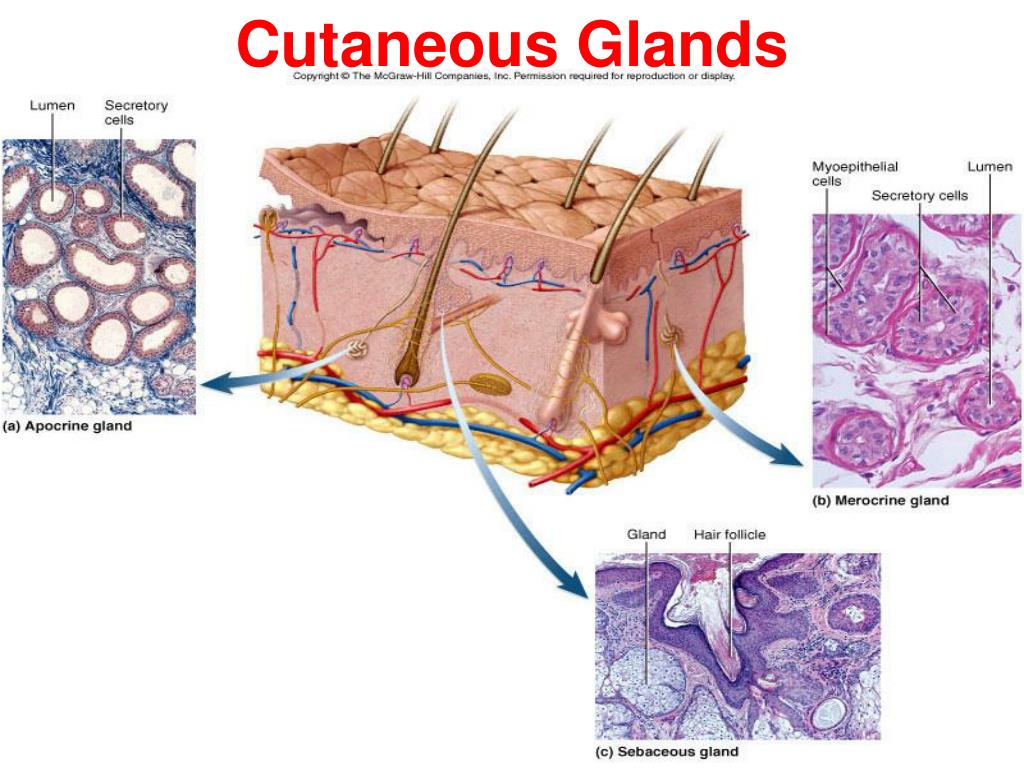
There are 3 main types of glands found on human skin:
- Eccrine glands - secrete sweat through pores found in the palms of hands, soles of feet, and forehead
- Sebaceous glands - secrete oily sebum and are found on the chest, back, scalp, face, and forehead
- Apocrine glands - secrete sweat via canals along hair follicles in the
What are the three types of glands in the skin?
Glands of the Skin. Two types of glands are present in the skin over most of the body. These are sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Sweat glands are of two types again, merocrine and apocrine - the latter are restricted to specific areas like the axilla, nipple of the breast, pubic region and around the anus. ...
What types of glands are in the human body?
Glands to know
- Thyroid gland. Your thyroid gland is located in the front of your neck, just below your larynx. ...
- Pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland at the base of your brain, just behind the bridge of your nose.
- Hypothalamus. ...
- Pineal gland. ...
- Adrenal glands. ...
- Pancreas. ...
- Sweat glands. ...
- Sebaceous glands. ...
- Salivary glands. ...
- Mammary glands. ...
What are glands help keep skin soft and hair lustrous?
Hair or oil gland. There's is one (blank) in each hair follicle. Epidermis. The growth layer is in the division of the skin is called. Oily. Sebaceous or (blank) glands help keep skin soft and lustrous. Dermis. The deepest and most active division f the skin is called the. Epithelial. Tissue Type (Epithelial or Connective) Mucous. Epithelial ...
What are the functions of the body glands?
- Prolactin: Stimulates milk production in mothers.
- Somatotropin: A hormone that regulates the growth of the body and tissues.
- Luteinizing hormone: Stimulates ovulation (egg formation) in females and testosterone production in males.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone: Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 & T4 hormones.
What are the functions of hormones?
Why is hyperthyroidism common?
Why does my salivary gland not work?
What are the symptoms of salivary gland disorders?
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
What causes a fatty hump in the shoulders?
Where is the thyroid gland located?
See 4 more
About this website
What are the three glands found in the skin?
Skin Glands: Sebaceous, Eccrine, and Apocrine Glands | Fitzpatrick's Dermatology, 9e | AccessMedicine | McGraw Hill Medical.
What are the 4 glands of the skin?
Associated Glands: There are four types of exocrine glands within human skin—sudoriferous, sebaceous, ceruminous, and mammary glands.
How many glands that the skin have?
The average square inch of skin holds 650 sweat glands, 20 blood vessels, 60,000 melanocytes, and more than a thousand nerve endings.
What are the two major exocrine glands associated with the skin?
The skin has a variety of exocrine glands, including the eccrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Eccrine sweat glands are the most widespread sweat gland in the body and are present on nearly every external body surface.
What are the 7 main glands?
While many parts of the body make hormones, the major glands that make up the endocrine system are the:hypothalamus.pituitary.thyroid.parathyroids.adrenals.pineal body.the ovaries.the testes.
What are the 5 major glands?
The hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland are in your brain. The thyroid and parathyroid glands are in your neck.
What type of glands are found in the skin quizlet?
Matchsebaceous glands = skin oil glands. ... sebum. ... sudoriferous glands = sweat glands. ... eccrine sweat glands. ... apocrine sweat glands. ... mammary glands. ... ceruminous glands. ... cerumen.
What are the 2 main types of glands?
Glands are important organs located throughout the body. They produce and release substances that perform certain functions. Though you have many glands throughout your body, they fall into two types: endocrine and exocrine.
What are examples of exocrine glands in the skin?
Examples of exocrine glands include sweat glands, lacrimal glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, and digestive glands in the stomach, pancreas, and intestines.
Which gland is known as 4's gland?
Adrenal glandGive the reason for the following statements :
Adrenal gland is also called 4 S-gland.
What is called 4S gland?
The adrenal gland is known as 4S gland. 4S stands for the source of energy, sugar metabolism, salt retention and sex hormones.
Which gland is 4 in no?
The parathyroid glands, of which there are 4–6, are found on the back of the thyroid glands, and secrete parathyroid hormone, This causes an increase in blood calcium levels by targeting bone, the intestine, and the kidneys. The parathyroid hormone is the antagonist of calcitonin.
Glands in the Human Body and their Functions - Epainassist
Endocrine Glands: Now coming to the endocrine glands, as stated these glands produce hormones which are directly released into the blood stream. They do not have any ducts which connect them to the surface of the body. Below mentioned are the glands which form the Endocrine Glands and their functions in detail.
The Endocrine System and Glands of the Human Body - WebMD
The endocrine system is a system of glands that make hormones. Your body uses hormones to control growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, mood, and other functions.
What glands excrete lipids?
The sebaceous glands excrete lipids by disintegration of entire cells, a process known as holocrine secretion. Human sebum, as it leaves the sebaceous gland , contains squalene, cholesterol, cholesterol esters, wax esters, and triglycerides.
What is a sebaceous gland?
AT-A-GLANCE. Sebaceous glands are multilobular structures that consist of acini connected to a common excretory duct and are usually associated with a hair follicle. Sebaceous glands vary considerably in size, even in the same individual and in the same anatomic area.
What are the two parts of the skin that release biochemical products?
INTRODUCTION. The human skin has several types of exocrine glands (Latin, glandulae cutis ), which release their biochemical products onto the skin surface. All skin glands consist by a secretory compartment, the gland or coil (tubulus), and an excretory part, the duct (ductus).
What are the three major types of skin glands?
Three major types of skin glands are recognized according to their product, the excretory function, and the location, where the excretory ducts release their products (diseases of these glands are listed in Table 6-1 ). Regarding their product, skin glands are classified into glands secreting sebum (sebaceous glands) and sweat (sweat glands).
What are the molecules that regulate the sebaceous gland?
Sebaceous glands are regulated by several molecules, among them androgens and retinoids.
Where do sweat glands release their products?
Regarding the location where their ducts release their product, the ducts of sebaceous glands, in most cases, and apocrine sweat glands excrete their products into the hair follicle canal, and the eccrine sweat glands excrete directly onto the skin surface.
What are the sebaceous glands?
Sebaceous glands (oil glands) are made up of spe-cialized epidermal cells and are primarily located near hair follicles. These glands are largest on the face, neck, and upper chest. They are actually holocrine glands, secreting sebum , which is an oily mixture of fatty material and debris from cells. The central alve-oli cells accumulate lipids until they burst, and the combined lipids and cell fragments make up sebum. The sebum is secreted through small hair follicle ducts, helping to keep both hair and skin pliable and waterproof. The sebum is a mixture of cholesterol, triacylglycerides, proteins, and electrolytes. Sebum inhibits bacterial growth, protecting the keratin of the hair shafts. Sebum is forced out of hair follicles to the skin surface via arrector pili contractions. This lubricates the hair and skin, keeping the hair supple and slowing the loss of water from the skin during times of low environmental humidity. Sebum has a strong bactericidal action. Its secretion is stimulated by androgens, primarily. Hence, sebaceous glands are less active until a human reaches puberty and andro-gen production rises.
What is the sweat gland?
Sweat glands consist of a small tube originating as a coil in the deep dermis or superficial subcutaneous layers. The coiled portion is lined with sweat-secreting epithelial cells. Sweat is carried out of the skin by tubes called pores that open at the skin surface. Sweat is made up of 99% water as well as salts, which are primarily sodium chloride, ascorbic acid, or vitamin C; antibodies; and waste products, including urea, ammonia, and uric acid, sweat tastes salty because of its electrolytes. Sweat also contains dermicidin, which is a peptide that kills microbes. Overall, sweat is a hypotonic filtrate of blood, passing through secre-tory cells via exocytosis. Its composition is based on diet, heredity, and partially certain drugs that are ingested. Sweat has a normal acidic pH of between 4 and 6. Sweating is regulated by the autonomic ner-vous system to prevent overheating. It begins on the forehead, spreading inferiorly to the rest of the body. When sweating is brought about by nervousness or fright (cold sweating), it starts on the palms, axillae, and soles before spreading throughout the body.
What are the two types of exocrine glands?
The skin contains two types of exocrine glands: sebaceous g lands and sweat glands. The sebaceous (oil) glands are simple and branched alveolar glands cov-ering the body, except on the palms and soles. The sweat (sudoriferous) glands are found all over the body except for the lips, nipples, and certain parts of the external genitalia.
Where are sweat glands found?
Apocrine glands are sweat glands that become active at puberty and number about 2,000. They are found mostly in the armpits and groin , with the sweat excreted at these places developing a scent as they come into contact with skin bacteria (FIGURE 6-8). This is the basis of body odor. Modified sweat glands include the ceruminous glands of the external ear (which pro-duce earwax) and the mammary glands (which produce milk). Cerumen or earwax is believed to block entry of foreign materials or insects into the ear.
What are the Three Layers of Skin?
The skin has a layered structure and is made up of many tissues. There are three main layers of skin, i.e. epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
What is the outermost layer of the epidermis?
The epidermis is the outermost layer made up of keratinized stratified squamous epithelial cells. These specialized cells are called keratinocytes. There are no distinct layers or division of the different layers present in the epidermis, but the keratinocytes show a gradual change in their structure.
What is the dermis made of?
It is made up of connective tissues, nerves, the blood supply, fibroblasts, etc., as well as sweat glands. It also contains hair follicles on most parts except soles and palms. The apical layers of the dermis are folded into dermal papillae. Hypodermis: This layer is present below the dermis.
What are the basal layers of the epidermis?
The basal layers of the epidermis are folded into dermal papillae. Dermal papillae provide adhesions between the epidermis and dermis and, in the areas of thick skin, nourish the epidermis. Dermis: This layer is present below the epidermis.
How long does it take for keratinocytes to mature?
The cells in the basal layer divide and move up in the layers above. This process takes about 2 − 4 weeks.
Where are Meissner's corpuscles located?
Meissner’s corpuscles: Also referred to as tactile corpuscles, are found in the upper dermis and project into the epidermis. They are mechanoreceptors for touch and are found on the palmar surface of fingers and plantar service of feet.
Where are Ruffini corpuscles found?
Ruffini corpuscles: They are found in the dermis and are slow adapting mechanoreceptors and detect the skin stretch and deformations with joints. They are also known as bulbous corpuscles. Krause’s end bulbs: Found in the dermis, and these are thermoreceptors cell and detect cold. Fig: Histology of Skin.
How many exocrine glands are there in the integumentary system?
The integumentary system has four types of exocrine glands, which secrete some type of substance outside the cells and body.
What is the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is made up of several organs and structures including the skin, hair, nails, glands, and nerves. The primary function of the integumentary system is to protect the inside of the body from elements in the environment—like bacteria, pollution, and UV rays from the sun. The skin and its associated structures also retain bodily ...
What are the layers of the skin?
Layers of the Skin. There are two layers of the skin: The epidermis: The outer layer of the skin that makes up its strong protective covering. The dermis: Located under the epidermis; most of the structures of the skin are located in the dermis (such as various types of glands and hair follicles). The fatty layer of the skin is a layer ...
What are the segments of the nail?
Nails. Just like other body parts, nails consist of several segments, including: The nail plate: The part of the nail that is visible. The nail bed: The skin that lies beneath the nail plate. The cuticle: The thin line of tissue that is located at the base of the nail and overlaps the nail plate.
What is the fatty layer of the skin?
The fatty layer of the skin is a layer of subcutaneous (under the skin) tissue , also known as the hypodermis. 1 The fatty layer serves many different functions, including: Providing a cushion for the skin. Storing fuel for the body (in the form of fat cells)
How thick is the skin?
To function as a protective barrier, it must cover the entire outside of the body, from the top of a person’s head to the end of the toes. The skin is approximately 2 mm (0.079 inches) thick and in its entirety weighs nearly 6 pounds.
Which system is very active in working with other organ systems to maintain the body's overall balance?
The integumentary system is very active in working with other organ systems to maintain the body’s overall balance (called homeostasis). Examples of how the skin helps each body system maintain homeostasis include:
What are the functions of hormones?
These hormones control a number of important functions in your body, such as: your growth and development. metabolism. mood. reproduction. Your endocrine glands include: adrenal glands. pituitary gland. hypothalamus.
Why is hyperthyroidism common?
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are common thyroid disorders. Hypothyroidism occurs because of an underactive thyroid that doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism is the result of an overactive thyroid that produces too much thyroid hormone. Both conditions can cause an enlarged thyroid gland, or goiter.
Why does my salivary gland not work?
The formation of stones or tumors, infections, and certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and HIV and AIDs, can prevent the salivary glands from functioning properly. When your salivary glands don’t produce enough saliva, it can affect chewing, swallowing, and taste.
What are the symptoms of salivary gland disorders?
Symptoms often include pain or swelling in your face, neck, or under your tongue, and dry mouth. Treatment of salivary gland disorders depends on the cause and may include medication or surgery.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus functions as a communication center for your pituitary gland, sending signals and messages to the pituitary to produce and release hormones that trigger the production and release of other hormones. Your hypothalamus influences a number of your body’s functions, including:
What causes a fatty hump in the shoulders?
Adrenal gland disorders are caused by too much or too little of a certain hormone, such as cortisol. Cushing syndrome, an adrenal disorder caused by high cortisol, causes weight gain, a fatty hump between the shoulders, and high blood pressure. It’s often caused by prolonged use of corticosteroids.
Where is the thyroid gland located?
Your thyroid gland is located in the front of your neck, just below your larynx. It measures approximately two inches and has a shape similar to a butterfly. It secretes hormones that affect virtually every tissue in your body. Thyroid hormones regulate your metabolism, heart, and digestive function.