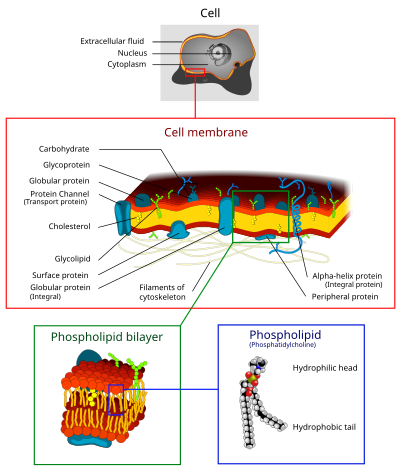
The main components of the cell membrane are lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
- Phospholipids and cholesterol are the two kinds of lipids present in cell membranes. ...
- There are two types of proteins in cell membranes based on how they are attached to the phospholipid bilayer – integral and peripheral. ...
- Carbohydrates are attached either to the phospholipids to form glycolipids, or to the proteins to form glycoproteins. ...
What are two main components of cellular membranes?
What are the components of cell membrane quizlet?
- Phospholipids. Hydrophobic head and fatty acid tail. …
- Cholesterol. Gives the membrane mechanical stability.
- Glycolipids. Phospholipid molecules that have a carbohydrate attached. …
- Channel Proteins. …
- Carrier proteins. …
- Glycoproteins.
What are the components the make up the cell membrane?
Other biochemical components of the membrane include:
- Amphipathic lipids: phospholipids, glycolipids, sterols, and cholesterol.
- Proteins, including integral proteins that act as membrane transporters and peripheral proteins that are loosely associated with the outside of the cell membrane and act as enzymes.
- Glycoproteins and glycolipids
What are the parts and functions of the cell membrane?
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
- Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.
- Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.
- Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues.
- Signal Receptors.
- intercellular junctions.
- Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
What are three characteristics of a cell membrane?
The main functions of the cell membrane are:
- Controls movement of fluids, ions, and other substances, such as organic molecules, in and out of the cells and organelles.
- Facilitate cell adhesion
- Regulate ion conductivity
- Cell signaling
- Attach to glycoproteins and an intracellular network of protein fibers, collectively called the cytoskeleton
What 4 components make up the cell membrane?
The major components of the cell membrane are phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids such as cholesterol. Together these components make up the fluid mosaic model.
What is the main component of the cell membrane quizlet?
The major components of a cell membrane are phospholipids, glycolipids, proteins, and cholesterol. It provides the container for the cell contents and allows only small uncharged molecules to pass through while keeping larger molecules at bay.
What are the two main components of the cell membrane quizlet?
Two main components are the phospholipid bilayer and the proteins.
Which of the following is the main component of the cell?
The cytoplasm, cell membrane and the nucleus are the 3 main parts of a cell.
Are the main component of all cell membranes quizlet?
What is the main component of the cell membrane? phospholipids; Although phospholipids have a polar head, the long fatty acid tails are nonpolar, making the membrane mostly nonpolar.
What is the major lipid found in membranes?
phospholipidsThe most abundant membrane lipids are the phospholipids. These have a polar head group and two hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails. The tails are usually fatty acids, and they can differ in length (they normally contain between 14 and 24 carbon atoms).
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What are the three major parts of a cell?
A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell. The nucleus is a structure inside the cell that contains the nucleolus and most of the cell's DNA.
What are the components of the cell membrane?
Cell membrane components. Cell membranes are made up of about 40% lipids, about 60% of proteins, and 5 to 10% of carbohydrates. The lipids in the cell membrane consist of phospholipids and cholesterol molecules. And 60% of proteins include lipoproteins, glycoproteins, enzymatic proteins, carrier proteins, structural proteins, etc.
What is a cell membrane?
Nageli and C. Cramer. A cell membrane is the outside part (protoplasm) of a cell that is covered by a fine, elastic, and semipermeable membrane. Hence it is a delicate, living, and microscopic membrane outside the cytoplasm that is made up of proteins and lipids. The cell membrane also has a role in interconnection, growth, and movement.
What are the features of phospholipid molecules?
The feature of phospholipid molecules is that they are active all the time (1). There are many different kinds of lipids located in the cell membrane. The following table discusses the lipids present in the cell membrane. Cell membrane.
What is the second most abundant component of the cell membrane?
Proteins are the second most abundant component in the cell membrane after lipids and composed of about 60% of the membrane. It is the structural block of cell membranes. There are many protein molecules floating between phospholipid and cholesterol molecules. Proteins are attached to the phospholipid layer.
What are the two main components of lipids?
Hence is the primary and significant component. Lipids are mainly in the form of phospholipid, cholesterol, and glycolipid. Cholesterol molecules are located between phospholipid molecules. The lipids of cell membranes have two ends, the head is called hydrophilic ends and the tail is called hydrophobic ends.
Where are hydrophilic proteins located?
They contain only hydrophilic parts. These proteins are located on the inner or outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer. About 30% of the total protein in the cell membrane is formed by the Peripheral proteins. These proteins are the outer or inner adjacent proteins of the phospholipid layer (2) & (4). 3.
Which proteins act as receptors?
The glycoproteins and lipoproteins which are present in the cell membrane act as receptors.
What are the components of the cell membrane?
The main component of the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer membrane. In between the phospholipids there are cholesterol molecules. Other biochemical components of the membrane include: Amphipathic lipids: phospholipids, glycolipids, sterols, and cholesterol. Proteins, including integral proteins that act as membrane transporters ...
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane surrounds individual animal cells and forms an important barrier between the external environment or extracellular space and the intracellular space. In so doing, it helps to maintain proper fluid and ion concentrations within the cell. The main component of the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer membrane.
What are the factors that regulate membrane fluidity?
Membrane fluidity is regulated by several factors including the amphipathic nature of the phospholipid bilayer, integral membrane proteins, physical properties of the membrane, and the unsaturated or saturated states of the phospholipid bilayer. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What are the functions of proteins in the cell membrane?
Proteins, including integral proteins that act as membrane transporters and peripheral proteins that are loosely associated with the outside of the cell membrane and act as enzymes. Glycoproteins and glycolipids. The main functions of the cell membrane are:
What is the lipid bilayer?
A phospholipid is a type of lipid that has glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-associated head region.
How many amino acids are in a transmembrane protein?
Transmembrane proteins may span the membrane a single time or up to 12 different regions of the membrane. Most transmembrane proteins contain 20-25 hydrophobic amino acids that are organized in an alpha-helix fashion.
Why is cholesterol important for membrane fluidity?
Cholesterol is important in maintaining normal membrane fluidity and acts as a buffer by preventing cold temperatures from inhibiting fluidity and suppressing increased fluidity that might come from higher temperatures.
What is the cell membrane structure?
The cell membrane structure is most commonly described using the 'fluid mosaic model' . This model describes the cell membrane as a phospholipid bilayer containing proteins and cholesterol which are distributed throughout the bilayer.
What factors affect the cell membrane structure?
We previously discussed the cell membrane functions which included regulating what enters and exits the cell. To perform these vital functions, we need to maintain the cell membrane shape and structure. We will explore the factors that can affect this.
Investigating cell membrane permeability
Betalain is the pigment responsible for the red color of beetroot. Disruptions to the cell membrane structure of beetroot cells cause the betalain pigment to leak out into its surroundings.
Cell Membrane Structure - Key takeaways
The cell membrane has three main functions: cell communication, compartmentalization and regulating what enters and exits the cell.
What is the main component of the cell membrane?
If we count molecules, the main component of the cell membrane is phospholipid material.
Which cell membrane contains more protein?
The cell membrane contains more protein by mass, but the molar mass of a protein is about 100 times that of a lipid. So, bacterial and mitochondrial membranes have about 30 lipid molecules for every protein, and most of these are phospholipids.
What is the function of the phospholipid bilayer?
1. As a container for the cell contents. It separates the cell contents from the surrounding environment. 2. As a police officer to control the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. The interior of the phospholipid bilayer is nonpolar, so only small uncharged molecules like oxygen ...
What are the two fatty acids that make up phospholipids?
Most phospholipids contain two fatty acids, glycerol, a phosphate group, and a simple organic molecule such as choline. The phospholipids form a lipid bilayer or membrane in which the hydrophobic tails all line up to avoid the water inside and outside the cell, while the hydrophilic heads point toward the water.
Can water pass through a phospholipid bilayer?
The interior of the phospholipid bilayer is nonpolar, so only small uncharged molecules like oxygen ( O2 ), carbon dioxide ( CO2 ), and water ( H2O) can pass freely through the membrane , either by diffusion or by osmosis. Large molecules cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer. Answer link.
What does transport across the membrane mean?
transport across the membrane. they can bring something from outside to inside or inside to outside
Is phospholipid soluble in water?
it is a lipid in a fused ring structure. it is insoluble in water and non polar. resides between the tails of the phospholipids
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.