.
What are the parts of the inner ear?
The inner ear includes: 1 oval window - connects the middle ear with the inner ear 2 semicircular ducts - filled with fluid; attached to cochlea and nerves; send information on balance and head position to the brain 3 cochlea - spiral-shaped organ of hearing; transforms sound into signals that get sent to the brain 4 auditory tube - drains fluid from the middle ear into the throat behind the nose
What is the middle ear?
The middle ear includes: eardrum. cavity (also called the tympanic cavity) ossicles (3 tiny bones that are attached) malleus (or hammer) - long handle attached to the eardrum. incus (or anvil) - the bridge bone between the malleus and the stapes. stapes (or stirrup) - the footplate; the smallest bone in the body.
Why do children have ear infections?
Children are more likely to have ear infections like otitis media that come from bacteria or viruses than adults because of their developing ear anatomy. The middle ear is connected to the back of the nose by the auditory tube (also called the eustachian tube) and its location allows easier access to germs. This may lead to a buildup of fluid and pressure, painful infections, and even hearing loss. Infections in children can affect early speech and language development.
Why do people lose their hearing?
There are diseases, infections and cancers that affect specific parts of the ear and can lead to hearing loss in children and adults.
Where does sound travel?
Sound travels through the auricle and the auditory canal, a short tube that ends at the eardrum. Sound entering the outer ear travels through the middle ear and causes the eardrum and ossicles in the middle ear to vibrate. As it travels, it amplifies (gets louder) and changes from air to liquid.
How do the brain and auditory system work together?
The brain and auditory system work together to control how we hear and how we balance ourselves. The human ear is a complex organ and many scientists consider hearing to be the most complex of the human senses.
Overview
Structure
- The outer ear is divided into several sections, but they all work together toward one purpose: The helix, antihelix, superior and inferior crus, the tragus and antitragus, the concha, and the external acoustic meatus all work together to funnel and direct sound waves from the world around you to the inner parts of your ears. Sound waves are carried...
Function
Clinical significance
Additional images
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
See also
The visible part is called the auricle, also known as the pinna, especially in other animals. It is composed of a thin plate of yellow elastic cartilage, covered with integument, and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles; and to the commencement of the ear canal by fibrous tissue. Many mammals can move the pinna (with the auriculares muscles) in order to focus their hearing in a certain direction in much the same way that they can turn their eyes. Most hum…