G1 phase is the first stage of interphase which is considerably a longer process. S phase is the middle phase in which the cell makes an extra copy of its chromosome set. G2 phase is the last stage of interphase which is relatively a short phase.
What is g1 g2 and S phase?
These three phases are collectively known as interphase. They are G1, S, and G2. The G stands for gap and the S stands for synthesis. The G1 and G2 phases are times of growth and preparation for major changes. The synthesis phase is when the cell duplicates the DNA in its entire genome. Click to see full answer.
What happens in interphase G2?
What happens during the g2 phase of interphase
- G2 phase of Interphase. This is the gap after S phase and before cell division; what happens during the G2 phase of interphase is continuous growth of the and checking ...
- G2 phase. Following S phase, the cell enters G 2 phase. ...
- Gap 2 (G2). ...
- Thank you for asking. ...
- e if the cell can now proceed to.
- G2 phase. ...
What is G1'S and G2?
What does G1 and G2 mean? Stages of the cell cycle The G1 stage stands for “GAP 1”. The S stage stands for “Synthesis”. This is the stage when DNA replication occurs. The G2 stage stands for “GAP 2”. The M stage stands for “mitosis”, and is when nuclear (chromosomes separate) and cytoplasmic (cytokinesis) division occur.
What happens at G1 phase of cell cycle?
The G1 phase is often referred to as the growth phase, because this is the time in which a cell grows. During this phase, the cell synthesizes various enzymes and nutrients that are needed later on for DNA replication and cell division. The duration of the G1 phase is variable and it often depends on the nutrients that are available to a cell. The G1 phase is also when cells produce the most proteins.

What is G1, S and G2 in interphase?
G1 phase (Gap 1) - Cellular contents excluding the chromosomes, are duplicated. II. S phase (DNA Synthesis) - Each of the 46 chromosomes are duplicated by the cell. III. G2 phase (Gap 2) - The Cell “double checks” the duplicated chromosomes for error, making any needed repair.
What is G1 phase S phase and G2 phase?
Initially in G1 phase, the cell grows physically and increases the volume of both protein and organelles. In S phase, the cell copies its DNA to produce two sister chromatids and replicates its nucleosomes. Finally, G2 phase involves further cell growth and organisation of cellular contents.
What happens in G1 and G2 stage?
There are two stages in the cell cycle marked by the replication of organelles and protein synthesis: G1 and G2. G1 follows mitosis and allows the cell to grow. G2 occurs just before mitosis, and ensures that both daughter cells will have adequate organelles.
What is G1 phase in interphase?
The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis.
What is S phase in interphase?
The S phase of a cell cycle occurs during interphase, before mitosis or meiosis, and is responsible for the synthesis or replication of DNA. In this way, the genetic material of a cell is doubled before it enters mitosis or meiosis, allowing there to be enough DNA to be split into daughter cells.
What is G2 phase of interphase?
G2 phase. G2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. It follows the successful completion of S phase, during which the cell's DNA is replicated.
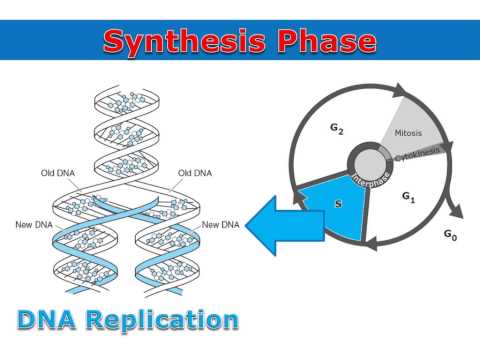
What happens in S phase?
S phase. In S phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus. It also duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure called the centrosome. The centrosomes help separate DNA during M phase.
Why are the G1 and G2 phases important?
Similarities Between G1 and G2 phase of Cell Cycle G1 and G2 phase of the cell cycle are the first and the last phase of the interphase. The main function of both phases is cell growth and preparation for their function. Furthermore, the synthesis of RNA and proteins are two major events of both phases.
What is the difference between S phase and G2 phase?
S phase or synthesis phase is the second sub-phase of interphase. G2 or Gap2 phase is the third and last sub-phase of interphase that directly leads to divisional phase. 2. It occurs in between the G1 (Gap 1) phase and G2 (Gap 2) phase.
What does the S phase stand for and its function?
S phase (Synthesis Phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S-phase are tightly regulated and widely conserved.
Why G1 and G2 are called gap?
After cell growth during the G1 phase and DNA replication during the S phase, the cell is ready to enter the G2 phase. G2 is called a gap phase because no further cell division-specific progress takes place.
How are G1 and G2 different?
G1 phase is the first phase of the interphase of the cell cycle in which cell shows a growth by synthesizing proteins and other molecules. G2 phase is the third phase of interphase of the cell cycle in which cell prepares for nuclear division by making necessary proteins and other components.
What are the 4 stages of cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
What is the difference between S phase and G2 phase?
S phase or synthesis phase is the second sub-phase of interphase. G2 or Gap2 phase is the third and last sub-phase of interphase that directly leads to divisional phase. 2. It occurs in between the G1 (Gap 1) phase and G2 (Gap 2) phase.
What is the function of G1 phase?
G1 phase (Gap 1) – G1 phase is the phase of the cell between mitosis and initiation of replication of the genetic material of the cell. During this phase, the cell is metabolically active and continues to grow without replicating its DNA.
What happens in S phase?
The S phase of the cell cycle occurs before the interphase and is involved in DNA synthesis or replication. In this way, the genetic material of the cell is replicated before entering mitosis or meiosis, leaving enough DNA to divide into daughter cells.
What happens in the G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle?
Cell division entails making more cells through duplication of the one cell’s contents and then splitting this cell into two equal and identical cells. These cells are identical to the parent cell. This is how we grow and replace injured cells.
What are the phases of interphase?
Interphase is divided into the first growth (G1), Synthesis (S), and the second growth (G2) phases (figure 1) . The growth phases are, as you may have suspected, for the growth of the cell, during the synthesis phase the DNA replication occurs in preparation for the second growth phase. Figure 1: The four phases of the cell cycle (G 1, S, G 2 and M).
What are the two major phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle has two major phases, the mitotic phase, and the interphase. Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle. Cell growth is central to the cell cycle, and this is the primary purpose for interphase. At the end of this phase, there is double the amount of DNA, centrioles have replicated, and the cell is big enough for cell division.
What are the functions of G1 cells?
In G1, cells accomplish most of their growth; they get bigger in size and make proteins and organelles needed for normal functions of DNA synthesis . Here, proteins and RNAs are synthesized, and, more especially the centromere and the other components of the centrosomes are made. The cells are fully functional; in addition to being on a dividing mission they can also perform their normal functions. In vertebrates and diploid yeasts the chromosome number is 2n at this phase, while in haploid yeasts the chromosome number is 1n.
Which phase of the cell cycle prepares the cell for DNA replication?
The growth phases, G1 and G2, of the cell cycle prepare the cell for DNA replication at S phase and cell division and M phase, respectively.
Does DNA replicate in the S phase?
It is important to note that the DNA replicated in the S phase has not condensed into chromosomes yet. The organelles necessary for the cell division (in M phase) are also synthesized in the S phase. The microtubules that will be used to mobilize the chromosomes in M phase are assembled at G2.
Is enter M checkpoint homologous?
The control of the Enter M checkpoint is mostly similar across eukaryotes, with most cyclins and their CDKs having homologs across different eukaryotic groups. Here we will focus on the fission yeast (Schizosaccharomycespombe) as an example. Four proteins are involved in the regulation of the protein kinase activity of the CDK in fission yeast in the control of entry into mitosis. Before we continue, it is worth noting that fission yeast has only one CDK while vertebrates have a family of CDKs.
What happens to cells during the G1 and S phase?
The cell has two choices at this point: to divide or not to divide. Between G1 and S phase, the cell decides if it wants to grow. Some cells that do not divide include bone cells and blood cells (they do not undergo mitosis). These cells do not go through S or G2.
What is the first stage of interphase?
The first stage of interphase is the G1 phase (first gap), the growing phase. All cells undergo G1. Here, the cell is quite active at the biochemical level. The cell grows and accumulates the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins as well as sufficient energy reserves to complete the task of replicating each chromosome in the nucleus. Cells increase in size and produce organelles.
What happens in the G0 phase?
Not all cells undergo mitotic phase. Cells in the G0 phase are not actively preparing to divide. The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle. Some cells enter G0 temporarily until an external signal triggers the onset of G1. No more DNA replication or cell division happens at this phase. The cells that never or rarely divide include mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells, and they remain in G0 permanently.
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
The Stages of Interphase and the Cell Cycle: The cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear DNA is duplicated. Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. The cytoplasm is usually divided as well, resulting in two daughter cells
What is the stage of the life cycle where the cell grows and DNA is replicated?
interphase:the stage in the life cycle of a cell where the cell grows and DNA is replicated. centrosome:an organelle near the nucleus of a cell that contains the centrioles (in animal cells) and from which the spindle fibers develop in cell division.
What are the two centrosomes?
The two centrosomesgive rise to themitotic spindle, the apparatus that orchestrates the movement of chromosomes during mitosis. At the center of each animal cell, the centrosomes of animal cells associate with a pair of rod-like objects, the centrioles, which are at right angles to each other.
Which phase of interphase takes the longest?
These cells do not go through S or G2. They stop at G1 or G0. S Phase (Synthesis of DNA) The synthesis phase of interphase takes the longest because of the complexity of the duplicated genetic material. The S phase is where DNA replication occurs, and centrioles replicate.
Answer
Explanation: It starts out in interphase and gets the cells ready for mitosis.
New questions in Biology
Four cells are produced at the end of meiosis II. Which of the following is TRUE about these cells? A. They are genetically identical. B. They each ha … ve 46 chromosomes. C. Each cell has 23 chromosomes and is genetically different from the others.

Introduction to G1 and G2 Phases
What Happens in G1of The Cell Cycle?
What Happens in G2 of The Cell Cycle?
- We have looked at what happens at the first growth phase, and what happens at the S phase is in the article “What happens in the S-Phase”; the details of DNA replication are provided in “What is DNA”. Now let us take a quick trip through the second growth phase, G2. The second growth phase follows the S phase (synthesis). Past the S phase, the cell goes through a quality control …
Checkpoints
- The Exit M and Enter S Checkpoints
Before the cell enters the G1 phase of the interphase, it goes through the Exit M checkpoint. Here the cell is checked to ensure that it has completed the mitosis phase and is ready for the first growth phase. Specifically, the cells are checked to see if they have completed the cell division a… - Enter M and the Regulation of the G2 Phase
The Enter M checkpoint influences the exit out of the G2 phase. At every transition of the cell cycle, the cells are continuously checked for the DNA integrity, where (in the case of the S into G2 transition) the newly duplicated DNA is checked for mutations and fixed if necessary. Once this t…
How Is G1 Different from G2?
- We hope you already gauged this from the sections above. Here is the gist of it, the whole of interphase encompasses cell growth and cell division, this we know. One significant difference between growth phases is that the first growth phase is about cell growth while G2 is about cell division. It is important to fully grasp the roles of these gaps...
Conclusion
- This is an introductory Biology overviewof the G phases of the cell cycle; it is by no means an exhaustive cover of this complex subject matter. The cell cycle is such a vital part of the existence of all eukaryotes. As such it is important for it to be tightly controlled (by tumor suppressors and proto-oncogenes). The growth phases are, perhaps, the most critical phases of the cell cycle. W…