
This table clarifies the location and limits of each ligament:
| Ligament | Spinal region | Limits |
| Alar | Axis - skull | Head rotation and lateral flexion |
| Atlantoaxial Anterior | Axis & Atlas | Extension |
| Atlantoaxial Posterior | Axis & Atlas | Flexion |
| Nucal ligament | Cervical | Flexion |
Are there joints in the spine?
There are two types of joint in the lumbar spine. Both of these articulations are not unique to the lumbar vertebrae, and are present throughout the vertebral column. Between vertebral bodies - adjacent vertebral bodies are joined by intervertebral discs, made of fibrocartilage. This is a type of cartilaginous joint, known as a symphysis.
What ligaments and tendons are in the skeletal system?
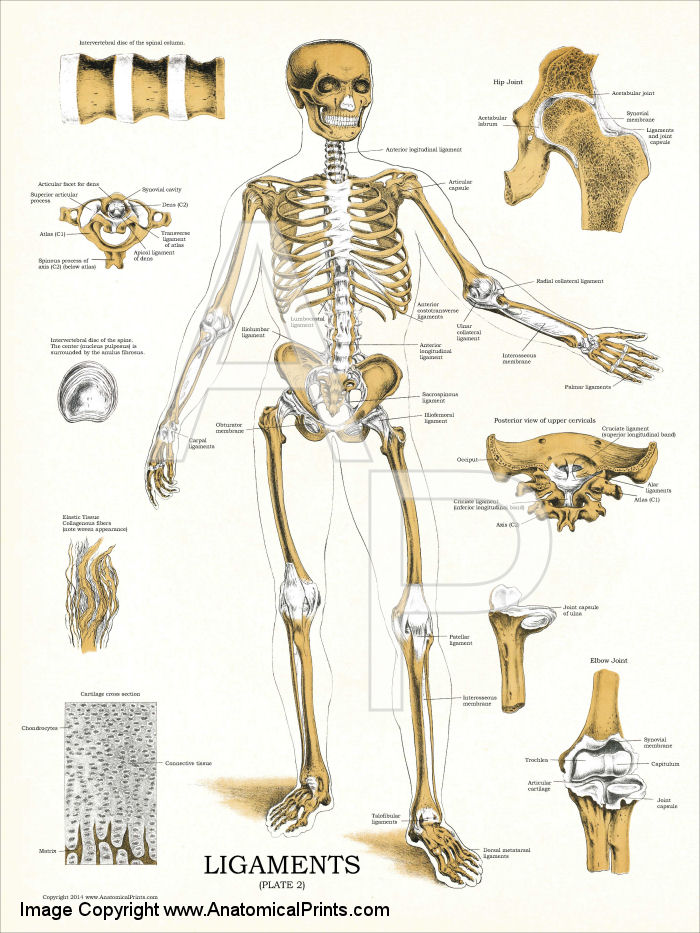
The muscles are attached to the bones via rope-like structures called tendons. Our skeletal system is made up of over 200 individual bones. Ligaments are strong ligamentous structures that typically anchor bones to one another. Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that typically exist at high friction points near joints.
Is a ligament the same as a joint?
Ligaments are bands of tough elastic tissue around your joints. They connect bone to bone, give your joints support, and limit their movement. You have ligaments around your knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders, and other joints. Stretching or tearing them can make your joints unstable. The most common ligament injuries come from playing sports.
Is the spine a long bone?
Long bones include the humerus (upper arm), radius ... spine, ribs, shoulder blades, pelvis, and skull. In babies, all bone marrow is red. 1. Long bone images are free for educational use. If you find this information useful then you are free to use these illustrations for educational use only, e.g. teachers or students.

What are the 5 ligaments of the spine?
There are five main ligamentous structures seen throughout the spinal column:Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)Ligamentum Flavum.Interspinous ligaments.Supraspinous ligament[1]
What are the 3 more important ligaments of the spine?
Three of the more important ligaments in the spine are the Ligamentum Flavum, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament.
Is there ligaments in spine?
The system of ligaments in the vertebral column, combined with the tendons and muscles, provides a natural brace to help protect the spine from injury. Ligaments aid in joint stability during rest and movement and help prevent injury from hyperextension and hyperflexion (excessive movements).
What are the 6 vertebral ligaments?
Ligaments of the vertebral archesLigamenta flava. Ligamenta flava. ... Interspinous ligaments. The interspinous ligaments connect adjacent vertebral spinous processes. ... Supraspinous ligament. ... Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) ... Intertransverse ligaments.
Where are the ligaments in your back?
The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament connects the front of each vertebra to each other. This ligament runs up and down the spine. 3. The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament extends up and down behind the spine and inside the spinal canal.
What are lumbar ligaments?
The iliolumbar ligaments are crucial in supporting the lower lumbar spine; they join the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae (L4 and L5) to the iliac bone crest at the back of the pelvis.
Which ligaments connect the bodies of the vertebrae together quizlet?
Ligaments related to Vertebral Bodies-- intervertebral discs (IVD), anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL).
What is ligamentum?
(lig'ă-mĕnt) [TA] 1. A band or sheet of fibrous tissue connecting two or more bones, cartilages, or other structures, or serving as support for fascias or muscles. 2. A fold of peritoneum supporting any of the abdominal viscera.
How many ligaments are in the human body?
900 ligamentsLigaments are made of fibrous collagen tissue that connects bones together at the joint to stabilize the joint, support the bones and prevent the bones from grinding into each other. Ligaments have a limited amount of stretching ability, which protects joints from injury. The human body has approximately 900 ligaments.
How many ligaments are in the spine?
threeThe three major ligaments of the spine are the ligamentum flavum, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), and posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) (Fig. 7). The ALL and PLL are continuous bands that run from the top to the bottom of the spinal column along the vertebral bodies.
What is the sacroiliac ligament?
Interosseous sacroiliac ligament Connects the outer surface of the sacrum (triangular part of the lower spine) to the inner surface ilium (hip bone) Receives the greatest stresses of the ligaments associated with the sacroiliac joint. 2. Forms the major connection between the sacrum and the ilium.
What is Sacrotuberous ligament?
The sacrotuberous ligament (STL) is a stabiliser of the sacroiliac joint and connects the bony pelvis to the vertebral column. The STL. Is in the shape of a fan located in the posterior pelvis, on both sides and connects the sacrum to the iliac tuberosities.
What are the primary spinal ligaments?
Primary Spinal Ligaments Include: Limits…. 1. Supraspinous Ligament (flexion) 2. Ligamentum Nuchae (fibrous membrane) As mentioned in the Vertebral Column, the Atlas (C1) and Axis (C2) are different from the other spinal vertebrae.
What are the two ligaments of the cervical spine?
Ligaments of the Back of the Cervical and Upper Thoracic Spine. 1. Supraspinous Ligament (flexion) 2. Ligamentum Nuchae (fibrous membrane) Ligament Systems – Atlas and Axis. As mentioned in the Vertebral Column, the Atlas (C1) and Axis (C2) are different from the other spinal vertebrae.
Which ligament connects the facet joints to the posterior openings of the vertebrae?
The Ligamentum Flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: a layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. This ligament connects under the facet joints to create a small curtain over the posterior openings between the vertebrae. The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front (anterior) of each vertebra.
Which ligaments prevent movement in certain directions?
Further, some ligaments prevent movement in certain directions. Three of the more important ligaments in the spine are the Ligamentum Flavum, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament . The Ligamentum Flavum forms a cover over the dura mater: a layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord.
What is a ligament?
Peer Reviewed. Ligaments are fibrous bands or sheets of connective tissue linking two or more bones, cartilages, or structures together. One or more ligaments provide stability to a joint during rest and movement. Excessive movements such as hyper–extension or hyper–flexion, may be restricted by ligaments.
Where is the anterior longitudinal ligament located?
The Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front (anterior) of each vertebra. This ligament runs up and down the spine (vertical or longitudinal). The Posterior Longitudinal Ligament runs up and down behind (posterior) the spine and inside the spinal canal.
Which vertebrae have the greatest range of motion?
Although the cervical vertebrae are the smallest, the neck has the greatest range of motion. Occipitoatlantal Ligament Complex (Atlas) These four ligaments run between the Occiput and the Atlas: Anterior Occipitoatlantal Ligament. Posterior Occipitoatlantal Ligament.
What is the role of ligaments in the spine?
The system of ligaments in the vertebral column, combined with the tendons and muscles, provides a natural brace to help protect the spine from injury. Ligaments aid in joint stability during rest and movement and help prevent injury from hyperextension and hyperflexion (excessive movements).
Which ligament is the strongest?
Ligamentum Flavum. The strongest ligament. This yellow ligament is the strongest. It runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis, in front of and between the lamina, and protects the spinal cord and nerves. The ligamentum flavum also runs in front of the facet joint capsules.
What is the tissue that attaches muscle to bone called?
Tendons consist of densely packed collagen fibers. Muscles, either individually or in groups, are supported by fascia. Fascia is strong sheath-like connective tissue. The tendon that attaches muscle to bone is part of the fascia. Muscle Name Thoracic Region.
What are the three parts of the spinal anatomy?
Understanding Spinal Anatomy: Ligaments, Tendons and Muscles. Ligaments and tendons are fibrous bands of connective tissue that attach to bone. Ligaments connect two or more bones together and help stabilize joints. Tendons attach muscle to bone.
What is the primary spine stabilizer?
A primary spine stabilizer. About one-inch wide, the PLL runs the entire length of the spine from the base of the skull to sacrum. It connects the back (posterior) of the vertebral body to the back of the annulus fibrosis. Supraspinous Ligament.
Which ligament is the only ligament that limits the movement of the vertebral column?
The anterior longitudinal ligament: This ligament is a strong, broad fibrous band that covers and connects the anterolateral aspects of the vertebral bodies and IV discs. The ligament extends from the pelvic surface of the sacrum to the anterior tubercle of vertebra C1 ( atlas) and the occipital bone anterior to the foramen magnum. It prevents hyperflexion of the vertebral column, maintaining stability of the joints between the vertebral bodies. The anterior longitudinal ligament is the only ligament that limits extension; all other ligaments of the vertebral column, like the IV ligaments, limit forms of flexion.
What are the ligaments in the somatic joints?
Also typical of most somatic joints are ligaments which serve to strengthen and stabilize such joints. Ligaments found in the joints of the vertebral column are ligaments of the vertebral column and they function to support/hold together articulating bones and structures forming the vertebral joints as well as resist hyperflexion and hyperextension of the vertebral column, e.g. the anterior longitudinal ligament, ligamenta flava.
How is the range of movement of the zygapophysial joints determined?
The range (amount) of movement of the zygapophysial joints is determined by the size of the IV disc relative to that of the vertebral body, and the joints permit gliding movements between the articular processes.
What are the joints of the vertebral column?
However, those of the vertebral column involve the vertebral bodies, and between the vertebrae and surrounding bones and cartilages e.g. the costovertebral joints.
How does the sacroiliac joint differ from the other joints?
The sacroiliac joint differs from most other synovial joints in that limited mobility is allowed, a consequ ence of their role in transmitting the weight of most of the body to the hip bones . As long as tight apposition is maintained between the articular surfaces, the sacroiliac joints remain stable.
What are the joints of the bodies?
Joints of the bodies - intervertebral discs made of the central nucleus pulposus surrounded by the annulus fibrosus; enhanced with the anterior longitudinal ligament (connects the anterolateral aspects of the vertebral bodies) and posterior longitudinal ligament (connects the posterior aspects of the vertebral bodies) ...
Which ligaments prevent hyperflexion?
It prevents hyperflexion of the vertebral column, maintaining stability of the joints between the vertebral bodies. The anterior longitudinal ligament is the only ligament that limits extension; all other ligaments of the vertebral column, like the IV ligaments, limit forms of flexion.
What is the anterior longitudinal ligament?
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament: Extends from occiput to sacrum. Thin and cord-like in the upper cervical region. Widens as it descends. Firmly attached to superior and inferior body endplates of vertebrae as it descends. Limits extension. Extension puts tension on this ligament.
What is the nuchal ligament?
Also called the Nuchal Ligament, this ligament attaches to spinous process tips of cervical vertebrae and extends between (interspinous ligament). Divides posterior neck into two compartments. Limits flexion. EOP to C7 spinous process, to dermis of midline of neck.
Function
- The spine has a number of ligaments that help bind the column as a whole. These ligaments connect the individual bones together, and they help form the intervertebral joints. Spinal ligaments also provide stability to the column. They do this by limiting the degree of movement in the direction opposite their location. For example, your anterior lon...
Clinical significance
- As we age, our ligaments may be subject to thickening, a condition called hypertrophy. Hypertrophy can cause symptoms such as nerve-related pain. Hypertrophy can develop further, into ossification, or hardening of the ligament(s). Ossification may increase the nerve symptoms, which may include compressing or otherwise irritating the spinal cord (called myelopathy). Depe…
Epidemiology
- Researchers from the Spine Clinic of the Good Samaritan Hospital in Los Angeles estimate that 25% of people with myelopathy symptoms which, as we discussed briefly above relate to the irritation or compression of the spinal cord, show signs of OPLL. (OPLL stands for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. See below for more information on the posterior longitudina…
Risks
- Should you experience trauma to your spine (for example, from a whiplash), its possible to injure your ligaments. If the injury to your ligament(s) is severe enough, it may cause spinal instability. Instability may be defined as when the bones and ligaments comprising your intervertebral joints (also known as the vertebral segments) can no longer maintain a normal alignment when they h…
Overview
- The anterior longitudinal ligament is a long dense band of connective tissue - all ligaments are made of some type of connective tissue - that goes from your first vertebra (the atlas) and the front of the base of your skull to the front of your sacrum. It is located on the front side of the vertebral bodies. This ligament also branches, at each individual level, into short fibers that go b…
Variations
- A big difference between the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments, and one that determines what movement direction the ligament limits, is location: The posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) is located in the spinal canal at the back of the vertebral bodies. The anterior (ALL) is located at the front of the bodies (and not in the spinal canal). The PLL is also narrower and w…
Structure
- The ligament flavum runs vertically from the axis vertebra (remember thats the 2nd bone in the neck) to the sacrum. It is located between the laminae of the vertebra. At each vertebral level, fibers originate from a superior lamina (the term superior refers to a location above, relatively speaking) and connect to the inferior lamina (i.e. the lamina just below). The ligamentum flavu…
Definition
- The phrase ligamentum flavum means \"yellow ligament\". The ligamentum flavum is made of a (pale) yellow colored elastic tissue. This tissue is similar to the type of connective tissue that comprises the other spinal ligaments, except theres a degree of elasticity to it. The elastic quality of the ligamentum flavum helps preserves your spinal curves during movement and assists the t…
Causes
- Also known as the nuchal ligament, this ligament is located at the back of your neck. It merges with the supraspinous ligament, which as weve discussed, is that long, strong cord that connects the tips of most (i.e. the lumbar and thoracic) of your spinous processes.
Location
- The ligamentum nuchae go from two places on or near the back of your skull and extend through all of the cervical (neck) spinous processes.