
Properties of Lipids
- Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body.
- Lipids are a heterogeneous group of compounds, mainly composed of hydrocarbon chains.
- Lipids are energy-rich organic molecules, which provide energy for different life processes.
- Lipids are a class of compounds characterised by their solubility in nonpolar solvents and insolubility in water.
- Lipids are significant in biological systems as they form a mechanical barrier dividing a cell from the external environment known as the cell membrane.
What are the 3 main functions of lipids?
- Growth and Maintenance. Share on Pinterest.
- Causes Biochemical Reactions.
- Acts as a Messenger.
- Provides Structure.
- Maintains Proper pH.
- Balances Fluids.
- Bolsters Immune Health.
- Transports and Stores Nutrients.
What are lipids and why do we need them?
What Are Lipids Used for in the Body?
- Energy Production and Storage. The primary role of lipids in your body is to provide energy for muscles and body processes. ...
- Insulation and Protection. Lipids are also used to insulate and protect your body. ...
- Digestion and Absorption. ...
- Cell Wall Structure. ...
- Hormone Production. ...
What are lipids and what do they do?
Lipids are a group of molecules in the body made up of fats, cholesterol, and animal waxes. They are everywhere in our bodies, including the membranes that line our cells, and they also make up bile, which helps break down fat for absorption.
Why are lipids good energy storage molecules because?
Why are lipids good for storing energy? they conserve more space because of their hydrophobicity than storage of hydrated glycogen and their is virtually no limit to storage space also they are less oxidized than glucose (give more energy) How do we get from large fat globules to small molecules which can be absorbed across the intestinal cell?
What are the characteristics of lipids quizlet?
What are the characteristics of lipids? Generally hydrophobic/ amphipatic. Water-insoluble organic compounds. Do not form large covalent polymers.
What are the two characteristics related to lipids?
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the recommended daily intake of lipids is 65 grams per day.Solubility. With the exception of phospholipids, which partially dissolve in water, all lipids are generally insoluble in water. ... High Energy Content. ... Digestion and Absorption. ... Types of Lipids.
What are the 4 main functions of lipids?
The Functions of Lipids in the BodyStoring Energy. The excess energy from the food we eat is digested and incorporated into adipose tissue, or fatty tissue. ... Regulating and Signaling. ... Insulating and Protecting. ... Aiding Digestion and Increasing Bioavailability.
What characteristics best allow you to identify a lipid?
Definition of Lipids Lipids can be distinguished from other organic molecules based on one characteristic: their inability to easily dissolve in water. On an atomic level this is related to a condition called polarity.
What are 5 characteristics of lipids?
Properties of LipidsLipids may be either liquids or non-crystalline solids at room temperature.Pure fats and oils are colorless, odorless, and tasteless.They are energy-rich organic molecules.Insoluble in water.Soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, chloroform, acetone, benzene, etc.No ionic charges.More items...•
What is a characteristic that all lipids share?
Fats, oils, and waxes are all examples of lipids. There are lots of lipids, but they all share the trait of being at least partially hydrophobic (meaning they won't mix with water).
What are the 7 functions of lipids?
5.3: Functions of LipidsFunctions of Lipids in the Body. Energy Storage. Regulating and Signaling. Insulating and Protecting. Transporting.Role of Lipids in Food. High Energy Source. Smell, Taste, Texture, and Satiety.
What are the 3 main lipids?
The three main types of lipids are triacylglycerols (also known as triglycerides), phospholipids, and sterols. 1) Triglycerides make up more than 95 percent of lipids in the diet and are commonly found in fried foods, butter, milk, cheese, and some meats.
What is lipids and its function?
A lipid is any of various organic compounds that are insoluble in water. They include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes and function as energy-storage molecules and chemical messengers.
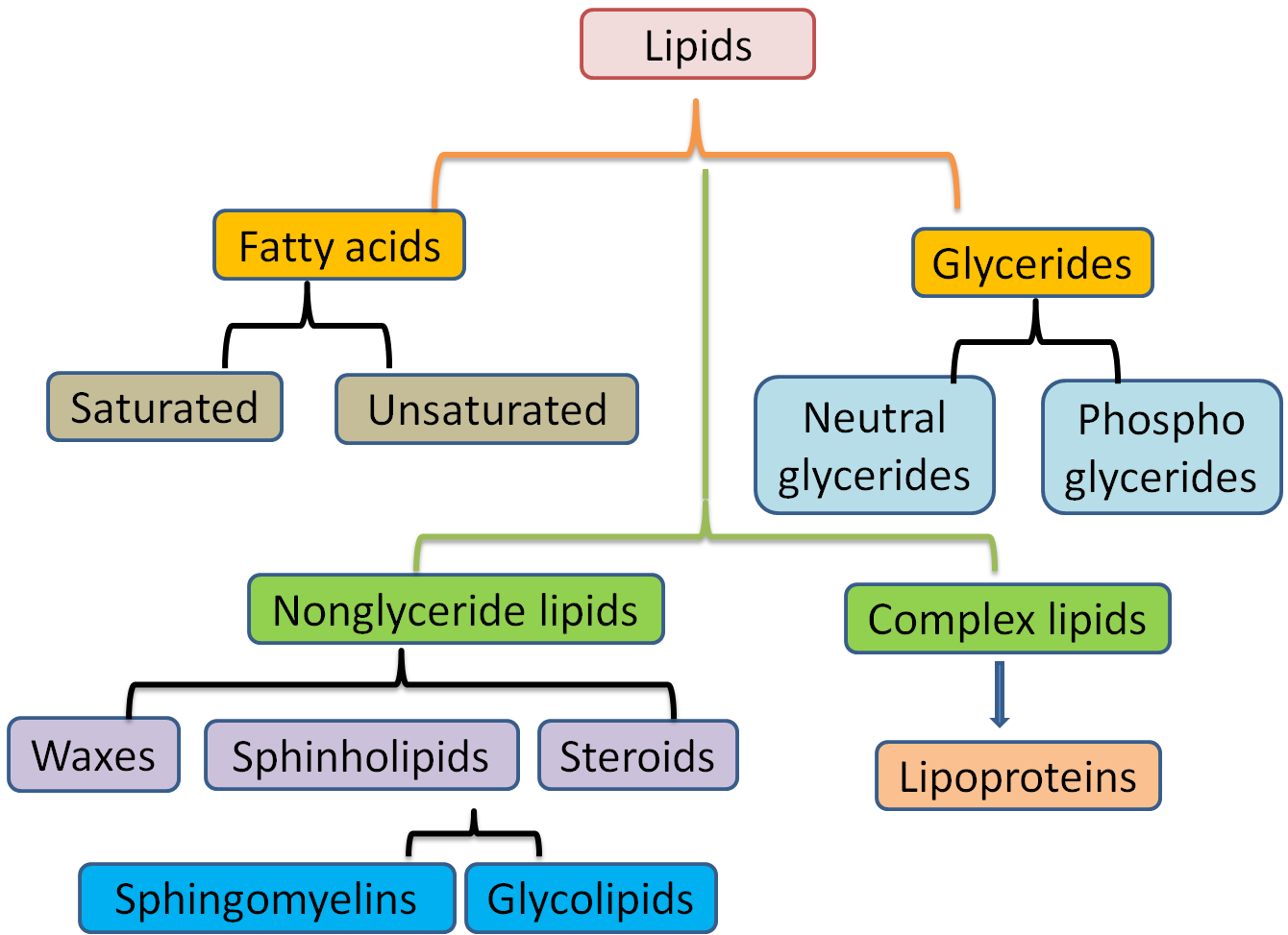
What are the 4 classification of lipids?
The first division (acid fats) contains long-chain and medium-chain fatty acids, the second one neutral fats) being divided into four groups : cholesterol, waxes, long-chain and medium-chain triglycerides.
What is one characteristic that lipids found in foods and in the body have in common?
What is one characteristic that lipids found in foods and in the body have in common? They are mostly in the form of triglycerides.
What are examples of lipids?
Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E and K), hormones and most of the cell membrane that is not made up of protein.
What are lipids made of?
Above all, they’re responsible for the storage of energy. Furthermore, they’re composed of carbon and hydrogen and contain sulfur, nitrogen, ...
What is the function of lipids?
The main function of lipids is as an energy reserve for the body. However, they also intervene in the production of hormones and the synthesis of vitamins, among others.
Why are lipids important?
The function of lipids is important as it impacts our overall health. Not only are they key as an energy reserve for the body, but they also intervene in other essential processes such as the transport of nutrients and the regulation of body temperature, among others. These substances are diverse and come from various sources.
Why are triglycerides high in blood?
That is they produce their energy reserves. As with cholesterol, an excess of triglycerides also tends to accumulate in the blood ves sels and in the rest of the body. This is why high levels could lead to health problems.
How many calories does fat provide?
The main function of this substance is as a body energy reserve. One gram of fat can provide 9 kilocalories to the body. When a person has an excess of sugars, these are stored in the form of fat deposits. They’ll be used when other sources of energy, such as carbohydrates, are lacking.
Why is cholesterol important?
Thus, a certain amount of cholesterol is essential for the body to function properly. However, too much of it can lead to accumulation in the blood vessels. This could be a problem because there’s a greater risk of heart attacks or ischemic problems when the vessels become clogged .
What is the function of fat deposits in the body?
The fat deposits that accumulate under the skin and around the organs act as protectors from the cold. Fat traps heat and thus keeps the body warm.
What are the properties of lipids?
Lipids are a family of organic compounds, composed of fats and oils. These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body.
What are Lipids?
These organic compounds are nonpolar molecules, which are soluble only in nonpolar solvents and insoluble in water because water is a polar molecule. In the human body, these molecules can be synthesized in the liver and are found in oil, butter, whole milk, cheese, fried foods and also in some red meats.
What is the process of oxidation of fatty acids?
Lipid metabolism involves the oxidation of fatty acids to generate energy to synthesize new lipids from smaller molecules. The metabolism of lipids is associated with carbohydrate metabolism as the products of glucose are converted into lipids.
What is the lipid structure?
Lipid Structure. Lipids are the polymers of fatty acids that contain a long, non-polar hydrocarbon chain with a small polar region containing oxygen. The lipid structure is explained in the diagram below: Lipid Structure – Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids.
Why do fatty acids have a straight rod shape?
The saturated fatty acids have higher melting points compared to unsaturated acids of the corresponding size due to their ability to pack their molecules together thu s leading to a straight rod-like shape.
What is saponifiable lipid?
A saponifiable lipid comprises one or more ester groups, enabling it to undergo hydrolysis in the presence of a base, acid, or enzymes, including waxes, triglycerides, sphingolipids and phospholipids. Further, these categories can be divided into non-polar and polar lipids.
What is the name of the lipid that contains a phosphate group?
The name phospholipid is derived from the fact that phosphoacylglycerols are lipids containing a phosphate group.
What is a lipid?
Tolu Ajiboye. Published on November 12, 2020. A lipid is an organic molecule that can only dissolve in nonpolar solvents and will not dissolve in water. Lipids include hormones, fats, and oils and sometimes refer to fatty acids or derivatives of fatty acids. Lipids play key roles in the function of the body in both health and disease.
Why are lipids synthesized?
Lipids are synthesized or stored to support the cells and assist in essential processes. Lipids also have many external uses.
Why are lipids added to drugs?
Lipids are also added to certain drugs to enhance their delivery. 5 These lipid-based drug carriers offer benefits like increased half-life, improved absorption, and the ability to target a specific area of the body with the drug.
What to do if you are concerned about your lipid levels?
If you're concerned about your lipid levels, contact your healthcare provider. The lipid panel tests will give you the information you need to begin making lifestyle changes, like getting more exercise and changing your diet.
Why are trans fats important?
They reduce the risk of sudden death by a heart attack and prevent thrombosis, the formation of blood clots. Trans fats are fats that have been artificially hydrogenated to achieve a consistency desired in processed food production.
How many chains of hydrocarbons are in a fatty acid?
Fatty acids have different lengths of chains of hydrocarbons, from four to 36. Triglycerides can be saturated or unsaturated, which refers to whether they have double bonds between carbon atoms (unsaturated) or not (saturated). This has a variety of effects, including whether they are liquid or solid at room temperature.
What is the outermost layer of a cell?
Phospholipids make up the outermost layer of cells in the bodies of both animals and humans. They create a protective layer around the cells to help maintain them.
Why do phospholipids form lipid bilayers?
Phospholipids of cell membranes form a lipid bilayer because of their amphiphilic (containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions) characteristics.
What are the two types of fats that are present in humans?
They are the main types of fat present in humans and other animals. They can be in two forms: saturated fats that lack C = C bond groups, and unsaturated fats that have at least one or more C = C groups . Fatty acids contain a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group. Dehydration creates an ester linkage between the carboxyl group of fatty acids and the hydroxyl group of glycerol.
What are the two essential fatty acids?
Two essential fatty acids of particular importance are omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids can exert beneficial cardiometabolic effects, reduce inflammation and risk for cancer, and lead to beneficial behavioral and mood effects. Phospholipids (PL) consist of a hydrophilic head that includes a phosphate group and two hydrophobic tails made up of fatty acids that are linked together with an alcohol moiety. Phospholipids of cell membranes form a lipid bilayer because of their amphiphilic characteristics. Steroids are comprised of four rings with varying molecular configurations and possess a variety of biological functions. In animals, steroids have two main functions: form part of the cell membrane and serve as hormones. Example steroids and steroid hormones include sterol, cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, glucocorticoids (cortisol), and mineralocorticoids (aldosterone).
How many carbons are in fatty acids?
Fatty acids contain a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group that may span 4 to 36 carbons, with the average being 12 to 18. Dehydration creates an ester linkage between the carboxyl group of fatty acids and the hydroxyl group of glycerol. Lipases act on this region to digest fats into their constituent fatty acids and glycerol.
Which fat has a lower melting point than saturated fat?
Unsaturated fats that include one or more C = C groups and generally have a lower melting point than saturated fats and are liquid at room temperature.
How many carbon atoms are in a steroid?
The main structural component of steroids includes seventeen carbon atoms that are linked together in four rings: three are six-member cyclohexane rings and one five-member cyclopentane ring. The variation between steroids is based on what is attached to one or more of these four ring structures and the oxidation state of each of these rings, i.e., whether it is aromatic. Examples of steroids in animals include:
1- Lipids and fats are not synonymous
The terms "lipid" and "fat" are often used interchangeably, as if they had the same meaning. They are not really the same.
2- Saturated and unsaturated
Based on the characteristics of lipids, a classification is usually made that includes two types: saturated and unsaturated.
3- Insoluble in water
The main characteristic of lipids is that they do not dissolve in water. This is the product of the apolar character, also called hydrophobic, which has most of the lipids, and which conflicts with the polar characteristic of water, causing them to repel each other.
4- Soluble in organic solvents
Unlike water, there are some organic solvents that are also apolar, such as lipids. So, under that scenario, lipids can be diluted.
5- They reserve energy
Lipids are the most important energy reserve in animals, since they have a fairly high caloric level.
6- They insulate thermally
There are biological membranes that surround cells and that fulfill a protective function, because they isolate organisms from the environment that surrounds them and protect them from impacts between themselves.
7- Sources of essential fatty acids
The intake of lipids is necessary to achieve a healthy and balanced diet. The main reason why their intake is recommended is because the human body needs them for innumerable functions, and is not capable of producing them itself, so the lipids must come from outside.

What’s The Function of Lipids
Types of Lipids
- As detailed in an article published in the scientific Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal, the term “lipids” groups together various compounds that have relevant biological functions. Therefore, it’s important to understand their classification when talking about these substances. What types of lipids are there?
What’s The Function of Lipids in The body?
- Depending on their type, lipids carry out many essential body functions. According to a publication in Molecular Biology of the Cell, these are structural or signaling functions. We’ll detail some of the most important ones below.
Final Notes About The Function of Lipids
- The types and functions of lipids are varied and complex, although, in general, these organic compounds are essential for life. Also, to a certain extent, they’re decisive for the proper functioning of the body. However, some of them are harmful in excess. As you can see, you must try to adopt and maintain healthy lifestyle habits, especially when it comes to food. Also, schedu…