The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis. Interphase is the 'daily living' or metabolic phase of the cell, in which the cell obtains nutrients and metabolizes them, grows, reads its DNA, an…Interphase
Full Answer
What are the 5 stages of the cell cycle?
what is cell cycle in biology
- Stage of cell division
- DNA replication
- Mitosis
- Stage of mitosis
- Mitosis: late
- Mitosis: the end stage
- Cell cycle summary
What are the steps in the cell cycle?
What are the steps in the cell cycle?
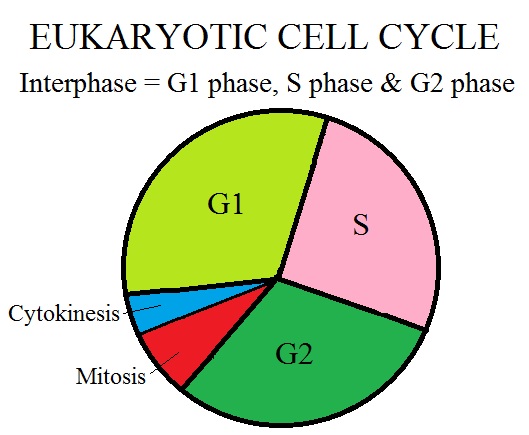
- G1 phase. Metabolic changes prepare the cell for division.
- S phase. DNA synthesis replicates the genetic material.
- G2 phase. Metabolic changes assemble the cytoplasmic materials necessary for mitosis and cytokinesis.
- M phase. A nuclear division (mitosis) followed by a cell division (cytokinesis).
What stage is the longest part of the cell cycle?
G1 is the longest phase of cell cycle, usually lasting about 10 hours. This reflects how new cells have to grow while existing ones are being built or repaired during mitosis; it’s also where we find our first chance for action in any given 24 hour period!
What is the correct order of the cell cycle?
- Gap1
- synthesis
- Gap2
- Prophase I ( further divided into leptotene>zygotene>pachytene>diplotene>dikinesis)
- metaphase I
- anaphase I
- telophase I
- interkinesis (not for every cell)
- Prophase II
- metaphase II

What is the G phase of the cell cycle?
G, phase of cell cycle varies in length from cell to cell within the same cell population. The length of this phase is more than the other three phases. This period represents in general 25 to 40% of the generation time of a cell. The cause of variability in G 1 is not known, although there is an evidence to suggest, ...
Which phase of synthesis is most of the histone protein synthesised?
Although some of the histone protein is synthesised during G 1, phase, most of it is synthesised during S phase. Further, synthesis of ribosomal RNA must continue from G 1, to S phase if DNA synthesis is to start. The eukaryotic chromosomes consist of DNA-histones complexes, called nucleosomes.
What happens to the nucleolus during telophase?
The nucleolus and nuclear wall break down goes side by side with the inhibition of RNA and protein synthesis. These structures are reformed in daughter nuclei in late telophase when the synthesis of RNA and proteins resume. The molecular signals for these changes are not known. The behaviour of chromosomes during different phases of cell cycle, as illustrated by De Robertis et al. (1975) is shown in (Fig. 11.1).
What happens after termination of replication?
Since DN A replication is dependent on protein and RNA synthesis for the overall replication of chromosome, it is necessary that new proteins must be synthesised .
What happens during the M phase?
M Phase: M phase follows G 2 phase. During this phase the cell divides into two daughter cells. The chromosomes are duplicated during interphase and they are distributed to the progeny cells by division process. After M phase, the resulting daughter cells then enter the G 1, phase of next cell cycle.
What are the events that lead to the initiation of DNA synthesis?
The events which lead to the initiation of DNA synthesis include synthesis of enzymes and other proteins required for DNA synthesis. Cell Cycle: Phase # 2. S Phase: After G 1, phase there comes the S phase. Biochemically, it is a phase of active DNA and histone synthesis.
When does RNA synthesis stop?
During M phase, RNA synthesis stops at late prophase and resumes at telophase. The protein synthesis drops drastically and during that period RNA synthesis also stops. These changes in the synthetic activity may be attributed to the non-availability of transcription sites owing to highly condensed state of the chromosomes. If no mRNA is available to ribosomes, protein synthesis cannot take place.
How many phases are there in the eukaryotic cell cycle?
The duration of the cycle, however, varies from organism to organism and cell to cell. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is divided into two main phases:-.
What is Cell Cycle?
It is a series of stages a cell passes through, to divide and produce new cells.
What is the interphase of a cell?
G1 phase (Gap 1) – G1 phase is the phase of the cell between mitosis and initiation of replication of the genetic material of the cell. During this phase, the cell is metabolically active and continues to grow without replicating its DNA.
What is the term for the series of events that results in the duplication of the cell alongwith the DNA?
Cell cycle refers to the series of events that results in the duplication of the cell alongwith the DNA.
What is the mitotic phase?
This is the mitotic phase or the phase of the equational division as the cell undergoes a complete reorganization to give birth to a progeny that has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What phase does centriole divide?
The centriole also divides into two centriole pairs in the cells which contain centriole. G2 phase (Gap 2) –During this phase, the RNA, proteins, other macromolecules required for multiplication of cell organelles, spindle formation, and cell growth are produced as the cell prepares to go into the mitotic phase.
What is the process of separating chromosomes and DNA?
Mitosis. The process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the nuclear DNA and chromosomes and divides into two different but similar sets of nuclei is known as mitosis. The chromosomes are pulled apart by a mitotic spindle, which is a specialized structure consisting of microtubules.
What are the two main stages of the cell cycle
What are the two main phases of the cell cycle? A. Prophase and anaphase B. Interphase and mitosis C. Replication phase and recombination phase D. Multiplication phase and division phase
The two main stages of the cell cycle are called
Which are the main stages of the cell cycle? Check all that apply. interphase mitosis metaphase cytokinesis anaphase
What are the two main functions of the large intestine
Select the structures and functions of the large intestine from the choices below
What are the main organelles of plant and animal cells
Summarize the functions of the organelles found in plant and animal cells
What are the two main functions of lipids in humans
Which of the following are functions of lipids? Choose three correct answers. A. forming the exoskeletons of insects B. forming waxy leaf coverings C. forming bones and cartilage D. storing …
What are the two main function of lipids in humans
Which of the following are functions of lipids? Choose three correct answers. A. forming the exoskeletons of insects B. forming waxy leaf coverings C. forming bones and cartilage D. storing …
Why did islam split into two main groups around 661
What was the original cause of the split between Shia and Sunni Muslims within Islam? A. disagreement over the role of women in Islamic society B. disagreement over interpretations of …
What are the two phases of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is separated into two major phases that alternate with each other: Interphase, during which the cell grows, preparing for mitosis and duplicating it's DNA, and then the mitotic phase, in which the cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells.
What is the stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows and synthesizes all materials required during its division?
The interphase is the stage of the cell cycle where occurs the replication of the genetic material (DNA) and the cell grows and synthesizes all materials required during its division.
What is the mitotic phase?
During the mitotic phase, also called 'M phase' the cell divides into two daughter cells. During this phase, the chromosomes separate into daughter cells.