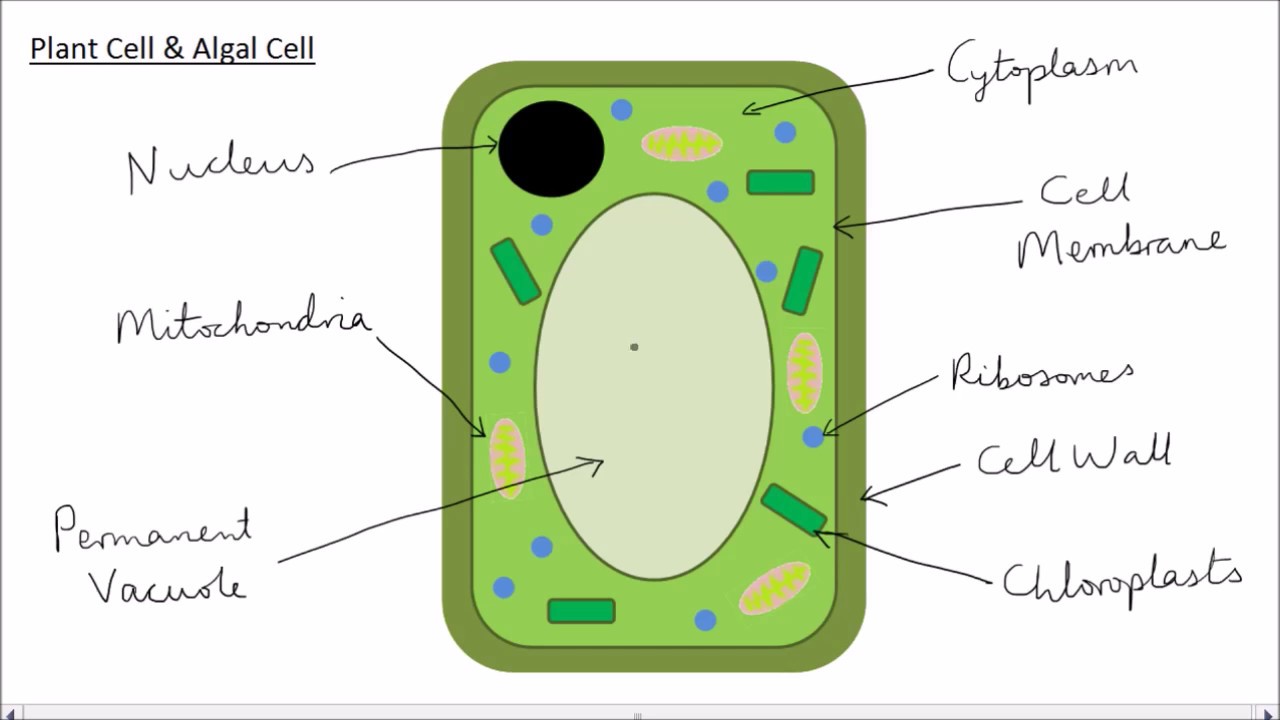
What are the seven parts of a plant cell?
What are the 7 most important organs?
- Cellular membrane. The thin, flexible outer layer of a cell and controls what goes in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm. The gel-like fluid inside a cell is mostly water and it holds other organs in place.
- Center.
- Vacuole.
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Cellular wall.
What are the parts of plant cell and their functions?
Plant Cell: Its 6 Main Parts and Their Functions
- Plastids (Chloroplasts) Chloroplasts are easy to find and observe. They are "chlorophyll-bearing plastids." Plastids are cellular structures of a plant cell that generally hold pigments.
- Cell Wall. The cell wall of plant cells comprises cellulose. ...
- Vacuoles. ...
- Cell Membrane. ...
- Nucleus. ...
- Cytoplasm. ...
What are all the parts of a plant cell?
What are the parts of a plant cell?
- 2: cell membrane.
- 3: cytoplasm.
- 5: mitochondrion.
- Golgi apparatus.
- Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Chromosome.
- Nucleus.
How many parts are there in a plant cell?
The plant cell has one. Nucleus. Body in the center of a cell that contains RNA and DNA. Is the control center of the cell and is responsible for activities like reproduction and growth. Nucleolus. In the Nucleus, contains RNA. Chloroplast. Contains chlorophyll, site of photosynthesis. Mitochondrion.
What are main parts of plant cell?
Plant Cell StructureCell Wall. It is a rigid layer which is composed of polysaccharides cellulose, pectin and hemicellulose. ... Cell membrane. It is the semi-permeable membrane that is present within the cell wall. ... Nucleus. ... Plastids. ... Central Vacuole. ... Golgi Apparatus. ... Ribosomes. ... Mitochondria.More items...
What are the 3 main parts of a plant cell?
Cell Structures (Cell Organelles)Cell Wall: This is the rigid outermost layer of a plant cell. ... Cell Membrane: This is a protective layer that surrounds every cell and separates it from its external environment. ... Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a thick, aqueous (water-based) solution in which the organelles are found.More items...•
What are the 5 main plant cells?
The common plant cell types are meristematic cells, parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, and reproductive cells.
What are the main parts of plant cell and animal cell?
Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm and mitochondria are four cell components that are found in both animal and plant cells.
What are parts of plants?
Plants typically have six basic parts: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
What are all the parts of a cell and their functions?
1:434:13Cell parts and their functions | Middle school biology | Khan AcademyYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can think of the nucleus. As the information database of the cell it contains dna which includesMoreYou can think of the nucleus. As the information database of the cell it contains dna which includes the cell's genes genes are special instructions that the cell uses to carry out its functions.
How many major parts does a plant cell have?
These components are organized into three major layers: the primary cell wall, the middle lamella, and the secondary cell wall (not pictured). The cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane and provides the cell tensile strength and protection.
What organelles are only in plant cells?
Vacuoles. Vacuoles are large, liquid-filled organelles found only in plant cells.
Which is present only in plant cell?
A chloroplast is an organelle that is only present in plant cells. It is a plastid that contains chlorophyll and is also where photosynthesis takes place.
What do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
Plant cells have a cell wall, but animals cells do not. Cell walls provide support and give shape to plants. Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. Chloroplasts enable plants to perform photosynthesis to make food.
Which is the plant cell?
plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells.
What are examples of plant cells?
Some examples of specialized plant cell types and tissues include: parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, xylem, and phloem.
How many types of cells are there in plants?
three basicThere are three basic types of cells in most plants. These cells make up ground tissue, which will be discussed in another concept. The three types of cells are described in Table below. The different types of plant cells have different structures and functions.
How many cells are in plants?
There are three basic types of cells in most plants, basically Parenchymal, Collenchymal and Sclerenchymal.
What are the 15 organelles in a plant cell?
Within the cytoplasm, the major organelles and cellular structures include: (1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (6) Golgi apparatus (7) cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytosol (12) lysosome (13) centriole.
What are the 13 parts of a plant cell?
Each plant cell will have a cell wall, cell membrane, a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, plastids, mito...
What is plant cell and animal cell?
Animal cells will not have chloroplasts or a cell wall. Plant cells usually have a larger central vacuole than animal cells. They also usually ha...
What are the main parts of a plant cell?
There can be no cell without a nucleus. Also, a plant cell will have a cell wall to give it shape and chloroplasts so it can photosynthesize its o...
What is a plant cell?
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell that contains a true nucleus and certain organelles to perform specific functions. However, some of the organelle...
What are the different types of plant cells?
The different types of plant cells include- collenchyma, sclerenchyma, parenchyma, xylem and phloem.
Which organelles are found only in plant cells?
The organelles found only in plant cells include- chloroplast, cell wall, plastids, and a large central vacuole. The chloroplasts contain a green p...
What is the composition of a plant cell wall?
The cell wall of a plant is made up of cellulose. Cellulose is a long, linear polymer of several glucose molecules.
Where does photosynthesis occur in plant cells?
Photosynthesis occurs inside the chloroplast of the plant cells. Chloroplast consists of a green pigment called chlorophyll. The light reactions oc...
What is the most important part of a plant cell?
The Chloroplast. The chloroplast is one of the most important parts of the plant cell and is crucial to its function. As is commonly known, plants use photosynthesis to harness the power of the sun to create nutrients. The sunlight is used to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen, a waste product.
What is the membrane of a plant cell?
The plasma membrane, found in all living cells, encloses the plant cell and is surrounded by the cell wall. In plant cells, this membrane adds an additional layer of protection and regulation to the cell wall.
Why are plants unique among eukaryotic cells?
Plant cells are unique among eukaryotic cells because they are capable of creating their own food. “A dried plant is nothing but a sign to plant ...
Where are ribosomes found?
Ribosomes are found throughout the cell but are generally concentrated around the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear envelope. They can range from the thousands to the millions.
Where is the endoplasmic reticulum located?
These can include proteins, energy compounds, and nutrients. It is located near the nucleus and surrounded by ribosomes.
Why are cell walls porous?
Besides providing the structure, strength, and rigidity of the cell, the cell walls are also porous and allow the movement of materials into and out of the cell. These channels are regulated to ensure that harmful compounds are kept out.
Why are plant cells so rigid?
Plant cells are very rigid because of their cell wall, a component that does not exist within animal cells. The plant cell wall was inherited from our prokaryotic ancestor and became a highly specialized part of the cell. The rigidity comes from a complex series of cross-linked structures made of cellulose and lignin that reinforce the wall.
What are the parts of a plant cell?
The parts of a plant cell and plant cell components, which will be discussed, are plant cell wall, plant cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, vacuole, nucleus, peroxisomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, and plastids.
What is the outermost part of a plant cell?
The outermost portion of a plant cell is the cell wall. This is also a part that animal cells do not have. The function of a cell wall is to give the cell rigidity and support, as well as allow for the circulation of water and minerals. When a vegetable is bitten into, it gives off a nice crunchy sound. This is due to the cell wall. The cell wall is made up of complex polysaccharides (poly-many, saccharide-sugar) like pectin and glycan, along with some microfibers. The cell wall also helps fight off disease by being another barrier between the outside and the inside of the cell.
How does the Golgi apparatus work?
The Golgi works closely with rough ER to get the synthesized compounds to the right places. Those vesicles can either go somewhere else in the cell, to the cell membrane for repair or transported out of the cell altogether.
What is the cell membrane?
Every cell has a cell membrane, whether it be a plant or animal. A cell membrane is a division between the outside environment and the inside protoplasm of the cell. The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and proteins; it is said to be a lipoprotein layer. The cell membrane is also called the cytomembrane or plasma membrane. It allows for the passage of certain compounds through channels that are highly regulated, therefore it is a semipermeable layer.
What is the difference between plant and animal cells?
One specific difference between plant and animal cells is the function of photosynthesis.
What is the membrane around the cell of a plant?
Plants are eukaryotic organisms, meaning that their cell nucleus has a membrane around them. This nuclear wall or envelope is selectively permeable, meaning only certain things are allowed through it, like proteins or RNA.
Why was the cell wall called the cell wall?
He coined the term "cells" because they looked like the rooms monks would reside in in monasteries.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. The plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and to provide form and structure to the cell. It also filters the molecules passing in and out of the cell. The formation of the cell wall is guided by microtubules.
What is the cell wall?
Cell Wall. It is a rigid layer which is composed of cellulose, glycoproteins, lignin, pectin and hemicellulose. It is located outside the cell membrane. It comprises proteins, polysaccharides and cellulose. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. The plant cell wall is also involved in ...
Why are plant roots more rigid than collenchyma cells?
These cells are more rigid compared to collenchyma cells and this is because of the presence of a hardening agent. These cells are usually found in all plant roots and mainly involved in providing support to the plants.
How are cell walls formed?
It consists of three layers, namely, primary, secondary and the middle lamella. The primary cell wall is formed by cellulose laid down by enzymes. Also Read: Cell Wall.
What is the cell membrane?
It is the semi-permeable membrane that is present within the cell wall. It is composed of a thin layer of protein and fat. The cell membrane plays an important role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell.
Why are plants specialized?
Cells of a matured and higher plant become specialized to perform certain vital functions that are essential for their survival. Few plant cells are involved in the transportation of nutrients and water, while others for storing food.
Where are mitochondria found?
Mitochondria. They are the double-membraned organelles found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. They provide energy by breaking down carbohydrate and sugar molecules, hence they are also referred to as the “Powerhouse of the cell.”. Explore more: Mitochondria.
Where is the nucleus in a plant cell?
Remembering our factory analogy, we will look at each organelle. In the center of the plant cell within its own membrane lies the nucleus. The nucleus is like the command center of the factory. Vital genetic instructions for the cell are found here in the form of DNA.
Where are the organelles located in a plant cell?
Inside a Plant Cell. Now we will take a look at the parts of the cell located inside the cell membrane, which are known as organelles. Similar to the organs inside our bodies, each cell organelle has a specific job that contributes to the overall function of the cell. Remembering our factory analogy, we will look at each organelle.
What organelle is the ribosome attached to?
Although many ribosomes are found floating freely in the cell, many are attached to an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER for short. The endoplasmic reticulum comes in two forms: rough and smooth.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
This is a warehouse of sorts, where newly arriving vesicles are sorted, modified, and shipped out to various locations. Similar to the ER, the Golgi is made up of a series of membranes stacked together much like a pancake stack.
What is the outermost layer of a plant cell called?
As previously mentioned, a plant cell is a self-contained unit. It's surrounded by not one but two enclosures. The outermost layer is called the cell wall and is unique to plant cells. Like an actual wall, this layer is fairly rigid.
What is the second covering of the cell?
Inside the cell wall is the second covering, the cell membrane. Thin and flexible, it keeps the contents of the cell intact much like a balloon holding water. This sac-like covering is semi-permeable, meaning select particles can move through the membrane.
What are the ribosomes?
Ribosomes are the producers of our factory-like cell. They are responsible for making proteins, which are a crucial part of every living thing. The genetic instructions laid out by the DNA are brought to the ribosomes by the traveling messenger of our factory, which is a molecule known as mRNA.
What are the structures of a plant cell that hold pigments?
Chloroplasts are easy to find and observe. They are "chlorophyll-bearing plastids." Plastids are cellular structures of a plant cell that generally hold pigments. Plants have other kinds of plastids besides chloroplasts. For instance, one type of plastid called chromoplastid contains two kinds of dyes: carotene, which gives cream, white, yellow, orange, and red colors and xanthophylls, which provide bright yellow and brown colors. Not all plant pigments are inside plastids. For instance, anthocyanin, a purple dye, is dissolved in the cytoplasm.
Which part of a plant cell stores proteins and fat lipids?
This part of a plant cell contains digestive enzymes that are perfect for cell metabolism. Lysosomes store proteins and fat lipids for the metabolic processes of a plant cell. Lysosomes are responsible for the removal of wastes in a plant cell. 6c.
Which organelle is responsible for the creation of lysosomes in a plant cell?
Golgi bodies are responsible for the creation of lysosomes in a plant cell. 6e. Endoplasmic Reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum is the intricate system of small tubes or cavities, the endoplasmic reticulum, which connects the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane at several points.
Why are plastids important?
Plastids have many essential metabolic pathways that are important for plant growth and development.
How does the cell wall differ from the cell membrane?
First, it contains a combination of fat, protein, and carbohydrate molecules. Second, it is relatively rigid, while the cell membrane is elastic. Its rigidity permits the plant cells to maintain their shape.
What is the most abundant organic matter in a cell?
This water is found mainly in the cytoplasm. The table shows that the most abundant organic matter of the cell is protein. Proteins are the building materials of cells.
What are the two nucleic acids?
Two nucleic acids are deoxyribose nucleic acid (sometimes called as DNA) and nucleic ribose acid (sometimes called as RNA). DNA is the genetic material. It is responsible for the passing on of hereditary traits from parents to offspring. The principal role of RNA is the synthesis of proteins.
Which part of the cell contains DNA?
Nucleus. Contains DNA which carries the genetic code for making enzymes and other proteins used in chemical reactions such as photosynthesis and respiration. Cell membrane. Allows gases and water to diffuse freely into and out of the cell.
What is the function of plants in life?
Plant cells. Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. Plants capture light from the sun and use it to build up chemical stores of energy. This is called photosynthesis. The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below. Photosynthesis relies on many structures in the cell all working together, each playing its role.
What are the parts of a plant cell?
However, its the presence of three additional parts, namely; cell wall, chloroplasts and vacuole, which make it a plant cell.
Which part of the cell contains chlorophyll?
Chloroplasts (found only in green leaf cells): Contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis to take place.
What are the functions of the cell?
Cell wall provide rigidity to cell. Inside the cell there are double membranous cell organelles like nucleus, chloroplast and mitochondrion. All the activities of cell are controlled by nucleus. Chloroplast is the most important cell organelle which perform the function of photosynthesis. Mitochondrion perform the function of respiration. Ribosomes present in the cell participate in protein synthesis. Vacuoles present in plant cell store water. Peroxysomes are involved in photorespiration along with Chloroplast and mitochondrion in C3 plants.
What are ribosomes made of?
ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
What is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus?
nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
What is the cell wall made of?
Cell wall- has a role in providing strength to the cell. It is mainly made up of pectin, cellulose and hemicellulose.
Which organelle allows chemical reactions to take place in the cell?
Cytoplasm: Contains cell parts and organelles and allows chemical reactions to take place in it.
How many components are there in a plant cell?
The following points highlight the nine components of a typical plant cell.
Why do plants have more than one nucleus?
Even in some higher plants more than one nucleus may arise due to disease and other reasons. Formation of many nuclei in a cell may be due to (i) repeated division of the nucleus without corresponding cytoplasmic division; and (ii) absorption of walls between the cells.
What is the smallest part of a cell?
Protoplast is the organized mass of protoplasm of each cell. It is the smallest part of die essential living substance. It possesses a highly organized more or less rounded body known as nucleus, what figuratively means the centre of activities.
What is protoplasm in plants?
Protoplasm exhibits streaming movements of different types which are commonly noticed in amoebas, slime moulds, and particularly in the plant cells with large vacuoles.
Where are plastids found in plants?
Plastids are distinct living bodies or organs embedded in the cytoplasm of the plant cells. They are much smaller than the nuclei and usually a good number of them occur in a cell. Plastids are of universal occurrence in the plant cells with the exception of lower plants like bacteria, fungi, slime moulds and blue-green algae. Like nucleus plastids do not arise de novo, but originate from pre-existing ones.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Due to pressure of hydrolytic enzymes lysosomes take active role in breakdown of different cell substances. The materials in the lysosome often form crystals. The function of lysosome membrane is that of separating the hydrolytic enzymes from other parts of the cell, thus avoiding self-digestion.
What is the most important component of a chromosome?
The most important constituent of the chromosome seems to be the nucleic acid —DNA, deoxyribose nucleic acid, which is the actual chromatic material causing staining of the chromosomes. Differential staining at different regions of chromosome means difference in its chemical nature. The nucleus contains the basic genetic information of the cell in form of long strands of this chemical material DNA, the molecules of which are believed to be in the form of double strands of intertwined helices in the chromosomes.
