Muscular System Levels of Organization Microscopic level — sarcomere and myofibrils. Cell level — myoblasts and myofibers. Tissue level — neuromuscular junctions and fascicles. Organ level — major skeletal muscles of the body. Microscopic level — sarcomere and myofibrilsmyofibrilsWithin each muscle
What is the most highly organized tissue in the body?
nervous tissue function most highly organized tissue in the body; controls and coordinates body activites; allows us to perceive our environment and to adapt to changing conditions; coordinates skeletal muscles; allows for sight, tast, smell and hearing; controls our emotions and reasoning capabilities; allows us to learn through the memory process
What is the strongest muscle in the body Quizlet?
The strongest muscle based on its weight is the masseter. With all muscles of the jaw working together it can close the teeth with a force as great as 55 pounds (25 kilograms) on the incisors or 200 pounds (90.7 kilograms) on the molars. The uterus sits in the lower pelvic region.
What is the level of organization?
What are the 5 levels of organization in order? The correct sequence of the levels of biological organization are organism, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere. Molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere. Cell, tissue, organ, system, and finally, organism.
Do muscles work together to form tissue?
From left to right: single muscle cell, multiple muscle cells together forming muscle tissue, organ made up of muscle tissue (bladder), and organ system made up of kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra. At each level of organization—cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems—structure is closely related to function.
What is the organization of muscle cells?
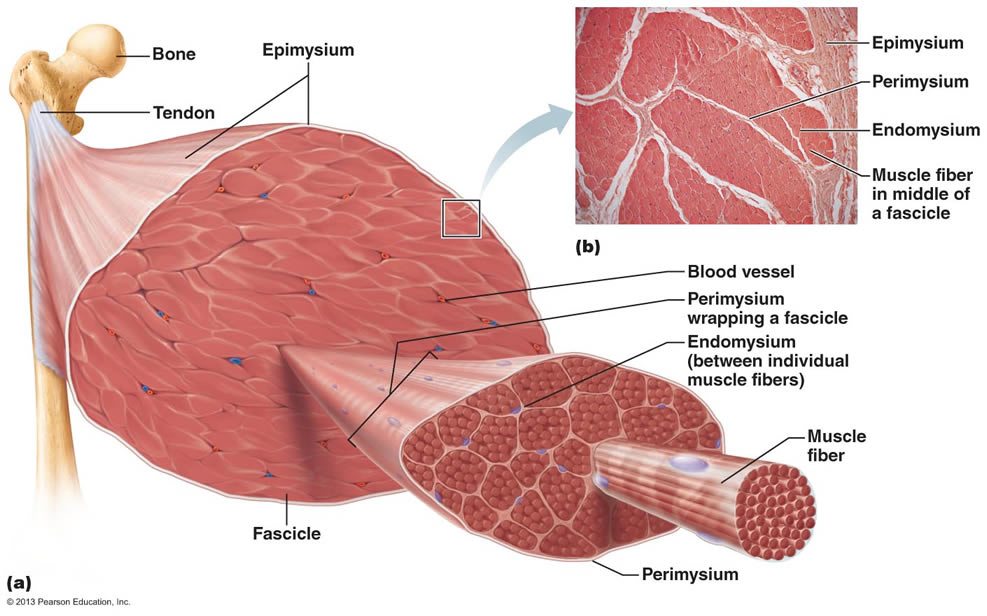
The organization of skeletal muscle Each fascicle is joined together to form one muscle cell. Muscle fibers are connected by various kinds of connective tissue. A thin fiber of connective tissue called endomysium surrounds each muscle fiber. In endomysium, elastic fiber collagen is found in areolar connective tissues.
What are the three levels of muscle structure?
How are the skeletal muscles structured?Epimysium: The outermost layer of tissue surrounding the entire muscle.Perimysium: The middle layer surrounding bundles of muscle fibers.Endomysium: The innermost layer surrounding individual muscle fibers.
What are the organizational levels of muscle from smallest to largest?
Terms in this set (6)smallest. myofilament.myofibril.muscle fiber (cell)fascicle.muscle.largest. muscle group.
What is the simplest level of organization in muscle?
The simplest level is the chemical level, which includes tiny building blocks such as atoms. Cells are the smallest functional units of life. Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function.
What are the 3 types of muscles and their characteristics?
The three main types of muscle include:Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. ... Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. ... Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
What are the 4 main characteristics of muscle tissue?
All muscle tissues have 4 characteristics in common:excitability.contractility.extensibility - they can be stretched.elasticity - they return to normal length after stretching.
Which is the smallest unit of muscle organization and structure?
The sarcomere is the smallest functional unit of a skeletal muscle fiber and is a highly organized arrangement of contractile, regulatory, and structural proteins.
What level of organization is the highest?
The organism level is the highest level of organization. An organism is a living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life.
What are the six levels of organization of the body?
Life processes of the human body are maintained at several levels of structural organization. These include the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism level.
What are the levels of organizations?
Typical levels of organization that one finds in the literature include the atomic, molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organismal, group, population, community, ecosystem, landscape, and biosphere levels.
How are whole muscle organized?
An individual skeletal muscle may be made up of hundreds, or even thousands, of muscle fibers bundled together and wrapped in a connective tissue covering. Each muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath called the epimysium. Fascia, connective tissue outside the epimysium, surrounds and separates the muscles.
What are the different levels of organization in order and define each?
There are five levels: cells, tissue, organs, organ systems, and organisms. All living things are made up of cells. This is what distinguishes living things from other objects. Cells are the basic building blocks of all organisms.
What is the structure of muscles?
Each muscle is made up of groups of muscle fibers called fascicles surrounded by a connective tissue layer called perimysium. There are multiple units of individual muscle fibers within each fascicle surrounded by endomysium, a connective tissue sheath.
What are the three components of a muscle quizlet?
Muscle fascicle- A bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue. Muscle fiber- The muscle cell, functional contractile unit of muscle tissue. Sarcomere- Smallest functional unit of the muscle fiber containing myosin and actin.
What is the structure of the muscle tissue?
The muscular tissues are bundled together and surrounded by a tough connective tissue similar to cartilage known as epimysium. The bundle of nerve cells that run in long fibers called fascicles are surrounded by the epimysium. The fascicles are surrounded by a protective layer known as perimysium.
What are the three types of muscle tissue which type is voluntary?
Muscle tissue can be categorized into skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, and cardiac muscle tissue. Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control.
What is the structure of a muscle cell?
Structure of a Muscle Cell. As seen in the image below, a muscle cell is a compact bundle of many myofibrils. Each myofibril is made of many sarcomeres bundled together and attached end-to-end. A specialized form of the endoplasmic reticulum, known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum, extends in and around these myofibril bundles.
What is muscle cell?
A muscle cell, known technically as a myocyte, is a specialized animal cell which can shorten its length using a series of motor proteins specially arranged within the cell. While several associated proteins help, actin and myosin form thick and thin filaments which slide past each other to contract small units of a muscle cell. These units are called sarcomeres, and many of them run end-to-end within a larger fiber called a myofibril. A single muscle cell contains many nuclei, which are pressed against the cell membrane. A muscle cell is a long cell compared to other forms of cells, and many muscle cells connect together to form the long fibers found in muscle tissue.
What happens when myosin heads attach to the actin filament?
This allows the myosin heads to attach to the actin filament. Once this happens, myosin can used the energy gained from ATP to crawl along the actin filament. When many sarcomeres are doing this at the same time, the entire muscle contract.
What makes up the thin filament of a muscle?
Repeating units of the protein actin make up the thin filament. Actin is supported by a number of accessory proteins which give the strands stability and allow the muscle to be controlled by nerve impulses. The actin filaments are supported on each end by specialized proteins.
How does ATP help muscle contraction?
While only a small percentage of the heads are attached at any one time, the many heads and continual use of ATP ensures a smooth contraction . The myosin crawls until it reaches the Z plate, and full contraction has been obtained. The SR is continually removing Ca 2+ from the cytoplasm, and once the concentration falls below a certain level troponin rebinds to tropomyosin, and the muscle releases.
Which protein connects the Z plates together and prevents the sarcomere from being overstr?
Another large protein, titin, connects the Z plates together and prevents the sarcomere from being overstretched when it is not contracting. These proteins cannot be seen in the image below. Actin is covered by two additional proteins, troponin and tropomyosin.
What is the mitochondrion?
Mitochondria are densely packed throughout muscle cells, to provide a constant flow of ATP. The entire cell is covered in a specialized cell membrane known as the sarcolemma. The sarcolemma has special opening which allow nerve impulses to be passed into transverse tubules. Below is a blown up view of each sarcomere.
What are the layers of organization in the muscular system?
Layers of Organization in the Muscular System. Individual muscles are composed of bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. Different kinds of connective tissue aid the organization of muscle fibers into muscles.
What organs are skeletal muscles made of?
Individual muscles are the organs of the muscular system. Each skeletal muscle is composed of individual muscle cells called muscle fibers. Muscle fibers are arranged into a bundle called a fascicle that is surrounded by connective tissue.
What is the tissue that surrounds muscles?
And these bundles of fascicles together compose the whole muscle, which is encased with epimysium. Epimysium is a thick, elastic tissue made of collagen that surrounds whole muscles and prevents them from rubbing against other muscles or bones.
What is the tissue that connects the muscle fibers together called?
Each individual muscle fiber is surrounded by a thin, wispy connective tissue called endomysium. Endomysium is made of areolar connective tissues containing the elastic fiber collagen. Endomysium provides a thin, loose structure that connects the muscle fibers together within the fascicle and provides a supportive environment for the muscle fibers ...
What is the pennate muscle?
Another major type of muscle⎯pennate muscle⎯contains tendons that run along its entire length. Fascicles extend from this tendon at an angle; the word pennate comes from penna, the Latin word for feather. In pennate muscles, shorter fascicles are arranged like barbs of a feather extending from the quill.
What determines the strength and directionality of a muscle contraction?
The orientation of the muscle fascicles , bundles of muscle fibers, determines the strength and directionality of a muscle contraction. The orientation of the fascicles within a muscle determines the strength and directionality of that muscle's contraction.
What is the bundle of connective tissue that makes up the muscle fibers?
Muscle fibers are arranged into a bundle called a fascicle that is surrounded by connective tissue. Many fascicles are bundled together to make up the muscle. Different kinds of connective tissue aid this organization of muscle fibers into muscles. Each individual muscle fiber is surrounded by a thin, wispy connective tissue called endomysium.
Which level of the body consists of groups of tissues working together to perform a higher-level function?
The organ level, which consists of groups of tissues working together to perform a higher-level function
What is the hierarchy of organization within the body?
We can model the hierarchy of organization within the body as comprised of organs, tissues, cells, cell organelles, macromolecules, molecules and finally atoms.
How does an alteration in the structure of a protein affect other levels?
An alteration in the structure of a protein (macromolecule level) can prevent a cell from functioning properly; this improper function can affect the tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole body. And the reverse is true: changes to the body (organism level) can affect organs, tissues, cells and molecules.
How is structure related to function?
At every level of organization, structure is related to function. For example water is able to perform many of its unique and life-sustaining properties because of its structure. It is a bent polar molecule that can form attractions with neighboring water molecules through hydrogen bonds. At the macromolecular level, the unique structures of enzymes allow these proteins to help speed up reactions. On the cell and tissue level, the rigid matrix structure of your bones allows them to be able to support the weight of your body. At the organ level, the “J” shape of the stomach allows for partial segregation of its contents at the early stages of digestion.
What is sickle cell anemia?
This example describes sickle cell anemia, a genetic blood disorder. We can clearly see the connections between levels of organization. A seemingly tiny error at the genetic (chemical) level causes significant changes in the body’s systems at higher levels. Many genetic diseases arise in this way—through small alterations in the genetic code.
Which level contains the smallest living entity?
The cell level, which consists of individual cells; this is the smallest level that contains living entities
Is the human body a complex system?
The human body is a complex, hierarchical system—that is, a system made up of smaller subsystems, which are themselves made up of even smaller systems. We commonly study these different hierarchical levels—levels of organization—separately. By breaking down the complex system into simpler parts, we can make the whole system easier to understand. This “reductionist” approach, reducing a complex system to simpler components, is central to how we practice modern science.
Where are molecules found?
They can be found in all matter, living and non-living. Molecules make up the most basic structures of living beings. Two biological disciplines that focus on this level are biochemistry and molecular biology.
What is the basic unit of life?
Cell. A cell is the basic unit of life. There are two kinds of cells: plant cells, which have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose molecules, and animal cells, which have flexible cell membranes.
What is tissue made of?
Tissue is made of cells that work together to perform a certain task. Muscle tissue, connective tissue, and neural tissue are some types of tissue. Histologists are an example of biologists who work at this level.
What is a group of multiple organisms of the same species within a specific area?
A population is a group of multiple organisms of the same species within a specific area. For example, a pride of lions in Kenya, Africa, is a population .
What is biology in biology?
Updated October 07, 2019. Biology is the study of life. Since life is such a broad topic, scientists break it down into several different levels of organization to make it easier to study. These levels start from the smallest unit of life and work up to the largest and most broad category.
Which system uses the lungs, airways, and respiratory muscles to inhale oxygen and release carbon dioxide in animals?
The respiratory system , for example, uses the lungs, airways and respiratory muscles to inhale oxygen and release carbon dioxide in animals. Physiologists study the function of parts of the body as they work together.
What are the components of an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is made up of all the communities in a certain area, as well as all the non-living, physical components of the environment. Rocks, water and dirt are a part of an ecosystem. Ecologists may study populations, communities, or whole ecosystems.
