There are three main categories of neurotransmitters in the brain:
- Small molecules used for fast-action excitatory / inhibitory information transmission (glutamate, GABA)
- Small molecules used for slower modulation of network activity (dopamine,serotonin, and 3 others)
- Peptides (large protein molecules) used for even slower modulation of circuit function (endorphins, cannabinoids, oxytocin, many others)
What are the 7 main neurotransmitters?
- acetylcholine. A neurotransmitter used by neurons in the PNS and CNS in the control of functions ranging from muscle contraction and heart rate to digestion and memory.
- norepinephrine.
- serotonin.
- dopamine.
- GABA.
- glutamate.
- endorphin.
What is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Role of GABA in Mental Health
- Anxiety Disorders. GABA activity helps you have a healthy response to stress by preventing neurons from sending out messages that would "fire up" the body.
- Schizophrenia. A lack of GABA is associated with problems carrying out normal mental functions. ...
- Autism Spectrum Disorder. ...
- Major Depression. ...
What is the most common neurotransmitter?
The list of neurotransmitters include
- Rapidly acting type. These neurotransmitters act very fast, like in a fraction of seconds. ...
- Slow acting type. From specific tissues. ...
- Classical neurotransmitters. ...
- Acetylcholine. ...
- Dopamine. ...
- Norepinephrine. ...
- Epinephrine. ...
- Serotonin. ...
- Glutamate. ...
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) GABA is another neurotransmitter present predominantly in the brain. ...
What part of the brain controls neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters: Functions, Types, and Examples
- Classification By Function. Researchers categorize neurotransmitters by their brain and bodily functions. ...
- Types of Neurotransmitters. In addition to the different classifications based on how they interact, different chemicals work as neurotransmitters.
- Disorders Associated With Neurotransmitters. ...

What are 3 major neurotransmitters?
These neurotransmitters are involved in most functions of your nervous system.Glutamate. This is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter of your nervous system. ... Gamma-aminobutryic acid (GABA). GABA is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter of your nervous system, particularly in your brain. ... Glycine.
What are the 7 major neurotransmitters?
Fortunately, the seven “small molecule” neurotransmitters (acetylcholine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, histamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin) do the majority of the work.
What are the 5 main neurotransmitters?
SubstancesNeurotransmitter Agents.Serotonin.Glutamic Acid.gamma-Aminobutyric Acid.Acetylcholine. Dopamine.
What are the 4 major types of neurotransmitters?
Based on chemical and molecular properties, the major classes of neurotransmitters include amino acids, such as glutamate and glycine; monoamines, such as dopamine and norepinephrine; peptides, such as somatostatin and opioids; and purines, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What are the 9 neurotransmitters?
Here is a list of some of the most common neurotransmitters discussed in neuroscience.Acetylcholine. Acetylcholine (Ach) was the first neurotransmitter discovered. ... Dopamine. ... Glutamate. ... Serotonin. ... Norepinephrine. ... gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) ... Other Neurotransmitters.
What is serotonin dopamine and norepinephrine?
Serotonin and noradrenaline strongly influence mental behavior patterns, while dopamine is involved in movement. These three substances are therefore fundamental to normal brain function. For this reason they have been the center of neuroscientific study for many years.
Which neurotransmitter is the most important?
Glutamate. Glutamate (Glu) is the most powerful excitatory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system which ensures homeostasis with the effects of GABA. It is secreted by neurons of the many of the sensory pathways entering the central nervous system, as well as the cerebral cortex.
What does GABA do in the brain?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid that functions as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter for the central nervous system (CNS). It functions to reduce neuronal excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission.
How many neurotransmitters does the brain have?
The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine.
What neurotransmitter causes anxiety?
GABA The neurotransmitter GABA is known to be the regulatory center for anxiety. Research has shown a strong association between GABA levels and the development of mood disorders, indicating that GABA also has an effect on emotions.
Does GABA increase dopamine?
gamma-Aminobutyric acid (Gaba) has been shown to influence dopamine activity in the brain. The author suggests that Gaba could be involved in the hypothesized dopamine hyperactivity in schizophrenia.
Is dopamine a neurotransmitter?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus of the brain.
How many neurotransmitters are there in the human body?
There are more than 40 neurotransmitters in the human nervous system; some of the most important are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, serotonin, and histamine.
What are the different types of neurotransmitters and their functions?
Types of neurotransmittersExcitatory neurotransmitters encourage a target cell to take action.Inhibitory neurotransmitters decrease the chances of the target cell taking action. ... Modulatory neurotransmitters can send messages to many neurons at the same time.
What are the neurotransmitters and their functions?
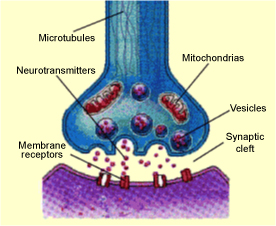
Neurotransmitters are often referred to as the body's chemical messengers. They are the molecules used by the nervous system to transmit messages between neurons, or from neurons to muscles. Communication between two neurons happens in the synaptic cleft (the small gap between the synapses of neurons).
What does GABA do in the brain?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid that functions as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter for the central nervous system (CNS). It functions to reduce neuronal excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission.
What is the name of the neurotransmitter in the brain?
For example, the neurotransmitter “dopamine” is abbreviated “DA” and its receptors have names like D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5.
What are the three main categories of neurotransmitters?
There are three main categories of neurotransmitters in the brain: Small molecules used for fast-action excitatory / inhibitory information transmission (glutamate, GABA) Small molecules used for slower modulation of network activity (dopamine,serotonin, and 3 others)
Which receptors are A?
adenosine – receptors are “A” (caffeine affects these)
What are the neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are the language of your brain. They allow neurons to communicate to other brain cells. That’s not it, though. Muscles receive cues from neurotransmitters, too. In fact, these chemical messengers send information throughout the body.
Which neurotransmitter plays the most important role in the brain's reward system?
The most thrilling neurotransmitter has to be dopamine. That’s because it plays a major role in your brain’s reward system.
How many types of neurotransmitters are there?
While there are dozens of known neurotransmitters, there are seven major ones to focus on. They fall into two different types, depending on their actions. Some are excitatory neurotransmitters. This means they encourage other brain cells to fire commands. Other neurotransmitters are considered inhibitory.
Why is glutamate bad for your brain?
Too much glutamate can be tricky for your brain. Excesses can over-excite cells. So much so that neurons can’t bring their energy back down again. This toxic excited state causes brain cells to lock up and stop working. Good thing those transporter proteins are there to clear away the extra glutamate and protect your brain by cleaning up the synapse after each action potential.
How do neurotransmitters help the body communicate?
Communication is key to your health. Neurotransmitters do that work, sending instructions from one brain cell to the next and transferring information throughout the brain and body. The process starts where these chemical messengers are stored in tiny compartments at the end of neurons.
Why does neuroplasticity depend on glutamate?
Neuroplasticity also relies on glutamate. That’s because your brain uses glutamate to build pathways between neurons that reinforce your memory and help you learn.
What are the chemical messengers that affect your body?
Familiarize yourself with each of the major chemical messengers that influence your health. They do a lot to keep your body and brain working in tandem. 1. Glutamate. This amino acid is common in your diet. And it acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter, stimulating neurons to fire commands.
What is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the body?
Acetylcholine is the “memory chemical” and is one of the most abundant neurotransmitters in the body. It’s an excitatory neurotransmitter and is responsible for alertness, attention, learning, and short and long-term memory. It also aids in skeletal muscle contraction to help you perform all your daily activities, from sweeping the floor to lifting weights.
What is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter of the nervous system?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter of the nervous system. This means it’s an inhibitory neurotransmitter, responsible for calming excited neurons. When GABA is released, you feel relaxed and have less anxiety. It also has anti-convulsive effects, though its role in treatment for epilepsy remains unclear.
What is the role of dopamine in the brain?
Dopamine is serotonin’s buddy and helps regulates your daily mood. It’s also responsible for attention, learning, motivation and reward, cognition, and making sure you’re coordinated enough to get through life.
What is glutamate in the brain?
Glutamate is the most abundant neurotransmitter in the body, present in nearly every excitatory brain function . Its job is to get neurons excited and ready to work. It’s also a metabolic precursor to GABA. Glutamate plays a vital role in synaptic plasticity—the strengthening or weakening of the signals between neurons over time. This is how your memories are formed, not by the creation of new neurons, but by strengthening the connections between them.
What is the purpose of endorphins?
Their main job is to minimize pain and discomfort and understanding how they work led to the development of opioid drugs like codeine, morphine, fentanyl, and oxycodone.
