
Ligaments are soft tissue structures that connect bones to bones. There are several important ligaments in the shoulder. Glenohumeral Ligaments (GHL): A joint capsule is a watertight sac that surrounds a joint. In the shoulder, the joint capsule is formed by a group of ligaments that connect the humerus to the glenoid.
Why is the shoulder joint also called the glenohumeral joint?
Where the rounded top of the arm bone (humerus) contacts the shoulder blade is called the glenohumeral joint. A second joint on the top of the shoulder is where a different part of the shoulder blade, the acromion, connects to the collarbone.
What is the strongest ligament around the hip joint?
- The femoral nerve innervates the anterior aspect
- The obturator nerve supplies the inferior aspect
- The superior gluteal nerve supplies the superior aspect
- The nerve to the quadratus femoris innervates the posterior aspect.
What movements occur at the glenohumeral joint?
- Function: Adduction and medial rotation of the arm, stabilize glenohumeral joint
- Origin: Anterior aspect of the scapula
- Insertion: Lesser tubercle of the humerus
- Innervation: Subscapular nerves (C5, C6, C7)
What is meant by joint ligaments and cartilage?
• Ligament acts as strong binding material that fasten bones together, whereas cartilage protects bones and stops them from knocking together by acting as a cushion in between bones. • Ligaments are more elastic than cartilages. • Ligaments have little resistance to compression or shear than cartilages. • Cartilages are stiffer than ligaments.
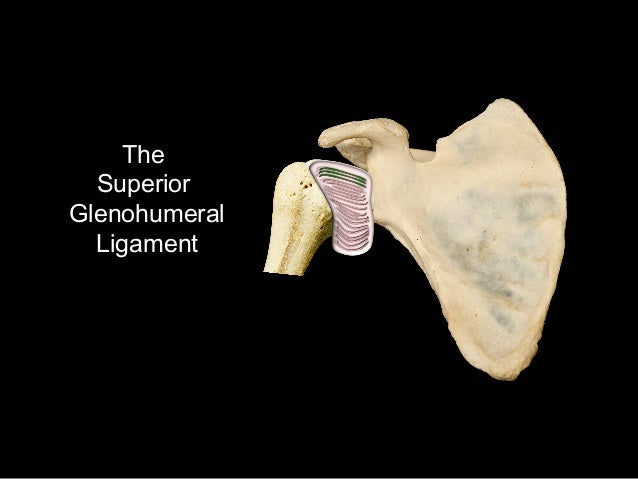
What are the 4 glenohumeral ligaments?
They are the superior, middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. They help hold the shoulder in place and keep it from dislocating . Coraco-clavicular Ligaments (CCL): These two ligaments (trapezoid and conoid ligaments) attach the clavicle coracoid process of the scapula.
What are the five ligaments of the shoulder?
The superior glenohumeral ligament (SGHL), middle glenohumeral ligament (MGHL), anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (AB-IGHL), glenoid, and humeral head are labeled as each ligament from its origin on the glenoid to its insertion on the humerus.
Where do the glenohumeral ligaments attach?
The superior glenohumeral ligament inserts into the cartilaginous surface of the anterior margin of the bicipital groove and the upper part of the lesser tubercle into a dimple known as the fovea capitis humeri.
What is the glenoid ligament?
Description. The glenoid labrum (glenoid ligament) is a fibrocartilaginous rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint.
What makes up the glenohumeral joint?
The glenohumeral joint is the one most people think of as the shoulder joint. It is formed where a ball (head) at the top of the humerus fits into a shallow cuplike socket (glenoid) in the scapula, allowing a wide range of movement.
What is anterior glenohumeral ligament?
In human anatomy, the glenohumeral ligaments (GHL) are three ligaments on the anterior side of the glenohumeral joint (i.e. between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus; colloquially called the shoulder joint).
What are the three glenohumeral ligaments?
Glenohumeral ligaments- Composed of a superior, middle, and inferior ligament, these three ligaments combine to form the glenohumeral joint capsule connecting the glenoid fossa to the humerus.
How many intrinsic glenohumeral ligaments are there?
three glenohumeral ligamentsThere are three glenohumeral ligaments (GHL), which are thickenings of the glenohumeral joint capsule and are important passive stabilizers of the joint.
How many ligaments are in the shoulder?
The ligaments in the shoulder are all named after the bones they connect. The clavicle has two ligaments involving the shoulder that help with stabilizing it to nearby bony structures: The acromioclavicular ligament and the coracoclavicular ligament both stabilize the clavicle to the shoulder blade.
What is the middle glenohumeral ligament?
The middle glenohumeral ligament (IGHL) runs oblique and posterior to the superior margin of the subscapularis muscle and blends with the anterior capsule. Distally it is attached to the anterior aspect of the proximal humerus, below the insertion of the superior glenohumeral ligament (SCGHL).
Are the glenohumeral ligaments intracapsular?
0:077:18Glenohumeral Ligaments, ligaments of the shoulder - Dr. Nabil EbraheimYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe glenohumeral ligaments. There are three important villa neuroma ligaments the superior venaMoreThe glenohumeral ligaments. There are three important villa neuroma ligaments the superior vena amoris ligament. The middle glenohumeral ligament. And the inferior glenohumeral ligament then feel your
Which group of ligaments contributes to the formation of the glenoid labrum?
Cards In This SetFrontBackWhich group of ligaments contributes to the formation of the glenoid labrum?GlenohumeralWhich rotator cuff muscle inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus?SubscapularisWhich nerve is compressed in carpal tunnel syndrome?Median12 more rows
What is the glenohumeral ligament?
Glenohumeral ligaments. In human anatomy, the glenohumeral ligaments (GHL) are three ligaments on the anterior side of the glenohumeral joint (i.e. between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus; colloquially called the shoulder joint). Reinforcing the anterior glenohumeral joint capsule, the superior, middle, ...
Where are the ligaments located in the humerus?
The ligaments may be best seen by opening the capsule at the back of the joint and removing the head of the humerus: One on the medial side of the joint passes from the medial edge of the glenoid cavity to the lower part of the lesser tubercle of the humerus.
Which ligament is most important for shoulder stability?
The most important ligament involved in shoulder joint stability is the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament. During abduction of the arm the middle and inferior ligaments become taut while the superior ligament relaxes.
Where is the GHL located?
In human anatomy, the glenohumeral ligaments (GHL) are three ligaments on the anterior side of the glenohumeral joint (i.e. between the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus; colloquially called the shoulder joint).
Why is the humerus delayed?
By rotating the humerus laterally, this contact is delayed because the greater tubercle is pulled back so that the bicipital groove faces the coracoacromial ligament. This slightly slackens the inferior fibres of the glenohumeral ligament, allowing an abduction of 90°.
Which ligaments play a role in the stability of the head of the humerus?
Reinforcing the anterior glenohumeral joint capsule, the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments play different roles in the stability of the head of the humerus, depending on arm position and degree of rotation. The ligaments of glenohumeral joint.
What happens to the humerus when you abduct your arm?
During abduction of the arm, the middle and inferior ligaments become taut while the superior ligament relaxes. The radius of curvature of the head of the humerus is greater superiorly than inferiorly, which further stretches these ligaments so that they keep the articular surfaces of the joint in their close-packed position.
Where is the middle GHL?
The middle GHL on the medial side of the joint passes from the medial edge of the glenoid cavity to the lower part of the lesser tubercle of the humerus. The inferior GHL at the lower part of the joint extends from the under edge of the glenoid cavity to the under part of the anatomical neck of the humerus. In addition to these, the capsule is ...
Why is the humerus delayed?
By rotating the humerus laterally, this contact is delayed because the greater tubercle is pulled back so that the bicipital groove faces the coracoacromial ligament. This slightly slackens the inferior fibers of the glenohumeral ligament, allowing an abduction of 90°.
What is the glenohumeral joint?
Glenohumeral joint (Articulatio glenohumeralis) The glenohumeral, or shoulder, joint is a synovial joint that attaches the upper limb to the axial skeleton. It is a ball-and-socket joint, formed between the glenoid fossa of scapula (gleno-) and the head of humerus (-humeral). Acting in conjunction with the pectoral girdle, ...
Which ligaments limit the movement of the GH joint?
Several ligaments limit the movement of the GH joint and resist humeral dislocation. These are the coracohumeral, glenohumeral and transverse humeral ligaments. Glenohumeral and transverse humeral are capsular ligaments while coracohumeral is an accessory ligament.
What muscles are involved in the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff muscles are four muscles that form a musculotendinous unit around the shoulder joint. These are the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis muscles. The function of this entire muscular apparatus is to produce movement at the shoulder joint while keeping the head of humerus stable and centralized within the glenoid cavity.
What nerve innervates the glenohumeral joint?
The glenohumeral joint is innervated by the subscapular nerve (C5-C6), a branch of the posterior cord of brachial plexus. The joint capsule is supplied from several sources; suprascapular nerve supplies the posterior and superior aspects. axillary nerve innervates the anteroinferior part of the capsule.
What is the articulation between the spherical head of the humerus and the conca
The glenohumeral joint is the articulation between the spherical head of the humerus and the concave glenoid fossa of the scapula. Being a synovial joint, both articular surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage. The glenoid fossa is a shallow pear-shaped pit on the superolateral angle of scapula.
What ligaments support the humerus?
It acts to limit inferior translation and excessive external rotation of the humerus. The superior, middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments support the joint from the anteroinferior side. They have a weak stabilizing function, each acting to limit the maximum amplitude of certain arm movements;
Which muscle is the prime flexor of the glenohumeral joint?
Teres minor, infraspinatus, deltoid. The prime flexors of the glenohumeral joint are the deltoid (anterior fibers) and pectoralis major (clavicular fibers) muscles. While coracobrachialis and the long head of biceps brachii assist as weak flexor muscles.
Which ligaments are in the anterior capsule?
The anterior portion of the capsule is reinforced by the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments which form a Z-shaped pattern on the capsule. The muscles of the rotator cuffact to reinforce the joint capsule superiorly, posteriorly, and anteriorly.
What is the open packed position of the GH joint?
The open packed position of the GH Joint is around 50 degrees of Abduction with slight Horizontal Adduction and External Rotation. However, the point of maximal capsular laxity has been found to be 39 degrees of Abduction in the Scapular Plane, which suggests that the open packed position may be close to neutral position of the shoulder.
What is the function of the labrum?
The labrum serves to deepen the glenoid fossa by around 50%, allowing for more contact area between the surface of glenoid and the humeral head. The increase in contact area also enhances joint stability. Common pathologies of the labrum include SLAP lesions and Bankart lesions.
What are the pathologies of the labrum?
Common pathologies of the labrum include SLAPlesions and Bankart lesions. Bursae[edit| edit source] Multiple bursae are distributed throughout the shouldercomplex, however, the subacromial bursa is one of the largest bursae in the body.
Which plane is the humerus on?
Elevation of the humerus on the glenoid in the scapular plane, which is midway between the coronal and sagittal planes. Horizontal Adduction[edit| edit source] Movement of the humerus on the glenoid in a medial direction, usually accompanied with some degree of shoulder flexion.
What are the three bands of the glenohumeral ligament?
The glenohumeral ligaments are three bands, called the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligament, that radiate inferolaterally from the glenoid labrum to blend with the joint capsule, where it attaches to the anatomical neck of the humerus. These ligaments reinforce the anterior part of the joint capsule.
Which ligament runs from the scapula to the humerus?
There are the glenohumeral ligaments, which are thickenings found within the joint capsule; the coracohumeral ligament, which runs from the scapula to the humerus; and the coraco- acromial ligament, which runs from the coracoid process to the acromial process of the scapula.
What is the glenoid cavity of the humerus?
So, the head of the humerus fits into this shallow glenoid cavity. The glenoid cavity is actually so shallow that it only covers one-third of the humeral head. Having a shallow glenoid cavity allows for exceptional mobility as the humeral head can rotate freely to allow us an impressive range of motion.
What is the glenoid labrum?
At the same time, the contour of the glenoid cavity is lined by a fibrocartilaginous rim, called the glenoid labrum, which makes the cavity a little bit deeper, reducing the chance for dislocations. Like any respectable synovial joint, the glenohumeral joint is covered by a tough, but loose, joint capsule with an internal synovial lining.
Where are the bursae in the glenohumeral joint?
There is one between the capsule and the tendon of the subscapularis muscle called the subtendinous bursa of the subscapularis and another one right under the acromion called the subacromial bursa.
Where is the joint capsule located?
The joint capsule extends from the anatomical neck of the humerus, to the margin of the glenoid. This capsule has two apertures, or passageways. The first one is between the tubercles of the humerus, which provides passage for the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii.
What is the most mobile joint in the body?
The glenohumeral joint, also known as the shoulder joint, is a ball and socket type of synovial joint: the ball being the head of the humerus, and the socket being the glenoid cavity of the scapula. The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in our body, and it allows us to do everything from pull ups, to throwing a baseball, ...
What is the most remarkable feature of the glenohumeral joint?
The most remarkable feature of the glenohumeral joint is its ability to precisely stabilize the humeral head in the center of the glenoid on one hand and to allow a vast range of motion on the other. This balance of stability and mobility is achieved by a combination of mechanisms particular to this articulation.
Which joint does not have isometric articular ligaments?
In contrast to hinge-like joints with shallow sockets such as the knee interphalangeal joints elbow and ankle the glenohumeral joint does not offer isometric articular ligaments which provide stability as the joint is flexed around a defined anatomical axis.
What is a glenoid version?
Glenoid version is the angle that the glenoid center line makes with the plane of the scapula (see figure 22). The glenoid center line usually points a few degrees posterior to the plane of the scapula (see figure 22). Changing the version of the glenoid articular surface imposes a corresponding change in the humeroscapular positions in which the net humeral joint reaction force will be contained by the effective glenoid arc. Glenoid version may be altered by glenoid dysplasia (see figure 23) (Wirth et al 1993) fractures glenoid osteotomy (Wirth et al 1994) and glenoid arthroplasty. Abnormal glenoid version positions the glenoid fossa in an abnormal relationship to the forces generated by the scapulohumeral muscles. Normalizing abnormal glenoid version is often a critical step in glenohumeral reconstruction.
What is the net humeral joint reaction force?
Footnote 1: The "net humeral joint reaction force" is the resultant of all muscular ligamentous inertial gravitational and other external forces applied to the head of the humeral head (other than the force applied by the glenoid).
What is the effective shape of the glenoid?
As the humeral head is translated from the center of the glenoid to the rim in a given direction the center of the humeral head traces the glenoidogram which has a characteristic gull-wing shape.
Which muscles are oriented to compress the humeral head into the glenoid fossa?
When the humerus is in this position most of the humeroscapular muscles are oriented to compress the humeral head into the glenoid fossa. Alternatively if the scapula is maximally retracted the humerus is almost at right angles to the glenoid center line.
Does the glenohumeral joint have a stabilizing socket?
About the glenohumeral joint. In contrast to the hip joint the glenohumeral joint does not offer a deep stabilizing socket. An acetabular-like socket would limit motion by contact of the anatomic neck of the humerus with its rim. Instead the small arc of the glenoid captures relatively little of the humeral articular surface ...
