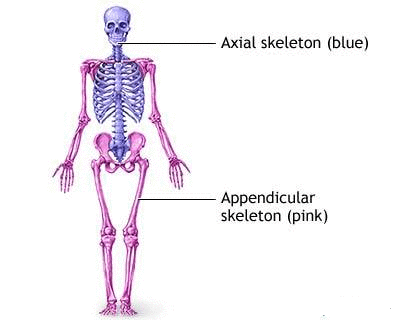
The functions of Axial Skeleton are:
| Components of Axial Skeleton | Function |
| Skull | It provides protection to the brain, for ... |
| Vertebral Column | It provides protection to the spinal cor ... |
| Thoracic Cage | It protects and supports the internal or ... |
What are the three parts of the axial skeleton?
- Malleus (2)
- Incus (2)
- Stapes (2)
What are the main functions of the axial skeleton?
Structure Function Of Axial Skeleton
- The functions of the major bones of the appendicular skeleton.
- Clavicle. This bone connects the upper arm to the trunk of the body. ...
- Scapula. ...
- Arm. ...
- Hand. ...
- Pelvis. ...
- The Leg. ...
- The Foot. ...
- Compact bone or (cortical bone) Cortical bone, synonymous with compact bone, is one of the two types of osseous tissue that form bones.
- Cancellous bone. ...
What bones are part of the axial skeleton?
- Frontal Bone: It is a flat bone that forms our forehead and the upper part of our eye sockets.
- Parietal Bone: These are pairs of flat bones present behind the frontal bones on either side of the head.
- Temporal Bone: This pair of irregular bones are present under the parietal bones on the lateral sides.
What are the joints of the axial skeleton?
• Joint types restricted mainly to the axial skeleton where firm attachments and protection of internal organs are priorities include: o Synarthroses – immovable joints o Amphiarthroses – slightly moveable joints • Joints predominate in the limbs where mobility is important: o Diarthroses – freely moveable joints
What are the parts of the skull?
What is the name of the bone that articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of
What bone is the sphenoid bone?
Which process is associated with the superior and inferior articular processes?
What is the mandible fossa?
Which bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
Which opening on the body transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw?
See more
About this website

What are the major components of the axial skeleton quizlet?
Terms in this set (4)Skull. Cranium and facial bones.Hyoid bones. In next between lower jaw and larynx.Vertebral column. Vertebrae and intervertebral discs; sacrum and coccyx.Thoracic cage. 12 pairs of ribs and sternum.
What are the three components of the axial skeleton and their functions?
The axial skeleton supports the head, neck, back, and chest and thus forms the vertical axis of the body. It consists of the skull, vertebral column (including the sacrum and coccyx), and the thoracic cage, formed by the ribs and sternum. The appendicular skeleton is made up of all bones of the upper and lower limbs.
What are the three components of the axial skeleton and their functions quizlet?
Can be divided into three parts: the skull, vertebral column, & the thorax. Composed of the cranium & the facial bones.
What is the major function of the axial skeleton quizlet?
The axial skeleton serves as a framework that supports and protects organs, provides and extensive surface area for muscle attachment, and it also stabilizes and positions parts of the appendicular skeleton that support the limbs.
What is the major function of the axial skeleton?
The function of the axial skeleton is to provide support and protection for the brain, the spinal cord, and the organs in the ventral body cavity. It provides a surface for the attachment of muscles that move the head, neck, and trunk, performs respiratory movements, and stabilizes parts of the appendicular skeleton.
What is the axial skeleton quizlet?
Axial skeleton. The part of the skeleton that consists of the bones of the head and trunk of a vertebrate. In the human skeleton, it consists of 80 bones. Skull. a framework of bone or cartilage enclosing the brain of a vertebrate.
What is not a part of the axial skeleton?
Detailed Solution. The correct answer is Forelimb. The axial skeleton is a type of skeleton that comprises 80 bones and is present along the main axis of the body like the skull, vertebral column, sternum, and ribs construct the axial skeleton system.
What are the 4 parts of the appendicular skeleton?
The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the shoulder girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs.
Axial Skeleton- Pictures Flashcards | Quizlet
Start studying Axial Skeleton- Pictures. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Free Anatomy Quiz - Quizzes on the Axial Skeleton
Test your knowledge of the bones of the axial skeleton, the skull, the spine and the teeth with these free multiple-choice picture quizzes, and learn more about human anatomy. You'll find over 200 quizzes on the anatomy and physiology of the human body here; all free!
Axial Skeleton (Anatomy & Physiology) Flashcards | Quizlet
Start studying Axial Skeleton (Anatomy & Physiology). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Axial Skeleton Quizzes Online, Trivia, Questions & Answers - ProProfs
A comprehensive database of axial skeleton quizzes online, test your knowledge with axial skeleton quiz questions. Our online axial skeleton trivia quizzes can be adapted to suit your requirements for taking some of the top axial skeleton quizzes.
Overview
Made up of the bones in your head, neck, back and chest, your axial skeleton supports and cushions your brain, spinal cord and organs in your body.
Function
Your axial skeleton provides support and cushioning for your brain, spinal cord and organs in your body. Muscles in your body that move your head, neck and trunk attach to your axial skeleton. These muscles help you breathe and steady parts of your appendicular skeleton.
Conditions and Disorders
Many conditions can cause problems with your axial skeleton. Some develop due to wear and tear as you age. Others happen as a result of disease or injury. Conditions that may affect your axial skeleton include:
Care
The best way to take care of your axial skeleton is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. To keep your bones strong and healthy:
What are the parts of the skull?
Divided into 3 parts: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. Skull. Composed of the cranium and facial bones. Frontal bone. Anterior portion of cranium; forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and floor of anterior cranial fossa.
What is the name of the bone that articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of
Thin, delicately coiled plates of bone extending medially from the lateral masses of the ethmoid into the nasal cavity. Mandible. The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of the skull.
What bone is the sphenoid bone?
sphenoid bone. Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull. Keystone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones. Greater wings. Portions of the sphenoid seen exteriorly anterior to the temporal and forming a part of the eye orbits.
Which process is associated with the superior and inferior articular processes?
The superior articular process typically face toward the spinous process, whereas the inferior articular processes face away from the spinous process. Intervertebral foramina.
What is the mandible fossa?
Mandibular fossa. Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process; forms the socket for the condylar process of the mandible, where the mandible joins the cranium. External acoustic meatus. Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear.
Which bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
Foramen spinosum. Opening lateral to the foramen ovale through which the middle meningeal artery passes. Ethmoid bone. Irregular shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls.
Which opening on the body transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw?
Mental foramen. Prominent opening on the body (lateral to the midline) that transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw) Mandibular foramen. Must open the lower jaw of skull to identify this prominent foramen on the medial aspect of the mandibular ramus.
What are the components of the axial skeleton?
Axial Skeleton Components. The main components of axial skeleton are: The Skull. The Vertebral Column. Thoracic Cage. Fig: Axial Skeleton Components. 1. Skull: The skull is a bony framework of the head that protects the brain. It acts as a cover to the brain and supports the structure of the face.
What are the bones of the limbs attached to the axial skeleton?
The skull, the vertebral column, sternum, and ribs constitute the axial skeleton.” (Source: NCERT). Definition: The bones of the limbs are attached to the axial skeleton via girdles. The axial skeleton forms the main frame of the body in the longitudinal axis.
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
It consists of 80 bones that include the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes all bones of the pectoral girdle, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle, and the lower limbs. Q.2.
What are the two parts of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system of humans can be basically divided into two parts (i) the axial skeleton and (ii) the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton constructs the central axis of the body, while the appendicular skeleton comprises the limbs and girdles.
How many vertebrae are there in the thorax?
Thoracic: Thoracic vertebrae are 12 in number. It forms the vertebral spine and it supports the rib cage. It is present on the dorsal side of the thorax region and forms the dorsal part of the thoracic cage. Lumbar: Lumbar vertebrae are 5 in number. They form the dorsal part of the abdomen, i.e. lower back.
How many bones are there in the skull?
The two parts of the skull are the cranium and facial bones. The skull of humans is said to be dicondylic. The skull consists of 29 bones, i.e. 8 in the cranium, 14 in the face, 6 ear ossicles and 1 hyoid bone.
What are the two bones that make up the jaw?
Palatine: These pairs of bones are located at the back of the oral cavity and make part of the hard palate. Maxilla: These are two bones comprised of the upper jaw and hard palate. Vomer: It makes the rear side of the nasal septum. Mandible: The mandible is the lower jawbone.
What are the bones in the axial skeleton?
As stated previously, the axial skeleton is made up of the bones along the center of the body. This includes: 1 The skull, which includes various bones making up the cranium, which houses the brain, and facial portion, which makes up the face 2 The vertebral column, which includes 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, and 5 lumbar vertebrae, as well as the sacrum, or tailbone, and coccyx 3 The ribcage, which includes 12 sets of ribs 4 The sternum, or breastbone
Which skeleton is responsible for attaching the upper extremity to the axial skeleton?
The pectoral girdle, which is responsible for attaching the upper extremity to the axial skeleton and is made up of the scapula, or shoulder blade, and clavicle, or collar bone. The appendicular skeleton also includes the bones of the lower extremities, including:
What is the appendicular skeleton made of?
The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the extremities and the bones that attach the extremities to the axial skeleton. This includes the pectoral girdle, made up of the scapula and clavicle, and the upper extremity, including the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges, the pelvic girdle, ...
What are the two main divisions of the skeletal system?
The two main divisions of the skeletal system are the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton is made up of the bones along the center, or axis, of the body. Think about how the Earth spins on its axis - that means it spins along an imaginary line down the center of the Earth. The same applies to the body.
What are the bones of the lower extremities?
The femur, or thigh bone. The patella, or kneecap.
What is the cranium of the human body?
This includes: The skull, which includes various bones making up the cranium, which houses the brain, and facial portion, which makes up the face. The vertebral column, which includes 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, and 5 lumbar vertebrae, as well as the sacrum, or tailbone, and coccyx.
Is the axial skeleton the same as the appendicular skeleton?
The same applies to the body. The axial skeleton is along the center. The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the extremities. The appendicular skeleton is appended to the axial skeleton, or in other words, it's attached to the axial skeleton.
What is the Axial Skeleton?
When human babies are born, they have more than 300 bones. As they age, some of these bones fuse together to form one bone. In fact, an adult will end up with only 206 total bones. Some of the bones that fuse together are part of the axial skeleton.
Parts of the Axial Skeleton & Axial Skeleton Diagram
What makes up the axial skeleton? The parts of the axial skeleton contain the bones located in the:
Axial Skeleton Bones: What Bones are in the Axial Skeleton?
Out of the 206 bones found in an adult human body, the axial skeleton makes up 80 of these bones. Below are more details regarding each section of the axial skeleton.
What are the parts of the skull?
Divided into 3 parts: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. Skull. Composed of the cranium and facial bones. Frontal bone. Anterior portion of cranium; forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and floor of anterior cranial fossa.
What is the name of the bone that articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of
Thin, delicately coiled plates of bone extending medially from the lateral masses of the ethmoid into the nasal cavity. Mandible. The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of the skull.
What bone is the sphenoid bone?
sphenoid bone. Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull. Keystone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones. Greater wings. Portions of the sphenoid seen exteriorly anterior to the temporal and forming a part of the eye orbits.
Which process is associated with the superior and inferior articular processes?
The superior articular process typically face toward the spinous process, whereas the inferior articular processes face away from the spinous process. Intervertebral foramina.
What is the mandible fossa?
Mandibular fossa. Rounded depression on the inferior surface of the zygomatic process; forms the socket for the condylar process of the mandible, where the mandible joins the cranium. External acoustic meatus. Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear.
Which bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
Foramen spinosum. Opening lateral to the foramen ovale through which the middle meningeal artery passes. Ethmoid bone. Irregular shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls.
Which opening on the body transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw?
Mental foramen. Prominent opening on the body (lateral to the midline) that transmits the mental blood vessels and nerve to the lower jaw) Mandibular foramen. Must open the lower jaw of skull to identify this prominent foramen on the medial aspect of the mandibular ramus.
