What are the 7 layers of the abdominal wall?
The abdominal wall. Though its major part is muscular, the abdominal wall consists of at least seven layers: the skin, subcutaneous fat, deep fascia; abdominal muscles, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and the parietal peritoneum.
What are the 4 layers of the abdominals?
AnatomyTransversus abdominis – the deepest muscle layer. ... Rectus abdominis – slung between the ribs and the pubis at the front of the pelvis. ... External oblique muscles – these are on each side of the rectus abdominis. ... Internal oblique muscles – these flank the rectus abdominis and are located just inside the hipbones.
What are the 4 layers of abdominal muscles going from superficial to deep?
Classically the anterolateral abdominal wall has been described as separate layers from superficial to deep as follows:Skin.Subcutaneous tissues (further divided into the more superficial Camper's fascia and the deeper Scarpa's fascia)External oblique muscle.Internal oblique muscle.Transversus abdominis muscle.More items...•
What is the strongest layer of abdominal wall?
transversus abdominis – the deepest muscle layer. Its main roles are to stabilise the trunk and maintain internal abdominal pressure.
What are the 8 layers of the abdominal wall?
LayersSkin.Subcutaneous tissue.Fascia. Camper's fascia - fatty superficial layer. Scarpa's fascia - deep fibrous layer. Superficial Abdominal fascia.Muscle. External oblique abdominal muscle. Internal oblique abdominal muscle. Rectus abdominis. Transverse abdominal muscle. ... Transversalis fascia.Extraperitoneal fat.Peritoneum.
What are the 3 layers of stomach muscle?
Layers of Stomach Wall The three layers of smooth muscle consist of the outer longitudinal, the middle circular, and the inner oblique muscles. Construction of these muscles helps mix and break the contents into a suspension of nutrients called chyme and propels it into the duodenum.
What is the lining of the abdominal wall called?
peritoneumYour peritoneum is the tissue that lines your abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in your abdomen. A liquid, peritoneal fluid, lubricates the surface of this tissue.
What is the most superficial abdominal layer?
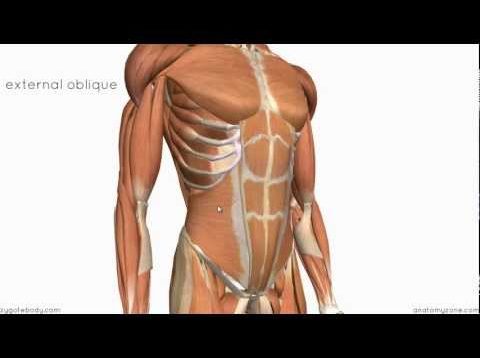
External Oblique - the most superficial and also the largest flat muscle of the abdominal wall. It runs in an inferior-medial direction and at the midline, its fibers form an aponeurosis and in the midline merge with the linea alba.
What is the correct order of abdominal layers that the doctor must go through in order to reach the patient's abdominal area from superficial to deep )?
The layers of the anterior abdominal wall which may be encountered in a laparotomy include the following from superficial to deep: skin, subcutaneous fat, fascia of Camper, fascia of Scarpa, external oblique muscle, internal oblique muscle, rectus abdominis muscle, transverse abdominis muscle, pyramidalis muscle, ...
What is the thickest layer of the stomach?
SubmucosaSubmucosa is thick, vascular, has glands embedded in it and nerve plexus. It has loose connective tissues that support the mucosa present below it. Mucosa is the innermost layer of the alimentary canal that is found surrounding the lumen.
How many layers are cut during C section?
At the beginning of a caesarean section, six separate layers of the abdominal wall and uterus are opened individually. Once the baby is delivered the uterus is closed with a double layer of stitching.
What is the most important organ in the abdomen?
The liver is the most important organ of the metabolic system. It helps convert nutrients into usable substances, detoxifies certain substances, and filters blood coming from the digestive tract through a vein before it joins venous blood flow from other parts of the body.
What are the 4 main muscles of the core?
Key global muscles include: Erector Spinae External Oblique Rectus Abdominis Quadratus Lumborum For more information please see the Physiopedia Page on the Muscles of Respiration.
What are the core 4 muscles?
Your core actually consists of 4 interconnected muscle groups: your transversus abdominis, your multifidus, your diaphragm, and your pelvic floor. I call this the “Core-4.” All 4 of these core muscles work together to provide strength and create balance and stability.
How many layers of muscle are in the abdominal wall?
The majority of the digestive tract is composed of two muscular layers to allow for peristalsis — that is, the movement of food. The stomach, however, is composed of three layers, and is designed to account for mechanical digestion.
What nerves run between the muscles of the abdominal wall?
In the layers of abdominal wall, there are a large number of nerves that go between the skin and muscles of the abdomen. They include: Thoracoabdominal nerves – There are five pair of these nerves and they run between the muscles of the abdominal wall to the muscles of the anterolateral wall of the abdomen. The cutaneous, lateral, and anterior ...
What is the purpose of the abdominal wall?
The wall that encases the cavity of the abdomen has a number of things it is responsible for, including: 1 Keeping the abdominal viscera from being injured 2 Creating the wall that will keep the abdominal viscera within the cavity of the abdomen 3 Helping to keep the abdominal viscera in the proper position against gravity 4 Increasing intra-abdominal pressure that is used in actions such as vomiting or coughing 5 Working in a forceful manner to help push the abdominal viscera in an upward position
What are the muscles in the abdomen?
Muscles. There are two groups of five muscles that are located in the wall of the abdomen. The groups consist of vertical muscles and flat muscles. The Flat Muscles. These muscles laterally flex and rotate the trunk.
What is the layer above the umbilicus?
If it is above the umbilicus, it is made up of a single sheet of tissue; if it is below the umbilicus, it has two layers – the superficial layer that is fatty and the deep layer which has a lot of membranes. There are superficial nerves and vessels that go between these two layers. 5. Skin.
Which peritoneum is used for nerves?
While the visceral peritoneum shares the blood that is used by the nerves and lymphatic vessels of the organs of the abdomen, the parietal peritoneum utilizes the nerve supply and circulation from the layers of abdomen wall. 2.
How to keep abdominal viscera in proper position?
Helping to keep the abdominal viscera in the proper position against gravity. Increasing intra-abdominal pressure that is used in actions such as vomiting or coughing . Working in a forceful manner to help push the abdominal viscera in an upward position.
Where are the subcostal nerves located?
Subcostal nerves – Located at the 12th thoracic spinal of the anterior rami, the nerves from this area run inferior from the 12th ribs down to the lower area of the navel. These nerves innervate the muscles of the abdominal wall and the skin that is located from the umbilicus to the iliac crests.
What are the three layers of the abdominal wall?
In medical vernacular, the term 'abdominal wall' most commonly refers to the layers composing the anterior abdominal wall which, in addition to the layers mentioned above, includes the three layers of muscle: the transversus abdominis (transverse abdominal muscle), the internal (obliquus internus) and the external oblique (obliquus externus).
What is the abdominal wall?
In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.
What is abdominal wall closure?
The abdominal wall is defined cranially by the xiphoid process of the sternum and the costal margins and caudally by the iliac and pubic bones of the pelvis. It extends to the lumbar spine, which joins the thorax and pelvis and is a point of attachment for some abdominal wall structures [1].
How many layers are there in the abdominal wall?
Knowledge of the layered structure of the abdominal wall permits efficient and safe entry into the peritoneal cavity. There are nine layers to the abdominal wall: skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial fascia, external oblique muscle, internal oblique muscle, transversus abdominis muscle, transversalis fascia, preperitoneal adipose and areolar tissue, and peritoneum. Nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatics are present throughout.
What are the factors that affect the contour of the abdomen?
The contour of the abdomen is dependent upon age, muscle mass, muscle tone, obesity, intra-abdominal pathology, parity, and posture. These factors may significantly alter topography and become a major obstacle to proper incision selection and placement [2].
Is UpToDate a substitute for medical advice?
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of UpToDate content is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use. ©2021 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
How does deep adipose tissue differ from superficial adipose tissue?
Deep adipose tissue appears very different from the superficial adipose tissue, as its fat lobes are smaller, flatter, and less well defined (Fig. 1.5 ). This adipose layer shows significant variations in terms of thickness between different areas. Towards the points, at which the membranous layer of the subcutaneous tissue adheres to salient structures (e.g., the inguinal ligament, bony prominences, linea alba), they become thinner and tend to progressively reduce the fat component. However, the network of collagen fibres (retinacula cutis profunda) become stronger and more tightly packed and connects the deep aspect of the membranous layer to the deep fascia.
Why is liposuction performed above the umbilicus?
This is the reason why liposuction performed above the umbilicus and close to the midline is more prone to result in irregularities. The attachments of the retinacula cutis superficialis to the skin at 5–7 cm above the umbilicus can occasionally be stronger than usual and create a deep horizontal line.
What is the attachment of Camper's fascia to the skin above the umbilicus?
The attachments of Camper’s fascia to the skin above the umbilicus can occasionally create a deep horizontal line. Things to Remember. In order to mimic this ideal anatomy and to create a beautiful result, the superficial landmarks are to be recreated.
Which layer of the superficial fascia is continuous?
The superficial fascia comprises two distinct layers: an outer, adipose layer lying subjacent to the dermis and an inner fibroelastic layer termed Scarpa’s fascia, the membranous layer of superficial fascia [ 1 ]. The fibrous layer with a membranous appearance –the fascia superficialis – is continuous and well organized.
What are the layers of the dermis?
The deeper structure called the dermis has two layers with no threshold between them. They are: 1 The papillary layer which is thinner and external 2 The reticular layer which is deeper and denser
Which muscle is divided by the linea alba?
The abdominal muscular anatomy is well known with one vertical muscle anteriorly and three large lateral muscles overlying each other inversely. The vertical rectus muscle is divided by the linea alba.
How many layers does the epidermis have?
The epidermis is formed of five layers, and the epithelial cells transform itself into a keratin layer, which constantly peels off. Dermis. The deeper structure called the dermis has two layers with no threshold between them. They are: The papillary layer which is thinner and external.