
What are the kinds of duties?
- Legal Duties and Moral Duties: A legal duty is an act the opposite of which is a legal wrong.
- Positive or Negative Duties:
- Primary and Secondary Duties:
- Universal General and Particular Duties:
- Relative and Absolute Duties:
- Moral Duty. An obligation that is created by principles of right and wrong. ...
- Legal Duty. A duty created by the laws and regulations of a society. ...
- Contractual Duty. A duty created by agreement between parties. ...
- Professional Duty. ...
- Fiduciary Duty. ...
- Responsibility. ...
- Accountability. ...
- Due Diligence.
What is a duty?
The duty may be a percentage of the value of the goods or at a specific rate. The Central Government has the power to reduce or exempt any good from these duties.
What are the legal duties of a person?
Duties. Each person has a duty to uphold or respect another person’s rights, just as he has the duty to uphold your rights. Once a person accepts a right, or is told as in legal rights, he must uphold that right for himself and others. For instance, you have the right to free speech, but so does everyone around you.
What is the relationship between duties and wrongs?
Thus duties and wrongs are generally co-related. The commission of a wrong is the breach of duty. And the performance of a duty is avoidance of wrong. 1. Postitive and Negative Duty Positive Duties → to do an act. Negative Duties → not to do an act. 2. Primary and Secondary Duty A duty may be either primary or secondary.
What is the difference between rights and duties?
Duties are a direct result of the acceptance of rights. Each person has a duty to uphold or respect another person’s rights, just as he has the duty to uphold your rights.

What are the different kinds of duty?
Legal dutiesDuty of care.Duty of candour.Duty to defend and duty to settle, in insurance.Duty to rescue.Duty to retreat.Duty to report a felony.Duty to vote (in countries with mandatory voting)Duty to warn.More items...
What are the four types of duties?
There are four general categories of duties or responsibilities which are examined when segregation of duties are discussed: authorization, custody, record keeping and reconciliation. In an ideal system, different employees would perform each of these four major functions.
What are 3 examples of duties?
Mandatory Duties of U.S. CitizensObeying the law. Every U.S. citizen must obey federal, state and local laws, and pay the penalties that can be incurred when a law is broken.Paying taxes. ... Serving on a jury when summoned. ... Registering with the Selective Service.
How many types of duties are there?
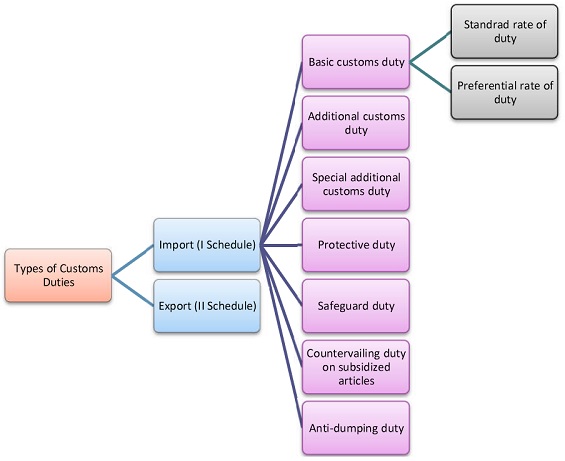
Import duties are further divided into basic duty, additional customs duty, true countervailing duty, protective duty, education cess and anti-dumping duty or safeguard duty. Basic Customs Duty:Basic customs duty is applicable on imported items that fall under the ambit of Section 12 of the Customs Act, 1962.
What are the basic duties?
Fundamental DutiesTo abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem;To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom;To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of India;More items...
What are 11 fundamental duties?
List of Fundamental DutiesAbide by the Constitution and respect national flag & National Anthem.Follow ideals of the freedom struggle.Protect sovereignty & integrity of India.Defend the country and render national services when called upon.Sprit of common brotherhood.Preserve composite culture.More items...
What are the duties of a person?
Duties are moral obligations, on the part of other individuals, to respect those rights. The individuals also having certain rights are under moral obligation to use them well for the common good. Rights and duties are ultimately based upon the same moral laws and relations.
What are the five duties of man explain?
He has to act and live according to the law of God. He has to find out the rules of conduct and the measure of his responsibilities. He must have a thorough knowledge of the moral code of Manu or Yajnavalkya and must act according to the rules laid down therein. Then only can he be rightly called a man.
What are sources of duties?
The source of duty rule developed where project participants sued their contractual privies in tort instead of contract. Both rules are designed to keep contract disputes on the con- tract side of the contract-tort divide.
What are the main types of custom duties?
Types of custom dutiesBasic Customs Duty (BCD)Countervailing Duty (CVD)Additional Customs Duty or Special CVD.Protective Duty,Anti-dumping Duty.Education Cess on Custom Duty.
What is the meaning of duties and taxes?
The key difference between taxes and duties is that duties are a type of tax on goods entering or leaving a country, while taxes are charges placed on almost all purchases. Both contribute to the total import and export costs of a product.
What is protection duty?
What is Protect Duty. Protect Duty is a proposed public space legislation which will set out standards to protect patrons and the general public from terrorist attacks when in crowded spaces.
What are the five duties of man explain?
He has to act and live according to the law of God. He has to find out the rules of conduct and the measure of his responsibilities. He must have a thorough knowledge of the moral code of Manu or Yajnavalkya and must act according to the rules laid down therein. Then only can he be rightly called a man.
What are the duties in law?
A legal duty is an obligation, created by law or contract. A legal duty requires a person to conform their actions to a particular standard. And it also carries with it a recognition that the law will enforce this duty to the benefit of other individuals to whom this duty is owed.
What are the duties of a person?
Duties are moral obligations, on the part of other individuals, to respect those rights. The individuals also having certain rights are under moral obligation to use them well for the common good. Rights and duties are ultimately based upon the same moral laws and relations.
What are sources of duties?
The source of duty rule developed where project participants sued their contractual privies in tort instead of contract. Both rules are designed to keep contract disputes on the con- tract side of the contract-tort divide.
What is the duty of a citizen?
The most important duty of the citizen is to obey the laws of the State. It is the hall-mark of good citizenship. A good citizen obeys a law even if he believes it to be against the common good or oppressive or bad. He must not disobey it, because such an act would destroy the basis of good government, peace and progress. Disobedience of laws is like a contagious disease: it spreads from citizen to citizen and from law to law. Hence to disobey a law because it is bad is-“a political mistake and a public calamity. A citizen has however constitutional and peaceful means of persuading his fellow-citizens of the desirability of changing the laws which he believes to be morally bad or oppressive. In a democratic State he can bring about this change by electing new representatives to the legislature.
Why is it important to pay taxes in time?
But this money must come from the pockets of the people. If they evade the payment of taxes, the government will fail to maintain law and order and discharge its responsibilities. Modern State is ‘Public Services State.’ The more funds it has the more services it can render to the people. Hence prompt and honest payment of the taxes by the citizens is the best guarantee of promoting common good and general welfare of the nation.
What is a citizen judged by?
If a State is known by the rights it maintains, a citizen is judged by the duties he fulfils. He has duties towards other citizens, associations and the State. We shall here enumerate some of his duties and obligations towards the State.
Is voting a duty?
Every democratic State has granted the right to its citizens to vote. But it is no less a duty than right. The form and functions of a government are determined by the votes of the people. The people should cast their votes honestly, intelligently and conscientiously in order to elect good representatives. Hence voting is a duty.
Customs : various types of duties
This article has been written by Sakshi Srivastav, am a fourth-year law student pursuing a degree in B.A.LL.B (Hons.) from the Rajiv Gandhi National University of Law, Punjab and Prakhar Mishra is a fourth-year law student pursuing a degree in BB.A.LLB (Hons.) from National Law University Odisha.
Abstract
The Customs Act and The Customs Tariff Act (hereinafter referred to as CTA), along with various Rules and Regulations in relation to them, serve as the consolidated codes of law on the levy of Custom duties on import and export in India. However, the purpose of these customs laws is more than regulating the export and import of goods.
Introduction
Custom duty, in simple language, is an indirect tax imposed on the export and import of goods from one country to another.
Types of duties
This chapter has been divided into two heads. The first head deals with different types of duties that are imposed on imported/exported goods. Further, there is a discourse on exemptions from Customs duty under the second head.
Exemption from customs duty
The Central Government has the authority to exempt certain goods or an entire description of goods from the levy of customs duty. The exemption can broadly be divided into two categories-
Conclusion
Ours was a closed economy with a very restrictive set-up for a long time since independence. The leaders weighed different parameters viz.
What is absolute duty?
Absolute duties are those duties that are owed only to the state; breach of which is generally called a crime and remedy is punishment. Relative duties are owed to any person; breach of which is a civil injury (tort), and the remedy is compensation.
What are proprietary rights?
A person’s proprietary rights constitute his estate, his assets, and his property. These rights have some economic or monetary significance and are elements of wealth.#N#For Example, Money in a man’s pocket or bank or land, houses, etc. are proprietary rights.
What are the types of customs duties in India?
Types of customs Duties in India. While Customs Duties include both import and export duties, but as export duties contributed only nominal revenue, due to emphasis on raising competitiveness of exports, import duties alone constituted major part of the revenue from Customs Duties and include the following: Basic Customs Duty.
What is the duty on imported goods in India?
All goods imported into India are chargeable to a duty under Customs Act, 1962 .The rates of this duty, popularly known as basic customs duty, are indicated in the First Schedule of the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 as amended from time to time under Finance Acts. The duty may be fixed on ad -valorem basis or specific rate basis.
What are cesses in agriculture?
Cesses are leviable on some specified articles of exports like coffee, coir, lac, mica, tobacco (unmanufactured), marine products cashew kernels, black pepper, cardamom, iron ore, oil cakes and meals, animal feed and turmeric. These cesses are collected as parts of Customs Duties and are then passed on to the agencies in charge of the administration of the concerned commodities.
What is antidumping duty?
Anti Dumping Duty on dumped articles. Often, large manufacturer from abroad may export goods at very low prices compared to prices in his domestic market. Such dumping may be with intention to cripple domestic industry or to dispose of their excess stock. This is called 'dumping'.
When is protective duty valid?
The protective duty will be valid till the date prescribed in the notification. If a country pays any subsidy (directly or indirectly) to its exporters for exporting goods to India, Central Government can impose Countervailing duty up to the amount of such subsidy under section 9 of Customs Tariff Act.
What is safeguard duty?
Central Government is empowered to impose 'safeguard duty' on specified imported goods if Central Government is satisfied that the goods are being imported in large quantities and under such conditions that they are causing or threatening to cause serious injury to domestic industry.
Is countervailing duty livable?
This countervailing duty is livable as additional duty on goods imported into the country and the rate structure of this duty is equal to the excise duty on like articles produced in India. The base of this additional duty is c.i.f. value of imports plus the duty levied earlier. If the rate of this duty is on ad-valorem basis, the value for this purpose will be the total of the value of the imported article and the customs duty on it (both basic and auxiliary).
What is the difference between ethical duties and rights?
Rights and Duties in Ethics. Ethics determines the difference between right and wrong. Laws are rules that must be obeyed, both voluntarily and involuntarily, whereas ethics are voluntary. Behaving ethically is more than obeying the law -- it is expecting your rights to be upheld and upholding the rights of others through ethical duties.
What are the duties of a person?
Duties. Duties are a direct result of the acceptance of rights. Each person has a duty to uphold or respect another person’s rights, just as he has the duty to uphold your rights . Once a person accepts a right, or is told as in legal rights, he must uphold that right for himself and others.
How to view ethical conflicts?
Ethical conflicts must be viewed by looking at the end results of any action and how they affect the freedom or rights of others. One instance of conflicting rights is the admission into private clubs. Although we have the freedom of association, our laws prevent discrimination.
What are some examples of rights?
Humans have all types of rights, including legal, moral, spiritual, natural and fundamental rights. Examples of rights include the right to education provided by society or the right to bear arms. Ethical behavior must recognize and respect a series of rights that belong to each person, animal or society.
Do corporations have the right to profit?
Corporations have the right to seek a profit. It is the duty of the employees to do whatever they were hired to do to promote profitability. The corporation cannot violate the rights of its employees or society just to seek a profit. For instance, the company cannot pay employees less than minimum wage or make them work dangerous hours to increase profits. Companies cannot resort to immoral behaviors such as bribery, substandard quality or false advertising, which may violate the rights of other companies, company stakeholders, individuals or society.
What is the duty of care?
The standard for the duty of care is based on what a person “in a like position would reasonably do under similar circumstances.” This standard is a fairly subjective one. However, under tort law, the standard is reverted to the traditional, objective standard of “what would a reasonable person do?” The former, more flexible standard better protects a director accused of abusing his duty of care because it takes into consideration the fact-specific circumstances that influenced his business decision.
What is the duty of care of an officer?
An officer or director’s duty of care is found in his duty to exercise good business judgment—thus using care—when making decisions for the business . Exercising proper duty of care looks like prudently considering business options and making a reasonable decision based on the information after proper due diligence has been applied to the situation. Furthermore, duty of care looks like acting in good faith, meaning that the officer genuinely believes the choice he is making for the company is a beneficial decision.
What is the duty of loyalty?
The duty of loyalty commands a director to act responsibly for the company at all times and to always act in the best interests of the company rather than oneself. Not only is the duty of loyalty expected when making decisions, but also when refraining or excluding oneself from making business decisions. For example, if a particular business deal is brought to the board of directors’ attention, any director who may have a conflict of interest with the deal is expected to recuse himself from weighing in on discussion. This is to protect both himself and the company because a conflict of interest for a director may tempt him to act in a way that would allow the director to personally gain from the business deal.
What is the rule of thumb for fiduciary duties?
The rule of thumb is to “act in the best interests of the company and shareholders.”. Don’t worry that you will suddenly be blindsided with criticism or a lawsuit if you are following that rule of thumb; but it’s still simply better to know more than the basics. If you are in a position that requires fiduciary duties to your company ...
What is the duty of an officer to act lawfully?
Duty to Act Lawfully. This duty is fairly self-explanatory. Part of an officer’s fiduciary duty lies in the fact that he is expected to act in accordance with the law. Reasonably, one would not merit trust from the shareholders of the company if an officer did not follow the law when making his business decisions for the company.
What is fiduciary duty?
Fiduciary Duties and the 4 Specific Types of Responsibility. To have fiduciary duty means to ensure the party you are serving can trust you. It sounds very simple, and that is true, but its simplicity is greatly overshadowed by its importance. One who acts as a fiduciary for another requires the actor to exercise a paramount level of selflessness.
Why is the final duty not always specifically recognized?
This final duty is not always specifically recognized because it can be inherent to the first duty. As briefly described above, this duty represents an officer or director’s genuine belief and trust that his decision for the business will be beneficial to the business.
Abstract
- The Customs Act and The Customs Tariff Act (hereinafter referred to as CTA), along with various Rules and Regulations in relation to them, serve as the consolidated codes of law on the levy of Custom duties on import and export in India. However, the purpose of these customs laws is more than regulating the export and import of goods. In addition, they keep a tab on smuggling …
Introduction
- Custom duty, in simple language, is an indirect tax imposed on the export and import of goods from one country to another. The use of the term “custom” in custom duty, which means an ancient practice so uniform and persistent in its usage that it becomes a source of law, indicates that the system of levying a tax on imported or exported goods is being followed since antiquity…
Types of Duties
- This chapter has been divided into two heads. The first head deals with different types of duties that are imposed on imported/exported goods. Further, there is a discourse on exemptions from Customs duty under the second head. Different types of duties that could be imposed on goods transported across international borders are as follows-
Exemption from Customs Duty
- The Central Government has the authority to exempt certain goods or an entire description of goods from the levy of customs duty. The exemption can broadly be divided into two categories-
Conclusion
- Ours was a closed economy with a very restrictive set-up for a long time since independence. The leaders weighed different parameters viz. newly achieved independence, our history, and the exploitation we underwent at the hands of the British and decided to create an economic environment suitable for the budding of our domestic industries by, inter alia, blockading foreig…