How many ligaments does the hip have?
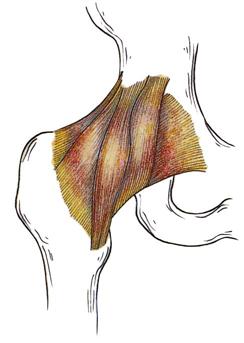
In the hip, the joint capsule is formed by a group of three strong ligaments that connect the femoral head to the acetabulum. These ligaments are the main source of stability for the hip.
Are there ligaments in the hip joint?
The hip joint is encircled with ligaments to provide stability to the hip by forming a dense and fibrous structure around the joint capsule. The ligaments adjoining the hip joint include: Iliofemoral ligament - This is a Y-shaped ligament that connects the pelvis to the femoral head at the front of the joint.
Which of the 3 ligaments of the hip joint is the strongest?
Iliofemoral ligament The central part of this ligament is thinner compared with its outer bands, giving the ligament an inverted Y-shape. It is the strongest ligament in the body and functions to prevent hyperextension of the hip joint when standing.
What are the muscles and ligaments in the hip?
They include the adductor magnus and adductor longus. The deeper muscles of the hip, or rotators, function to rotate the hip in and out. The hip rotators include the piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator internus, obturator externus, and quadratus femoris.
Which ligaments stabilize the hip joint?
Ligaments of the hip Outside of the hip joint, three ligaments help stabilize the joint from the outside. The iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, and ischiofemoral ligament. The iliofemoral ligament has a 'Y' shape and prevents hyperextension of the hip.
What does a torn ligament in the hip feel like?
Hip labral tear symptoms can include: Deep groin pain or pain in the buttocks on the side of the injured hip. A feeling or sound of clicking or locking when your hip is in motion. Hip pain, especially while it rotates in certain directions.
Can you tear your pubofemoral ligament?
In fact, the iliofemoral ligament, which connects the ilium (the largest bone of hip) to the femur (thigh bone), is the strongest ligament in the human body, with a tensile strength of 772 pounds. That means it would take more than 772 pounds of force to break that iliofemoral ligament.
What are the first signs of hip problems?
What Are the First Signs of Hip Problems?Hip Pain or Groin Pain. This pain is usually located between the hip and the knee. ... Stiffness. A common symptom of stiffness in the hip is difficulty putting on your shoes or socks. ... Limping. ... Swelling and Tenderness of the Hip.
What ligament prevents hip flexion?
The hip joint capsule and capsular ligaments The pubofemoral ligament prevents excess abduction and extension, ischiofemoral prevents excess extension, and the iliofemoral prevents hyperextension.
What is the ligament that runs from hip to knee?
The IT (iliotibial) band is a thick band of fibrous tissue that runs along the outside of your leg. It starts at the hip and extends to the outer side of the shinbone just below the knee joint. The IT band works with the muscles in your thigh to provide stability to the outside of the knee joint.
Can hip ligaments be repaired?
Surgery to repair a hip labral tear is usually done arthroscopically. This is a minimally invasive surgery in which the doctor makes small incisions (cuts) in the hip and uses miniature instruments to make the following repairs: Refixation or repair (stitching the torn tissue back together)
Where are hip ligaments located?
Pubofemoral ligament: Located on the anterior aspect of the hip joint, this ligament extends from the anterior portion of the pubic ramus to the anterior surface of the intertrochanteric fossa often blending with the inferior fibers of the iliofemoral ligament.
How do you treat a torn tendon in the hip?
For very small tears, treatment may begin conservatively with pain medication, corticosteroid injections and physical therapy. For more serious tears or when conservative treatment options don't provide relief and healing, surgery may be recommended.
What does a pulled hip muscle feel like?
Many people who experience hip flexor strain will have these symptoms as well: sudden, sharp pain in the hip or pelvis after trauma to the area. pain when lifting the leg. cramping, stiffness, and weakness in the muscles of the upper leg area.
What is the ligament that forms the hip called?
A special type of ligament forms a unique structure inside the hip called the labrum. The. labrum is attached almost completely around the edge of the acetabulum. The shape and the way the labrum is attached create a deeper cup for the acetabulum socket.
What are the three structures that make up the hip?
Ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Ligaments, tendons, and muscles play an important role in the function of the hip. Ligaments are soft tissue structures that connect bones to bones. A joint capsule is a watertight sac that surrounds a joint. In the hip, the joint capsule is formed by a group of three strong ligaments that connect ...
What is the band on the hip called?
A long tendon band runs alongside the femur from the hip to the knee. This is the iliotibial band. It gives a connecting point for several hip muscles. A tight iliotibial band can cause hip and knee problems, illustrating the interdependence of the ligaments, tendons, and muscles in the hip joint. A special type of ligament forms ...
What is the main source of stability for the hip?
These ligaments are the main source of stability for the hip. They help hold the hip in place. A small ligament connects the very tip of the femoral head to the acetabulum. This ligament, called the ligamentum teres, doesn’t play a role in controlling hip movement like the main hip ligaments .
Why do hamstrings help with hip extension?
Because the hamstrings cross the back of the hip joint on their way to the knee, they help to extend the hip, pulling it backwards. The interaction of the ligaments, tendons, and muscles in the hip joint plays a vital role in your ability to walk, run, move, and exercise.
Which muscle is in front of the hip?
The muscles that flex the hip are in front of the hip joint. These include the iliopsoas muscle. This deep muscle begins in the low back and pelvis and connects on the inside edge of the upper femur. Another large hip flexor is the rectus femoris. The rectus femoris is one of the quadriceps muscles, the largest group of muscles on the front ...
What causes clicking in the hip?
This small rim of cartilage can be injured and cause pain and clicking in the hip. The hip is surrounded by thick muscles. The gluteals make up the muscles of the buttocks on the back of the hip. The inner thigh is formed by the adductor muscles.
What are the two types of ligaments in the hip?
The intracapsular ligaments of the hip joint are found inside the capsule and include the transverse ligament of the acetabulum and the ligament of the head of the femur.
Which ligaments are in the capsule of the hip joint?
The capsule of the hip joint is reinforced inferiorly by the pubofemoral ligament and posteriorly by the ischiofemoral ligament.
What is the acetabulum made of?
The acetabulum is formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium and pubic bones. It plays a significant role in the stability of the hip joint as it almost entirely encompasses the head of the femur. The acetabulum bears a prominent semilunar region known as the lunate surface that is covered by articular cartilage.
How does hip flexion affect knee extension?
Hip flexion is limited by the tension in the hamstrings when the knee is extended. Extension of the hip joint moves the thigh away from the trunk. Extension of the joint beyond the vertical is limited to about 30o by the tension of the capsular ligaments and the shape of the articular surfaces.
What is the name of the joint that connects the pelvic girdle to the lower limb?
Last reviewed: May 31, 2021. Reading time: 16 minutes. Hip joint (Articulatio coxae) The hip joint is a ball and socket type of synovial joint that connects the pelvic girdle to the lower limb. In this joint, the head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvic (hip) bone. The hip joint is a multiaxial joint ...
Where is the iliofemoral ligament located?
Iliofemoral ligament. The iliofemoral ligament is a thick triangular ligament that lies on the anterior and superior aspects of the hip joint, and blends with the joint capsule. Its proximal attachment is between the anterior inferior iliac spine and the acetabular rim.
Where is the hip joint located?
The hip joint is the articulation between the ellipsoid head of the femur and the hemispherical concavity of the acetabulum located on the lateral aspect of the hip bone. The femoral head is covered with articular ( hyaline) cartilage with the exception of a rough central depression, the fovea capitis, which is a surface of attachment for the ligament of the femoral head (ligamentum teres capitis femoris).
What is the hip joint?
The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint, formed by an articulation between the pelvic acetabulum and the head of the femur. It forms a connection from the lower limb to the pelvic girdle, and thus is designed for stability and weight-bearing – rather than a large range of movement.
What is the function of the hip joint?
The primary function of the hip joint is to weight-bear. There are a number of factors that act to increase stability of the joint. The first structure is the acetabulum. It is deep, and encompasses nearly all of the head of the femur.
What is the cartilage of the femur?
Both the acetabulum and head of femur are covered in articular cartilage, which is thicker at the places of weight bearing. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck posteriorly.
What is the intracapsular ligament?
The only intracapsular ligament is the ligament of head of femur. It is a relatively small structure, which runs from the acetabular fossa to the fovea of the femur. It encloses a branch of the obturator artery (artery to head of femur), a minor source of arterial supply to the hip joint.
Where is the acetabulum located?
The acetabulum is a cup-like depression located on the inferolateral aspect of the pelvis. Its cavity is deepened by the presence of a fibrocartilaginous collar – the acetabular labrum. The head of femur is hemispherical, and fits completely into the concavity of the acetabulum.
Which artery supplies the hip?
The arterial supply to the hip joint is largely via the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries – branches of the profunda femoris artery (deep femoral artery). They anastomose at the base of the femoral neck to form a ring, from which smaller arteries arise to supply the hip joint itself.
What is the cause of hip dislocation?
Congenital hip dislocation occurs as a result of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). It occurs when the Acetabulum is shallow as a result of failure to develop properly in utero
Which ligaments are responsible for the stability of the hip?
The iliofemoral ligament in the hip. The stability of the hip is increased by the strong ligaments that encircle the hip (the iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral ligaments). These ligaments completely encompass the hip joint and form the joint capsule.
What are the bones that make up the hip?
Bony Structures of the Hip. The hip is formed where the thigh bone (femur) meets the three bones that make up the pelvis: the ilium, the pubis (pubic bone) and the ischium. These three bones converge to form the acetabulum, a deep socket on the outer edge of the pelvis.
What is the lesser trochanter?
The lesser trochanter serves as the attachment site of the iliopsoas tendon, one of the muscles that allows you to bend your hip. It is important to remember that the actual hip joint lies deep in the groin area. This is important, because true hip joint issues are typically associated with groin pain.
Where does the femoral head fit?
The femoral head (ball) fits into the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis. The large round head of the femur rotates and glides within the acetabulum. The depth of the acetabulum is further increased by a fibrocartilagenous labrum that attaches to the outer rim of the acetabulum.
How thick is the cartilage on the hip?
Hip Anatomy, Function and Common Problems. Normally, a smooth cushion of shiny white hyaline (or articular) cartilage about 1/4 inch thick covers the femoral head and the acetabulum. The articular cartilage is kept slick by fluid made in the synovial membrane (joint lining).
What is the ligamentum teres?
It contains the artery of the ligamentum teres. In infants, this serves as a relatively important source of blood supply to the head of the femur. In adults, the ligamentum teres is thought by most to be more of a vestigial structure that serves little function. The ischiofemoral ligament of the hip.
Which bone is the longest?
The femur is the longest bone in the body. The neck of the femur connects the femoral head with the shaft of the femur. The neck ends at the greater and lesser trochanters, which are bony prominences of the femur that various muscles attach to.
What is the ligament around the hip?
By: Henry Halse. Published: 05 October, 2017. The ligaments around your hip help keep your bones together. They're tough enough to resist hundreds of pounds of force, but sometimes the strain is too great and they get damaged. To avoid injuring them, you should be proactive and work to strengthen them.
What are tendons and ligaments?
What Ligaments Do. Ligaments and tendons are very similar. They're both bands of tight and tough connective tissue. They're mostly composed of collagen. Tendons connect bones to muscles and are slightly more elastic. Ligaments connect bones to other bones, so they have to be less giving.
Why do ligaments take longer to regenerate?
Ligaments don't have a very large blood supply, so it takes them longer to regenerate than other tissues like muscle. If a ligament becomes too stiff it's more prone to injury, similar to a rubber band that snaps when it loses its elasticity.
How to make ligaments regenerate faster?
According to an article from the Gatorade Sports Science Institute, you can make your ligaments regenerate faster than they normally would to help prevent or heal from injuries by combining exercise with nutritional supplements . Whichever supplement you use, try to ingest it 30 minutes before exercise.
How to get rid of a swollen hip?
How to: Start in an all-fours position on the ground. Your shoulders should be over your hands and your hips over your knees. Your spine should be flat. Raise your right knee off the ground and bring it forward as far as you can.
How long does it take for a hip to regenerate?
According to a 2017 study in Sports Medicine it takes about 10 minutes of exercise to fully stimulate your ligaments to regenerate.
Why is the hip so complex?
The hip is a complex joint because it can move in so many directions. There are five major ligaments in the hip and each holds a different part of the joint together. If you want to make your ligaments more resistant to injury or heal faster, you have to put them under tension.
Which ligaments are responsible for transferring forces from the legs to the upper body?
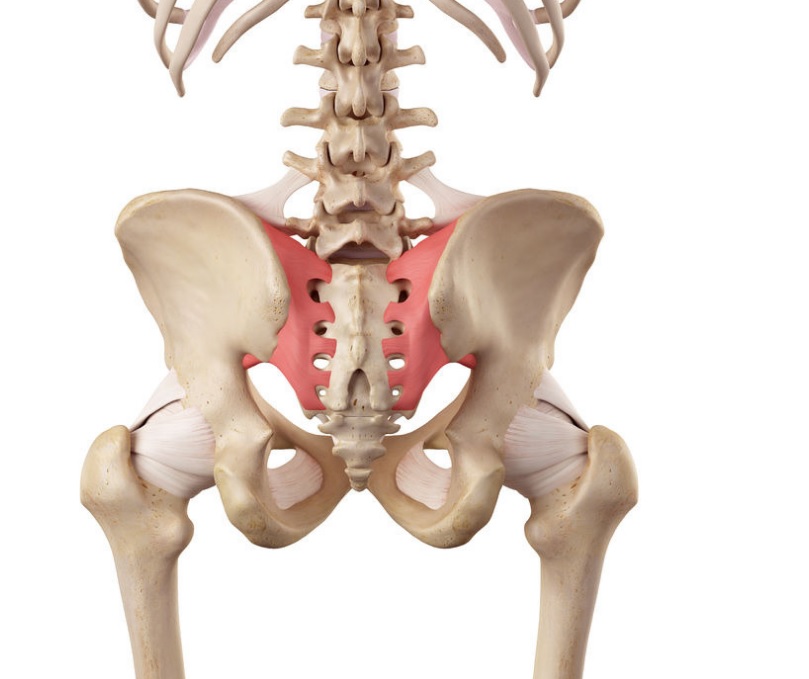
The long posterior sacroiliac ligament undergoes tension during the transmission of forces from the legs to the upper body and vice versa. 1. The back (posterior) part of the sacroiliac joint is stabilized by the posterior sacroiliac ligaments, which connect the back of the hip bones to the sacrum.
Which ligaments connect the sacroiliac joint?
The supporting and stabilizing ligaments of the sacroiliac joint connect the joint in several ways. While several ligaments connect the joint from the front and back, others are present between the joint surfaces, holding them together.
What is sacroiliac joint dysfunction?
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction Video. The distinctive bone structure and complex movement (s) of the sacroiliac joint are held together and powered by an extensive network of ligaments. The muscles surrounding the sacroiliac joint do not specifically move the joint, but the health of these muscles can influence the stability and motion of the joint.
What is the front portion of the sacroiliac joint?
The front portion of the joint is supplied by the iliolumbar artery, which originates either from the internal iliac or common iliac artery. 1,2. The venous drainage of the joint flows into the internal iliac vein. The vast majority of sacroiliac joint problems affect the joint’s ligaments and/or cartilage.
What is the posterior SI ligament?
The posterior SI ligament runs along the back of the sacroiliac joint and provides considerable stability. 2 The ligament connects the back of the hip bones (posterior-superior iliac spine and iliac crest) to the sacrum. There are two components of the posterior SI ligament: 2. Long posterior sacroiliac ligament.
What is the anterior sacroiliac ligament?
This ligament, sometimes called the ventral sacroiliac ligament, covers the front of the sacroiliac joint, which includes the articular (joint) capsule that encloses the joint in this area. The fibers of this capsule blend with the joint’s capsule in front and do not provide much support. 2.
Which ligaments create the greater sciatic foramen?
Iliolumbar ligament. The sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments create the greater sciatic foramen and the lesser sciatic foramen. 1,2 The largest nerve in the body, the sciatic nerve, passes through the greater sciatic foramen formed by these ligaments.