The most common GMO crops include soybean, maize, cotton, canola, and alfalfa Alfalfa, also called lucerne and called Medicago sativa in binomial nomenclature, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as well as a green manure and c…Alfalfa
- Corn: Corn is the most commonly grown crop in the United States, and most of it is GMO. ...
- Soybean: Most soy grown in the United States is GMO soy. ...
- Cotton: ...
- Potato: ...
- Papaya: ...
- Summer Squash: ...
- Canola: ...
- Alfalfa:
Which foods are GMO?
What common foods are GMO?
- Alfalfa. Much of commercially available alfalfa has been genetically modified to contain a gene that makes it resistant to the herbicide Roundup.
- Canola. It is estimated that about 90% of US canola crops are genetically modified.
- Corn.
- Cotton.
- Papaya.
- Potato.
- Soy.
- Sugar Beet.
What grains are GMO?
accepting genetically modified (GMO) corn and soybeans keep coming up. These concerns have arisen primarily due to increased consumer resistance to products containing genetically modified ingredients in Europe and Asia in recent weeks. This sentiment should not be underestimated. U.S. consumers are also becoming more aware of the issue of genetically
What countries have banned GMO crops?
- Algeria
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belize
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Denmark
- Ecuador
Are GMOs the same as conventional crops?
Of course not. But that is what the US government has been pretending. Action Alert! A new study states authoritatively, in scientific terms, that GMOs (genetically modified organisms) and conventional crops are different and explains why.

What are the top 3 GMO crops?
The top three GMO crops grown in the U.S. are soy, corn and cotton, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). During the past 12 years, the percentage of acreage planted with GMO crops soared to over 80 percent for each of the top three.
What are the top 4 GMO crops?
Although we don't have numbers specifically for the top 5 GM foods produced in the world, the infographic below from the International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-Biotech Applications (ISAAA) highlights the top 4 biotech crops: soybean, cotton, maize and canola.
What are the top 10 GMO crops in the world?
Here are the top ten most common GMO products:Soy. Of all crops, soy is the most heavily modified. ... Corn. Corn is one of the most heavily modified crops. ... Rice. ... Potato. ... Tomato. ... Canola Oil. ... Papaya. ... Beets.More items...•
What are the current GMO crops?
The most common GMO crops include soybean, maize, cotton, canola, and alfalfa. The following GMO crops were also planted in different countries in 2018: papaya, eggplant, potato, apple, safflower, pineapple, and sugarcane.
What is the most GMO food?
Successfully Subscribed! Corn. Almost 85 perecent of corn grown in the U.S. is genetically modified. ... Soy. Soy is the most heavily genetically modified food in the country. ... Yellow Crookneck Squash and Zucchini. ... Alfalfa. ... Canola. ... Sugar Beets. ... Milk.
What are the most common GMOs?
Most Common GMOsAlfalfa. Much of commercially available alfalfa has been genetically modified to contain a gene that makes it resistant to the herbicide Roundup. ... Canola. It is estimated that about 90% of US canola crops are genetically modified. ... Corn. ... Cotton. ... Papaya. ... Potato. ... Soy. ... Sugar Beet.More items...
What are examples of GMO foods?
The Most Common GMO ExamplesAlfalfa. Most of the alfalfa that is commercially available today consists of a genetically modified gene that allows the produce to be resistant to the herbicide roundup. ... Papaya. ... Soy. ... Canola. ... Cotton. ... Potato. ... Sugar Beet. ... Yellow Summer Squash and Zucchini.More items...•
What was the first genetically modified crop?
tobaccoThe first genetically modified plant (GMP) was a tobacco resistant to antibiotics in 1983. In 1996, the first genetically altered crop, a delayed-ripening tomato was commercially released.
Are seedless fruits GMO?
There are NO seedless fruits sold today which are GMO. None. It's actually a bit silly to think otherwise since biotechnology is used to produce genetically modified seeds meant to be useful in agriculture in some way, such as being resistant to drought or pests.
What are the 8 GMO foods?
Corn (field & sweet) The GM version of field corn protects the crop against corn rootworms and the Asian corn borer. ... Soybeans. The GM soybean plant is resistant to pests and disease as well as being tolerant of herbicides.Cotton. GM cotton protects against the cotton bollworm.Canola. ... Alfalfa. ... Sugar Beets. ... Papaya. ... Squash.
What fruits and vegetables are GMO?
Genetically modified organisms, often shortened to GMOs, have been used in the American food supply system for more than 20 years....Examples of the crops, including GMO vegetables, that are produced in the U.S. are:Corn.Soybeans.Cotton.Potatoes.Papaya.Squash.Canola.Alfalfa.More items...•
Are bananas GMO?
Are bananas GMOs? The short answer is no. The banana available in U.S. grocery stores is a cultivar called the Cavendish banana. This type of banana is a non-GMO banana that is not currently available as a GM variety, or GMO, in the United States.
What are 2 of the top 4 GMO crop?
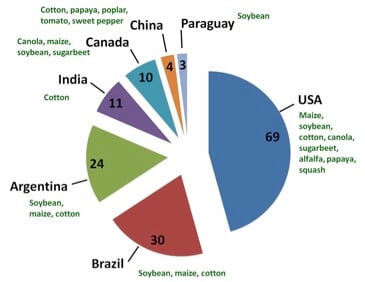
The top GM crop grown in 2015 was soybean (92.1 MHa), followed by maize (53.6 Mha), then cotton (24 Mha) and oilseed rape (canola) (8.5 Mha) (Figure 4). This represents 83% of the world production of soybean, and 75% of production of cotton.
What are the 11 GMO foods?
In the United States there are 11 commercially available genetically modified crops in the United States: soybeans, corn (field and sweet), canola, cotton, alfalfa, sugar beets, summer squash, papaya, apples and potatoes.
How many GMO crops are there in the world?
As of 2015, 26 plant species have been genetically modified and approved for commercial release in at least one country. The majority of these species contain genes that make them either tolerant to herbicides or resistant to insects.
Which vegetables are GMO?
A few fresh fruit and vegetables are available in GMO varieties, including potatoes, summer squash, apples, papayas, and pink pineapples. Although GMOs are in a lot of the foods we eat, most of the GMO crops grown in the United States are used for animal food.
What are the top 3 GMO crops?
The top three GMO crops grown in the U.S. are soy, corn and cotton, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). During the past 12 years, the percentage of acreage planted with GMO crops soared to over 80 percent for each of the top three. (See this graph at Mother Jones .)
What are the top 7 genetically modified crops?
Here are the Top 7 Genetically Modified Crops: 1. Corn: Corn is the No. 1 crop grown in the U.S. and nearly all of it — 88 percent — is genetically modified. In addition to being added to innumerable processed foods, genetically modified corn is a staple of animal feed. 2.
What percentage of cotton is genetically modified?
Cottonseed: According to the USDA, 94 percent of cotton grown in the U.S. is genetically modified. Cottonseeds are culled from cotton, and then used for vegetable oil, margarine or shortening production, or frying foods, such as potato chips. 4.
What is the fourth largest crop grown in the U.S.?
Alfalfa: Farmers feed alfalfa to dairy cows, the source of milk, butter, yogurt, meat and so much more. Alfalfa is the fourth largest crop grown in the U.S., behind corn, soybeans, and wheat (though there is no genetically engineered wheat on the market). 5. Papaya: 75 percent of the Hawaiian papaya crop is genetically modified to withstand ...
Where are transgenic soy plants?
Transgenic soy plants are seen in a field near Santa Fe city, some 500 Km northwest of Buenos Aires, Argentina, on April 10, 2012. Transgenic soy, corn and wheat plants, resistant to the drought and salinity were created by a team led by Dr. Raquel Chan at the vegetable biotechnology lab of the Universidad del Litoral.
Is canola oil a biofuel?
Canola oil is used in cooking, as well as biofuels. In North Dakota, genetically modified canola has been found growing far from any planted fields, raising questions about what will happen when “ escaped” GE canola competes with wild plants. 7.
Do you have to test for GMOs?
Research links GMOs to allergies, organ toxicity, and other health issues, though the U.S. Food and Drug Administration does not require safety testing for GMOs. Market watchers estimate that upwards of 70 percent of processed foods in your local supermarket contain genetically modified ingredients.
What is genetically modified?
The term genetically modified (GM), as it is commonly used, refers to the transfer of genes between organisms using a series of laboratory techniques for cloning genes, splicing DNA segments together, and inserting genes into cells. Collectively, these techniques are known as recombinant DNA technology. Other terms used for GM plants or foods derived from them are genetically modified organism (GMO), genetically engineered (GE), bioengineered, and transgenic. ‘Genetically modified’ is an imprecise term and a potentially confusing one, in that virtually everything we eat has been modified genetically through domestication from wild species and many generations of selection by humans for desirable traits. The term is used here because it is the one most widely used to indicate the use of recombinant DNA technology. According to USDA standards for organic agriculture, seeds or other substances derived through GM technology are not allowed in organic production.
What is GM technology?
Genetic modification (GM) technology allows the transfer of genes for specific traits between species using laboratory techniques. GM crops were first introduced in the U.S. in the mid-1990s. Most current GM crops grown in the U.S. are engineered for insect resistance or herbicide tolerance. Corn, soybeans, and cotton are ...
What is a GM plant?
Other terms used for GM plants or foods derived from them are genetically modified organism ( GMO), genetically engineered (GE), bioengineered, and transgenic. ‘Genetically modified’ is an imprecise term and a potentially confusing one, in that virtually everything we eat has been modified genetically through domestication from wild species ...
How do plant breeding programs work?
Most plant breeding programs rely on manual cross-pollination between genetically distinct plants to create new combinations of genes. The progeny plants are intensively evaluated over several generations and the best ones are selected for potential release as new varieties.
Why are GM crops so large?
Because several of them are major crops, the area planted to GM varieties is very large. Most current GM crops have been engineered for resistance to insects, tolerance to herbicides (weed control products) or both. Figure 1. Currently grown GM crops in the U.S., traits for which they are modified, and percent of total acreage ...
How do organisms store genetic information?
Most organisms store their genetic information in the form of DNA molecules in chromosomes. The sequence of chemical bases in a DNA strand encodes a specific order of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins . Proteins carry out many functions in cells and tissues, which together are responsible for an organism’s characteristics. Because most life forms share this same language of heredity—and due to scientific advances in molecular biology—it is now possible to transfer a gene from one species to another, for example from a bacterium to a plant, and have it function in its new host.
Is Roundup herbicide toxic to mammals?
The protein produced in the plant by the Bt gene is toxic to a targeted group of insects—for example European corn borer or corn rootworm—but not to mammals. The most common herbicide tolerant (HT) crops are known as Roundup Ready®, meaning they are tolerant to glyphosate (the active ingredient in Roundup® herbicide).
Why do farmers use GMO crops?
Most of the GMO crops grown today were developed to help farmers prevent crop loss. The three most common traits found in GMO crops are:
What is a GMO?
en Español (Spanish) Many people wonder what impacts GMO crops have on our world. “GMO” (genetically modified organism) is the common term consumers and popular media use to describe a plant, animal, or microorganism that has had its genetic material (DNA) changed using technology that generally involves the specific modification of DNA, ...
When were GMOs first used?
Scientists often refer to this process as genetic engineering. Since the first genetically engineered crops, or GMOs, for sale to consumers were planted in the 1990s, researchers have tracked their impacts on and off the farm.
Is rainbow papaya a GMO?
The GMO papaya, called the Rainbow papaya. External Link Disclaimer. , is an example of a GMO crop developed to be resistant to a virus. When the ringspot virus threatened the Hawaii papaya industry and the livelihoods of Hawaiian papaya farmers, plant scientists developed the ringspot virus-resistant Rainbow papaya.
How to make a GMO plant?
To produce a GMO plant, scientists first identify what trait they want that plant to have, such as resistance to drought, herbicides, or insects. Then, they find an organism (plant, animal, or microorganism) that already has that trait within its genes. In this example, scientists wanted to create insect-resistant corn to reduce the need to spray pesticides. They identified a gene in a soil bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), which produces a natural insecticide that has been in use for many years in traditional and organic agriculture.
What was the first GMO?
1990s The first wave of GMO produce created through genetic engineering becomes available to consumers: summer squash, soybeans, cotton, corn, papayas, tomatoes, potatoes, and canola. Not all are still available for sale.
Why do scientists grow corn?
In the laboratory, scientists grow the new corn plant to ensure it has adopted the desired trait (insect resistance). If successful, scientists first grow and monitor the new corn plant (now called Bt corn because it contains a gene from Bacillus thuringiensis) in greenhouses and then in small field tests before moving it into larger field tests. GMO plants go through in-depth review and tests before they are ready to be sold to farmers.
When did the FDA approve the first genetic modification in an animal for use as food?
2015 FDA approves an application for the first genetic modification in an animal for use as food, a genetically engineered salmon.
When did genetic engineering start?
After scientists developed genetic engineering in the 1970s, they were able to make similar changes in a more specific way and in a shorter amount of time. YouTube. U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Where are strawberries native to?
Today’s strawberries are a cross between a strawberry species native to North America and a strawberry species native to South America. Most of the foods we eat today were created through traditional breeding methods. But changing plants and animals through traditional breeding can take a long time, and it is difficult to make very specific changes.
What are GMO crops?
GMO crops grown and sold in the United States include corn, soybean, canola, sugar beet, alfalfa, cotton, potatoes, papaya, summer squash, and a few apple varieties ( 29. Trusted Source. ). In the United States, no regulations currently mandate the labeling of GMO foods.
What are some examples of GMO crops?
For example, one of the most common GMO crops is Bt corn, which is genetically modified to produce the insecticide Bt toxin. By making this toxin, the corn is able to resist pests, reducing the need for pesticides ( 3 ).
What is GMO in agriculture?
Definition. Pros. Cons. Identification. Bottom line. GMOs, short for genetically modified organisms, are subject to a lot of controversy. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), GMO seeds are used to plant over 90% of all maize (corn), cotton, and soy grown in the United States, which means that many of the foods you eat likely ...
How much has GMO technology reduced pesticide use?
In fact, an analysis of 147 studies from 2014 found that GMO technology has reduced chemical pesticide use by 37% and increased crop yields by 22% ( 8 ).
Why was the GMO study retracted?
However, this study was later retracted because it was poorly designed ( 18, 19, 20 ).
How much of food in supermarkets is genetically modified?
In fact, it’s estimated that up to 80% of foods in supermarkets contain ingredients that come from genetically modified crops.
Why is Roundup used on crops?
This has led to even more Roundup being sprayed on crops to kill the resistant weed s because they can affect the crop harvest ( 22, 23, 24 ).