
Sympathetic Nervous System Functions
- Fight or Flight Responses. When the entire SNS is activated, there is a cascade of reactions from all the organ systems of the body, which prepare the individual to deal ...
- Regulating Body Temperature. The SNS has a number of roles to maintain homeostasis. ...
- Cardiovascular Effects. ...
- General Effects. ...
What are the four main function of nervous system?
The four main functions of the nervous system are:
- Control of body’s internal environment to maintain ‘homeostasis’ An example of this is the regulation of body temperature.
- Programming of spinal cord reflexes. An example of this is the stretch reflex.
- Memory and learning.
- Voluntary control of movement.
What is the purpose of sympathetic nerves?
What is the purpose or function of the sympathetic nervous system quizlet? Its general function is to control homeostasis and the body's rest-and-digest response. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS). Its general action is to mobilize the body's fight-or-flight response.
How to stimulate your parasympathetic nervous system?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Making Lifestyle Changes Download Article
- Spend time relaxing in nature. Being in nature triggers your body’s calming response, so go outside!
- Use mindfulness instead of multitasking. Mindfulness means being focused on the present, and it can help activate your parasympathetic nervous system.
- Meditate on a calming word for 10 to 30 minutes daily. ...
What are nervous tissues and their functions?
Tissue types
- Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and molecules.
- Connective tissue underlies and supports other tissue types.
- Muscle tissue contracts to initiate movement in the body.
- Nervous tissue transmits and integrates information through the central and peripheral nervous systems.

What are the 5 functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
The main functions of the sympathetic nervous system are to dilate blood vessels, increase blood pressure, contract muscles, secrete sweat from sweat glands, dilate bronchi for more oxygen exchange and contraction of heart which helps the body prepare to face emergency situations.
What are the two functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
sympathetic nervous system, division of the nervous system that functions to produce localized adjustments (such as sweating as a response to an increase in temperature) and reflex adjustments of the cardiovascular system.
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system quizlet?
The sympathetic nervous system arouses the body and expends energy. It is responsible for our fight and flight response. The parasympathetic nervous system calms the body and conserves energy. It is responsible for our rest and digest response.
What are the functions of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic system controls “fight-or-flight” responses. In other words, this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity. The events that we would expect to occur within the body to allow this to happen do, in fact, occur. The parasympathetic system regulates “rest and digest” functions.
Which of the following is an action of the sympathetic nervous system?
eg, the sympathetic nervous system can accelerate heart rate, widen bronchial passages, decrease motility (movement) of the large intestine, constrict blood vessels, cause pupil dilation, activate goose bumps, start sweating and raise blood pressure.
What are the main components of sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic pathway can be divided into three following components: The preganglionic neurons, The sympathetic ganglia, The postganglionic neurons.
Which action is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system quizlet?
Sympathetic nervous system - stimulates the organ to increase its activity. It promotes the fight-or-flight response, which prepares the body for emergency situations.
What are the functions of parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system predominates in quiet “rest and digest” conditions while the sympathetic nervous system drives the “fight or flight” response in stressful situations. The main purpose of the PNS is to conserve energy to be used later and to regulate bodily functions like digestion and urination.
What happens when the sympathetic nervous system is activated quizlet?
When the Sympathetic Nervous System is triggered, glycogen is broken down to glucose to provide more energy. The Parasympathetic Nervous System is triggered to act by exposure to epinephrine.
Which is not a function of sympathetic nervous system?
Which among the following is not a function of Sympathetic nerves in Autonomic nervous system? Notes: contract urinary bladder is a function of Parasympathetic nerves.
What is the major difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems quizlet?
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
What nerves are in the sympathetic nervous system?
OrganizationOrganNervesSpinal column originpancreatic headPS: vagus nerves S: thoracic splanchnic nervesT8, T9appendixnerves to superior mesenteric plexusT10kidneys and uretersPS: vagus nerve S: thoracic and lumbar splanchnic nervesT11, T126 more rows
What are the types of sympathetic nervous system?
Structure. There are two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the sympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic.
What controls the sympathetic nervous system?
The hypothalamus is the key brain site for central control of the autonomic nervous system, and the paraventricular nucleus is the key hypothalamic site for this control.
What is the primary function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Your parasympathetic nervous system is a network of nerves that relaxes your body after periods of stress or danger. It also helps run life-sustaining processes, like digestion, during times when you feel safe and relaxed.
Which is not a function of sympathetic nervous system?
Which among the following is not a function of Sympathetic nerves in Autonomic nervous system? Notes: contract urinary bladder is a function of Parasympathetic nerves.
How does the sympathetic nervous system work?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system work in very close association, with contrasting, yet tightly coordinated effects. The sympathetic system is involved in energy-expending (catabolism), enabling the body to use energy appropriately to respond to stressful situations and emergencies, as in the “fight or flight” response. Activation of the sympathetic system results in pupil dilation, piloerection, vasoconstriction of cutaneous blood vessels, sweating, release of adrenaline, bronchodilation, increased cardiac contraction and reduced digestion.
Why is the sympathetic system important?
While the sympathetic system is also important at rest, it is essential for preparing us for emergencies, in other words, for “fight-or-flight” responses.
How do preganglionic fibers enter the sympathetic trunk?
In general, after passing briefly through the anterior rami, preganglionic fibers enter the sympathetic trunk via white rami communicantes. Inside the trunk, preganglionic fibers can follow one of four courses: 1. Ascend and synapse in a higher paravertebral ganglion.
What is the thoracolumbar division of the autonomic nervous system?
Definition. Thoracolumbar division of the autonomic nervous system which is in charge to initiate bodily stress response (“flight or fight”) Preganglionic neurons. Neurons of the intermediolateral column of the spinal cord, found within the levels T1-T12 and L1-L3. Preganglionic fibers.
Which nerves carry sympathetic innervation to the head, neck, upper limbs and thorax?
The axons of the ganglionic neurons that leave the ganglia in the form of gray rami communicantes which join the rami of the spinal nerves. - Spinal nerves C2-C8 carry sympathetic innervation to head, neck, upper limbs and thorax.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system can be divided structurally or functionally, as follows: Structurally, the nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) . The CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord , while the PNS consists of all the neural tissues outside the CNS.
How long does it take to read a sympathetic nervous system?
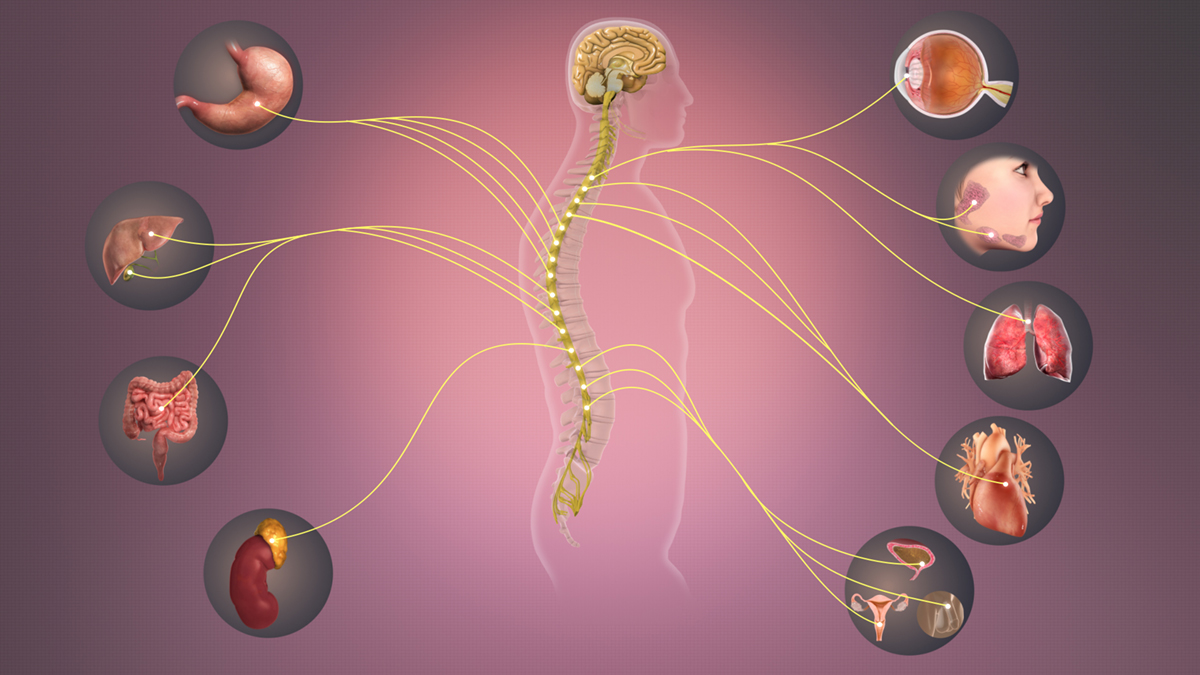
Reading time: 16 minutes. Sympathetic nervous system (diagram) The autonomic system is made up of two divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. They usually work antagonistically in the organs, but in a well integrated manner.
What are the functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system typically functions in actions requiring quick responses. Increase heart rate. Dilation of the pupils. Secretion of sweat glands. Dilated muscles. Increased alertness. Slowing down or stopping digestion. Relaxation of the bladder.
Which branch of the nervous system stimulates digestion and the urinary system when relaxed?
The parasympathetic branch however stimulates digestion and the urinary system when relaxed, whereas the SNS slows them down as these processes are not required during times of heightened stress.
How does the SNS maintain homeostasis?
The SNS can maintain homeostasis through actions such as sweating to cool down the body or in regulating heart rate. In contrast to the parasympathetic nervous system, which slows down physiological processes, the SNS typically stimulates organs.
Why is the SNS important?
In this situation, the SNS would trigger responses such as causing the eyes to dilate and the heart to beat faster. These autonomic responses to a threatening situation are therefore essential for survival. In evolutionary terms, the SNS would have been used in order to fight or escape prey and for hunting to eat and survive.
Why do people have autonomic dysfunction?
As their organs are not receiving signals to fight-or-flight, this may result in being under-prepared in these situations, due to lack of blood being pumped around the body or pupils not dilating . Autonomic dysfunction is a condition whereby the autonomic nervous system and its divisions do not work properly.
How does the SNS regulate body temperature?
Regulating Body Temperature. For homeostasis to be achieved, the SNS can control the body temperature of organisms through the use of fat reserves in the body. The SNS uses these reserves to increase the production of heat and through changing the flow of blood to the skin.
Why do we use the SNS?
In evolutionary terms, the SNS would have been used in order to fight or escape prey and for hunting to eat and survive. More modern-day stressors can also stimulate the SNS such as financial pressures, stresses at work, or anything that can cause high anxiety for individuals.
What is the function of the sympathetic nervous system?
They can depend on whether it is activated in a localized manner or across the body. The SNS can maintain homeostasis through actions like sweating to dissipate heat , or by altering cardiac output based on position and activity level.
Why is the sympathetic nervous system important?
This allows organisms the ability to activate many different responses at once , leading to a coordinated flight or fight response. This is important because a slow or ineffective response can lead to the death ...
What is sympathetic innervation?
Sympathetic Innervation. Acetylcholine is taken up by receptors on postsynaptic neurons. The activation of postsynaptic neurons leads to the transmission of an electrochemical impulse along the length of their axons until there is a release of noradrenaline at the synapses with peripheral tissues.
What is the difference between the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system?
By contrast, the parasympathetic system controls actions related to feeding and breeding.
What is the effect of sympathetic nervous system on heart failure?
During extreme conditions, like a blockage in the coronary artery leading to heart failure, the sympathetic nervous system can have a counterproductive effect, increasing the force of cardiac muscle contraction, and mediating higher blood pressure through vasoconstriction in peripheral blood vessels.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic Nervous System Overview. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) mediates actions that occur without voluntary control such as heart rate or blood pressure. It consists of both the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous systems (PNS), and they often act in a complementary manner. In general, the sympathetic nervous ...
Which endocrine receptors are stimulated to secrete epinephrine and norepin?
Among the key endocrine targets for the SNS is the adrenal medulla, which is stimulated to secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine, to enhance the effect of the neuronal activity of the SNS. In fact, presynaptic neurons directly synapse with cells in the adrenal gland, making it functionally similar to postsynaptic neurons of the SNS. During extreme conditions, like a blockage in the coronary artery leading to heart failure, the sympathetic nervous system can have a counterproductive effect, increasing the force of cardiac muscle contraction, and mediating higher blood pressure through vasoconstriction in peripheral blood vessels.
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System?
It is fairly simple to define sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system deals with helping the body rapidly respond to danger, stress, and perceived threats. Early humans relied heavily on the sympathetic nervous system to flee dangerous animals lurking in the environment.
Sympathetic Nervous System Function
Which function does the sympathetic nervous system affect? The overall sympathetic nervous system function is to evade perceived threats. This includes mental and emotional threats, also known as stress. At the sign of stress or danger, the brain sends signals to the rest of the body, including the adrenal gland to produce and release two hormones:
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
sympathetic nervous system, division of the nervous systemthat functions to produce localized adjustments (such as sweating as a response to an increase in temperature) and reflex adjustments of the cardiovascular system. Under conditions of stress, the entire sympathetic nervous system is activated, producing an immediate widespread response called the fight-or-flight response. This response is characterized by the release of large quantities of epinephrinefrom the adrenal gland, an increase in heart rate, an increase in cardiac output, skeletal musclevasodilation, cutaneous and gastrointestinal vasoconstriction, pupillary dilation, bronchial dilation, and piloerection. The overall effect is to prepare the individual for imminentdanger.
Which nervous system is the antagonistic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is one of two antagonistic sets of nerves of the autonomic nervous system; the other set constitutes the parasympathetic nervous system. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
What is the name of the nervous system that produces localized adjustments?
Alternative Titles: orthosympathetic nervous system, thoracolumbar nervous system. Sympathetic nervous system, division of the nervous system that functions to produce localized adjustments (such as sweating as a response to an increase in temperature) and reflex adjustments of the cardiovascular system. Under conditions of stress, the entire ...
Which nervous system produces sweating?
Sympathetic nervous system, division of the nervous system that produces localized adjustments (such as sweating as a response to an increase in temperature) and reflex adjustments of the cardiovascular system. Under stress, the entire sympathetic nervous system is activated, producing the fight-or-flight response.
Which system normally functions to produce localized adjustments?
The sympathetic nervous system normally functions to produce localized adjustments (such as sweating as a response to an increase in temperature)...
Which nervous system is one of two antagonistic sets of nerves of the autonomic nervous system?
The sympathetic nervous system is one of two antagonistic sets of nerves of the autonomic nervous system; the other set constitutesthe parasympathetic nervous system.
What hormones are produced during chronic stress?
In humans, chronic stress results in long-term stimulation of the fight-or-flight response, which leads to constant production and secretion of catecholamines (e.g., epinephrine) and hormones such as cortisol.
What is the role of the sympathetic nervous system in the body?
The sympathetic nervous system not only initiates responses required to deal with the stress condition but also makes necessary changes in the functioning of the body organs. regulate the vital functions.
Which nervous system controls your responses to stress?
The nervous system that controls your responses in stress conditions like facing a dog, having an accident or being afraid of an approaching deadline is the sympathetic nervous system. It is a division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for fight or flight response. It is a network of interconnected neurons ...
What are the different types of receptors?
The ganglia of the sympathetic system have nicotinic#N#receptors. However, four different types of receptors are present in the target#N#organs. These include: 1 Alpha-1 2 Alpha-2 3 Beta-1 4 Beta-2
What is the mechanism that releases epinephrine?
It is only rarely released by the post-ganglionic fibers. However, a large amount of epinephrine is released by the adrenal medulla in the blood. This circulating epinephrine binds on the receptors and generates response depending on the receptor.
Which neurotransmitter is released by the preganglionic fibers at the ganglia?
There are three types of neurotransmitters present in. the sympathetic nervous system: Acetylcholine: It is released by the preganglionic fibers at the ganglia.
What is the effect of sympathetic system activation on the digestive system?
Activation of the sympathetic system decreases the contraction of smooth muscles in the walls of the digestive tract. Thus, it inhibits the processes of digestion. Contrary to this, the smooth muscles present in sphincters are activated. Thus, the sphincters of the digestive tract remain closed that further hinders the process of digestion.
Why is it important to have sympathetic blood pressure?
In response to decreased blood pressure, the sympathetic system is activated. It causes constriction of the blood vessels.
What are the functions of the sympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic Nervous System has three main functions: *Regulating the cardiovascular system. *Regulating body temperature. *Implementing the "Fight-or-Fight" reaction. The sympathetic nervous system exerts multiple influences on the heart and blood vessels. *Release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla results in vasoconstriction in most vascular ...
How does the sympathetic nervous system help the body?
*Compensation for loss of blood, primarily by causing vasoconstriction. The sympathetic nervous system helps regulate body temperature in three ...
Which system is associated with the fight or flight response?
Sympathetic Nervous System is associated with the "Fight-or-Flight" response which corresponds with arousal & energy generation & inhibition of digestion.
What Does the Parasympathetic Nervous System Do?
Put simply, the PSNS keeps your bodily functions working as they should. It keeps your heart rate and blood pressure steady while stimulating activities related to digestive and sexual function. These include the production of saliva, tears, and urine, digestion, defecation, and sexual arousal.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Nervous System. The human nervous system is a sprawling network of nerves and cells which , together , regulate all of the vital functions that take place in our bodies. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) are both components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The SNS and PSNS are the two main parts of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls the functions of our internal organs. All of the functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, so we don’t always notice its effects on our bodies.
Why is the SNS important?
The SNS is, arguably, even more important than the PSNS because it controls our ‘fight or flight’ response. If we find ourselves in a dangerous situation, it is the SNS that prepares us to save ourselves by either fighting the threat or running away from it. When confronted with a potential threat, the SNS directs energy away from non-essential functions (like the digestive system) and towards functions that are essential to survival.
What is the function of the PSNS?
The PSNS controls the ‘rest and digest’ functions of the body and maintains the body’s internal environment. It is responsible for regulating digestive and sexual function while keeping heart rate and blood pressure steady.
What is the SNS?
The SNS is the driving force behind the ‘fight or flight’ response and triggers a number of physiological changes that prepare the body to confront or flee a perceived threat. The nervous system regulates the body’s vital functions.
Functions
Clinical significance
Behavior
Mechanism
Structure
- Additionally, the sympathetic nervous system regulates minute changes to the cardiovascular system. When there is a change in posture, from sitting to standing, for example, the cardiac output needs to change to accommodate this alteration. In people suffering from disorders of the SNS, one of the first signs of an ailment is postural dizziness. Si...
Mechanism of action
- It can even modulate circadian rhythms and there is usually a surge of SNS activity during the transition from sleep towards awakening.
Example
- In each of these actions, the parasympathetic nervous system can act as an antagonist and help the body recover after the threat has disappeared. Comparatively, the SNS has shorter axons than the parasympathetic nervous system and also acts more quickly. The classic case of SNS response is physical danger, especially with a potential predator, and the preparation of the bod…