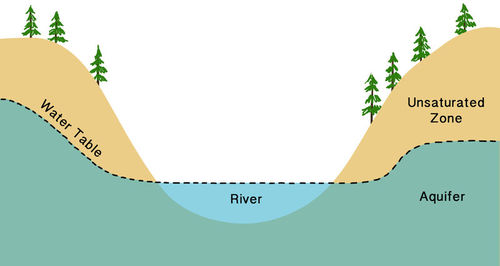
Groundwater forms when precipitation, rain, snow, sleet, hail, or freezing rain soaks into the ground It settles into three main layers- the saturated zone, the water table, and the unsaturated zone. is recharged by precipitation
What is the highest level of groundwater?
The groundwater level in the alluvial plains ranges from 192 masl to 216 masl (Figure 5.13) while the general groundwater level contour in the Delhi Ridge and its adjacent area is around 240 masl ( Figure 5.13 ).
What is the greatest use of groundwater?
Who uses the most water?
- China – 362 trillion gallons.
- United States – 216 trillion gallons.
- Brazil – 95 trillion gallons.
- Russia – 71 trillion gallons.
- Mexico – 53 trillion gallons.
- India – 30 trillion gallons.
- England – 20 trillion gallons.
- France – 20 trillion gallons.
What are the layers of the water?
The water falling on land collects in rivers and lakes, soil, and porous layers of rock, and much of it flows back into the oceans, where it will once more evaporate. The cycling of water in and out of the atmosphere is a significant aspect of the weather patterns on Earth.
Why does groundwater flow more slowly than surface water?
Why does groundwater flow more slowly than surface water? Groundwater flows faster where the hydraulic gradient and/or hydraulic conductivity are larger. Groundwater flow velocities are much slower than surface water flow velocities, except in limestone karst formations, where groundwater flows through caves and large solution channels.

What are the 3 zones of groundwater?
Water beneath the surface can essentially be divided into three zones: 1) the soil water zone, or vadose zone, 2) an intermediate zone, or capillary fringe, and 3) the ground water, or saturated zone.
What is a layer of underground water?
Aquifers are underground layers of rock that are saturated with water that can be brought to the surface through natural springs or by pumping.
What are the layers underground?
Rocks, clay, sand, silt and all nonliving things underground are explored. Earth's core, mantle, and crust are also discussed....Soil, Silt, and Sand: Layers of the Underground.Dewey577.5/7GenreInformationalReading LevelGrades 1-2Interest LevelGrades 1-3GRLN18 more rows
What are the 4 groundwater zones?
The unsaturated zone, capillary fringe, water table, and saturated zone.
Which is the top layer of groundwater?
The upper surface where the groundwater is available is the water table. Water table marks the upper boundary of saturated zone just below unsaturated zone where water infiltrates from the surface.
What is the main source of groundwater?
precipitationMost groundwater originates as meteoric water from precipitation in the form of rain or snow. If it is not lost by evaporation, transpiration or to stream runoff, water from these sources may infiltrate into the ground.
What is groundwater water cycle?
Groundwater flows underground Some of the precipitation that falls onto the land infiltrates into the ground to become groundwater. If the water meets the water table (below which the soil is saturated), it can move both vertically and horizontally.
What are examples of groundwater?
The definition of groundwater, or ground water, is water located beneath the surface of the earth. The water that your well draws from under the ground is an example of groundwater. Water that exists beneath the earth's surface in underground streams and aquifers.
How is groundwater formed?
Most groundwater comes from precipitation. Precipitation infiltrates below the ground surface into the soil zone. When the soil zone becomes saturated, water percolates downward. A zone of saturation occurs where all the interstices are filled with water.
What is the level of groundwater?
Groundwater level is a term that is used in a relatively loose way, normally referring to the level, either below ground or above ordnance datum, at which soil or rock is saturated. This is also referred to as the water table and represents the top of the saturated zone. Above the water table lies the unsaturated zone.
What is water table map?
A depth-to-water table map or isobath map, as these names imply, shows the spatial distribution of the depth of the water table below the land surface.
How many types of groundwater wells are found?
two typesOpen wells and tube wells are the two types of wells.
How long does groundwater stay in the aquifer?
The amount of time that groundwater remains in aquifers is called its residence time, which can vary widely, from a few days or weeks to 10 thousand years or more . The top of the saturated zone is called the water table, and sitting above the water table is the unsaturated zone, where the spaces in between rocks and sediments are filled ...
What are the threats to groundwater?
Another threat to groundwater is pollution by fertilizers, pesticides, and waste from septic tanks, all of which can seep down into aquifers from the soil surface. Groundwater is everywhere beneath the soil surface and can be ever-present in many places if allowed to recharge.
Why is groundwater extracted?
One important reason why groundwater is extracted through wells is to provide drinking water. In fact, groundwater provides drinking water for over 50 percent of the U.S. population, including almost 100 percent of the rural U.S. population. It is also used for domestic, industrial, and commercial purposes, though most groundwater is actually used ...
What is the water that has travelled down from the soil surface and collected in the spaces between sediments and the crack
Groundwater. Water that has travelled down from the soil surface and collected in the spaces between sediments and the cracks within rock is called groundwater. Groundwater fills in all the empty spaces underground, in what is called the saturated zone, until it reaches an impenetrable layer of rock. Groundwater is contained and flows ...
Where is the artesian well located?
An old well located in the Moroccan desert. Groundwater has been an extremely important source of water for many years, especially in arid climates. Photograph by Tatsiana Volskaya. aquifer. Noun. an underground layer of rock or earth which holds groundwater. artesian well. Noun.
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. The upper surface of the saturated zone is called the water table. Contrary to popular belief, groundwater does not form underground rivers. It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock, ...
How long does groundwater stay in an aquifer?
As a result, water could remain in an aquifer for hundreds or thousands of years. Groundwater is the source of about 40 percent of water used for public supplies and about 39 percent of water used for agriculture in the United States.
How many people rely on groundwater for drinking water?
The quality of our Nation's waters: Water quality in principal aquifers of the United States, 1991-2010. About 130 million people in the United States rely on groundwater for drinking water, and the need for high-quality drinking-water supplies becomes more urgent as our population grows.
What is the purpose of the USGS?
USGS scientist tests groundwater samples for water quality. The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling.
What is the name of the material that fills the pores and fractures in underground materials?
It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock, much the same way that water fills a sponge. If groundwater flows naturally out of rock materials or if it can be removed by pumping (in useful amounts), the rock materials are called aquifers.
How much groundwater was withdrawn in 2015?
In 2015, about 84,600 million gallons per day (Mgal/d) of groundwater were withdrawn in the United States for various uses including public supply, self-supplied domestic, industrial, mining, thermoelectric power, aquaculture, livestock, and irrigation.
When is Groundwater Awareness Week?
In recognition of National Groundwater Awareness Week, March 5–11, 2017, here’s an opportunity to put your knowledge of this vital resource to the test! Attribution: Water Resources.
What is Groundwater?
Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand and rock. It is stored in and moves slowly through geologic formations of soil, sand and rocks called aquifers.
How much do we depend on groundwater?
Groundwater supplies drinking water for 51% of the total U.S. population and 99% of the rural population.
What is the relationship between groundwater and surface water?
The hydrologic cycle. Groundwater and surface water are essentially one resource, physically connected by the hydrologic cycle in which water evaporates, forms clouds, and falls to the ground as rain or snow. Some of this precipitation seeps into the ground and moves slowly into an underground aquifer, eventually becoming groundwater.
Where is groundwater stored?
Groundwater is an important source of water stored in the earth beneath our feet, in spaces between sand, soils, and fractured rock known as an aquifer. Layers of aquifers make up a groundwater basin.
How much does groundwater contribute to the state?
During dry years, groundwater contributes up to 46 percent (or more) of the statewide annual supply, and serves as a critical buffer against the impacts of drought and climate change. Many municipal, agricultural, and disadvantaged communities rely on groundwater for up to 100 percent of their water supply needs.
What happens when groundwater is extracted in excess of what nature or manmade recharge efforts can replenish?
When groundwater is extracted in excess of what nature or manmade recharge efforts can replenish, groundwater elevations drop. Low groundwater elevations can cause the ground to gradually sink, a phenomenon known as subsidence.
There are rivers flowing below our feet ... a myth?
Have you ever heard that there are rivers of water flowing underground? Do you think it is true? Actually, it is pretty much a myth. Even though there are some caverns, lava and ice tubes, and horizontal springs that can carry water, the vast majority of underground water occupies the spaces between rocks and subsurface material.
Sometimes when you dig a hole ... watch out!
If an aquifer is under enough pressure, an artesian well tapping the aquifer can result in pressurized water shooting above the land surface.
How does groundwater form?
Groundwater forms when precipitation, rain, snow, sleet, hail, or freezing rain soaks into the ground It settles into three main layers- the saturated zone, the water table, and the unsaturated zone. is recharged by precipitation.
What is the meaning of "aquifer"?
aquifer. underground layer of permeable rock from which groundwater can be removed. impermeable. not allowing a fluid to pass through. permeable. allowing a fluid to pass through. porosity. amount of air space between soil or rock particles. water table.
Is the water table always in the same place?
always stays in the same place. The water table can be anywhere from a foot to hundreds of feet below the surface. It is not always in the same place, and it may rise or fall, depending on the amount of precipitation and the amount that people pump out of the ground.
