Is PKU a chromosome disorder or a gene disorder?
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive inborn error of phenylalanine (Phe) metabolism resulting from deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). Most forms of PKU and hyperphenylalaninaemia (HPA) are caused by mutations in the PAH gene on chromosome 12q23.2.
What does PKU do to the body?
Too much phenylalanine in the body causes problems with the brain and other organs. Damage from a buildup of phenylalanine can begin within the first month of life and, if undetected and/or untreated, PKU results in severe mental retardation, hyperactivity, and seizures. PKU affects about 1 baby in every 13,000 to 19,000 births.
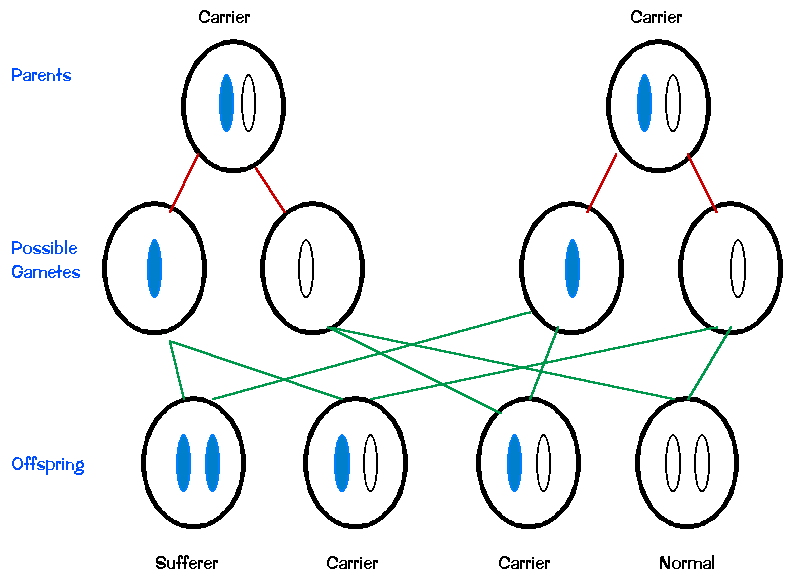
Is PKU a recessive or dominant trait?
Well, that means that people that have PKU have two recessive genes for the disorder. In scientific terms they are homozygous recessive for the PKU trait. The recessive gene which characterizes PKU is inherited from both parents.
Is PKU a sex linked trait?
The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition. PKU is a sex-linked disorder. At what age does this order first become evident?

What is the genetic pattern of inheritance in PKU?
PKU is inherited in families in an autosomal recessive pattern. Autosomal recessive inheritance means that a person has two copies of the gene that is altered. Usually, each parent of an individual who has PKU carries one copy of the altered gene.
What is the PAH gene?
The PAH gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase. This enzyme is responsible for the first step in processing phenylalanine, which is a building block of proteins (an amino acid) obtained through the diet. Phenylalanine is found in all proteins and in some artificial sweeteners.
What is the most common mutation in PKU?
Among the novel mutations, five were found in patients with MHP, and the remainder were found in patients with PKU. The most common mutations were R408W, IVS12nt1g-->a, and Y414C, accounting for 18.7%, 7.8%, and 5.4% of the mutant chromosomes, respectively.
How many mutations of PKU are there?
Abstract. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is heterogeneous. More than 400 different mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene have been identified.
What mutation in the PAH gene causes PKU?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase mutations in the phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency patients in China. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive genetic disease, caused by the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency in the metabolic pathway.
Is PKU more common in males or females?
The risk is the same for males and females. More than 300 different changes (mutations) in the PKU gene have been identified.
Is PKU caused by a point mutation?
Point mutations in the PAH gene are known to cause PKU in various ethnic groups, and large deletions or duplications account for up to 3% of the PAH mutations in some ethnic groups.
What is the genotype of PKU?
An untreated PKU patient with normal intelligence was found to be heterozygous for the IVS12nt1 and R408W mutations(21). This genotype would be expected to have no PAH activity. Therefore, something other than the activity of the PAH enzyme must be affecting the intellectual phenotype in some individuals.
On which chromosome PAH gene is located?
chromosome 12The human PAH gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 12 (12q23. 2). It contains 13 exons and 12 introns and spans about 90 kbp encoding a monomer of 452 amino acids (1, 9–12).
What is PAH deficiency?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency (PAH deficiency), also called phenylketonuria (PKU), is an inherited disease in which the body cannot properly process the amino acid phenylalanine due to a deficient enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase.
How big is the PAH gene?
approximately 100 kbThe human PAH gene (OMIM # 612349) covers approximately 100 kb of genomic DNA, consists of 13 exons and 12 introns, and has been mapped on chromosome 12, band region q23.
Is PAH hereditary?
Some cases of PAH are due to genetic changes in the BMPR2 gene and inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Most cases of PAH occur in individuals with no family history of the disorder. When PAH is inherited from an affected relative it is called "familial" PAH.
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
- Newborns with PKU initially don't have any symptoms. However, without treatment, babies usually develop signs of PKUwithin a few months. Signs and symptoms of untreated PKUcan be mild or severe and may include: 1. A musty odor in the breath, skin or urine, caused by too much phenylalanine in the body 2. Nervous system (neurological) problems that may include seizures …