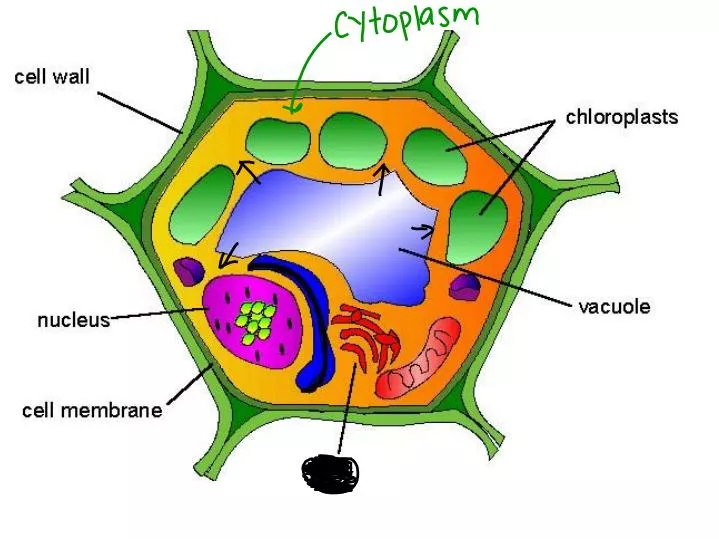
What are the three main parts of the cell?
what are the 3 main parts of a cell
- Parts of a cell
- Basic parts of the Cell
- Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media
- THE PARTS OF A CELL SONG | Science Music Video
What are the major components of a cell?
There are four main types of phospholipids that make up most of the cell membrane in animal cells:
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Phosphatidylethanolamine
- Phosphatidylserine
- Sphingomyelin
What are the four parts of a cell?
What Four Structural Characteristics Do All Living Cells Possess?
- Cell Membrane. The cell membrane is a protective layer that surrounds the cell and protects each of its organelles.
- Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm is the thick fluid that is encased within the cell membrane and holds the cell organelles.
- Ribosomes. Ribosomes consist of a protein complex as well as chains of ribonucleic acid (RNA). ...
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid. ...
What are the parts of cell and its functions?
Plant Cell Parts
- Cell wall. A plant cell has a rigid cell wall, which is the outermost of the cell. ...
- Cell membrane. This is also called a plasma membrane and is present adjacent to the cell wall. ...
- Cytoplasm. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
- Lysosomes. ...
- Peroxisomes. ...
- Chloroplast. ...
- Golgi apparatus. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
- Nucleus. ...

What are the 4 main parts of a cell?
Four Common Parts of a Cell. Although cells are diverse, all cells have certain parts in common. The parts include a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA.
What are the 3 most important parts of a cell and why?
However, all cells have three main parts, the plasma membrane, the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The plasma membrane (often called the cell membrane) is a thin flexible barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the environment outside the cell and regulates what can pass in and out of the cell.
How many major cells are there?
Summary. There are only two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What are the major parts of a cell and what is the function of each?
What's found inside a cellOrganelleFunctionNucleusDNA StorageMitochondrionEnergy productionSmooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)Lipid production; DetoxificationRough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell3 more rows
What are the 3 major parts of the cell?
A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell. The nucleus is a structure inside the cell that contains the nucleolus and most of the cell's DNA.
What are the 3 main parts of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G₁, S, and G₂ phases), followed by the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and G₀ phase.
What are the two major parts of the cell?
Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell has two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. cytoplasm - fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. -Prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm too. Eukaryotic cells contain many organelles - membrane bound structures that perform specialized tasks.
What are the 2 major types of cells?
There are two distinct types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
What are the main types of cells in the human body?
The Four Main Types of CellsEpithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another. ... Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication. ... Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction. ... Connective Tissue Cells.
What is the most important part of a cell?
NucleusNucleus is the most important part of a cell.
What are cells made of?
Cells are composed of water, inorganic ions, and carbon-containing (organic) molecules. Water is the most abundant molecule in cells, accounting for 70% or more of total cell mass.
How many nuclei are there in a cell?
There is normally one nucleus per cell, but this is not always the case, skeletal muscle cells, for instance, have two. The nucleus contains the majority of the cell’s DNA (a small amount is housed in the mitochondria, see below). The nucleus sends out messages to tell the cell to grow, divide, or die.
What is the interior of a cell?
The cytoplasm is the interior of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and is around 80 percent water; it includes the organelles and a jelly-like fluid called the cytosol. Many of the important reactions that take place in the cell occur in the cytoplasm.
What is the role of the cytoskeleton in cell division?
Cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton can be considered the scaffolding of the cell. It helps it maintain the correct shape. However, unlike regular scaffolding, the cytoskeleton is flexible; it plays a role in cell division and cell motility — the ability of some cells to move, such as sperm cells, for instance.
Why do cells need to divide?
Cells need to divide for a number of reasons, including the growth of an organism and to fill gaps left by dead and destroyed cells after an injury, for instance. There are two types of cell division: Mitosis and meiosis.
What are the two types of enzymes that break down large molecules?
Lysosomes and peroxisomes. Both lysosomes and peroxisomes are essentially bags of enzymes. Lysosomes contain enzymes that break down large molecules, including old parts of the cells and foreign material. Peroxisomes contain enzymes that destroy toxic materials, including peroxide.
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
To ensure each cell remains separate from its neighbor, it is enveloped in a special membrane known as the plasma membrane. This membrane is predominantly made of phospholipids, which prevent water-based substances from entering the cell. The plasma membrane contains a range of receptors, which carry out a number of tasks, including being: 1 Gatekeepers: Some receptors allow certain molecules through and stop others. 2 Markers: These receptors act as name badges, informing the immune system that they are part of the organism and not a foreign invader. 3 Communicators: Some receptors help the cell communicate with other cells and the environment. 4 Fasteners: Some receptors help bind the cell to its neighbors.
Why are daughter cells called diploids?
Both daughter cells have the same chromosomes as each other and the parent. They are referred to as diploid because they have two complete copies of the chromosomes.
What are the main parts of a cell?
What Are the Three Main Parts of a Cell? The three main parts of a cell are the plasma membrane, the region containing the DNA and the cytoplasm. However, not all cells have exactly the same basic parts. There is a difference between the structures of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The plasma membrane separates the cell from its environment ...
Where is DNA found in a cell?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. The DNA is simply found in the cytoplasm or the semi-fluid substance within the cell.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
There is a difference between the structures of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The plasma membrane separates the cell from its environment and regulates the substances that flow in and out of the cell. Additional structures, such as the flagella and cilia, may be found on the cell's external surface. All cells have DNA, but the region containing ...
How many types of cells are there in the human body?
This makes sense given that every part of our body is made up of them, but not all cells are the same. In fact, our bodies are made up of over 200 types of specialized cells. Being specialized means that even though they are similar, cells differ in size, shape, or function depending on their role in our bodies. In other words, each type of cell is modified to work in the way our bodies need it.
Which part of the cell provides medium to the cell contents?
Cytoplasm . Nucleus. These are the three major parts of the cell, because Cell membrane enclosed the cell contents by a boundary line to prevent contents from escaping. Cytoplasm is the living part of the cell that provides medium to the cell contents and also provide place for different cellular reactions.
What organelle is responsible for synthesis of proteins?
The smooth ER also helps in the detoxification of harmful substances in the cell. Ribosomes - Organelles that help in the synthesis of proteins.
What is the organelle that makes ribosomes?
Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus. The nucleolus is responsible for making ribosomes. The circles on the surface of the nucleus are the nuclear pores. These are where ribosomes, and other materials move in and out of the cell.
What is the ER in a cell?
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - It is a network of membranes throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. There are two types of ER. When ribosomes are attached it is called rough ER and smooth ER when there are no ribosomes attached. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is where most protein synthesis occurs in the cell.
What is the control center of a cell?
Nucleus - The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It is the largest organelle in the cell and it contains the DNA of the cell. (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) contains all the information for cells to live, perform their functions and reproduce. Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus.
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm - A term for all the contents of a cell other than the nucleus. Even though the cartoon drawings do not look like it, the cytoplasm contains mostly water. Some fun facts about water and the human body: Adult bodies are about 50 to 65 percent water. A child’s body has a little more water at 75 percent.
What are the structures that control cellular activities?
Collectively, these structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells both contain organelles, many of which are found in both types of cells. However, there are some organelles (such as chloroplasts, the cell wall, ...
What is the cell membrane?
The Cell Membrane (AKA The Plasma Membrane) All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane, which consist s of a semipermeable phospholipid bilayer. The cell membrane controls which substances enter and leave the cell, and also separates the interior of the cell from its external environment.
What is the function of lysosomes?
Their key function is to break down and recycle unwanted material for the cell, such as old cell parts or invading bacteria and viruses. Lysosomes also play an important role in apoptosis (AKA programmed cell death).
What is the cell wall of a plant?
The Cell Wall. Plant cells are surrounded by a tough structure called the cell wall, which is found outside of the cell membrane and is mainly made of cellulose. The cell wall supports and protects plant cells, giving them their characteristic rectangular or box-like shape.
What is the cytoplasm?
It is mainly composed of water, but also contains salts, enzymes, and other organic molecules. The cytoplasm surrounds and protects the organelles of the cell and is where many cellular processes (such as protein synthesis and glycolysis) take place.
How many nuclei do skeletal muscle cells have?
Usually, a cell has a single nucleus that contains all of its DNA molecules, but some (such as skeletal muscle cells) have more than one nucleus. The nucleus protects the cell’s DNA while controlling all other cellular activities, such as cell division, growth, protein production, and cell death. The nucleus contains all the DNA of a cell.
What is the energy that is released by the mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the site of respiration and the ‘powerhouses’ of cells, pumping out energy which is then stored in ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP molecules are the energy currency of cells and are used to fuel all ...
What are the three parts of cell theory?
The three parts of the cell theory are as follows: (1) All living things are made up of cells, (2) Cells are the smallest units (or most basic building blocks) of life, and (3) All cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division.
What is the cell theory?
The cell theory states that 1. cells are the unit of structure of all living things 2. cells are the unit of function of living things--they carry out life processes 3. all cells come from pre--existing cells. These three scientists are credited with arriving at the cell theory.
What are the three parts of life?
The three main parts are: 1) All living things are made of cells and their products, 2) New cells are created by old cells dividing into two, and 3) Cells are the basic building units of life. In 1665, Robert Hooke observed, with the aid of a crude compound microsope, the structure of a thin slice of cork. The structure resembled stacks of hat ...
Who first observed cells?
Cells were first observed by the natural philosopher Robert Hooke in 1665. Though many scientists contributed to the understanding of cells, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann are credited with describing the first two parts of the cell theory in 1839, and Rudolf Virchow with later contributing the third.
Who discovered that plants are made of cells?
The cell theory was arrived at after much study of living cells due to the intellectual contributions of Matthias Schleiden who noted all plants contains cells, and in 1838 added that different parts of plants were composed of cells.
Who said all living things contain cells and cell products?
Theodor Schwann noted all living things contained cells and cell products and Rudolph Virchow, who noted that cells come from pre-existing cells. He pusblished his work in 1858 which rejected the idea of spontaneous generation, which was believed at the time.
Who discovered the cell theory?
He probably was looking at Spyrogira, but he called these small organisms "animal-cules". Theodore Schwann and Matthias Schleiden are responsible for formulating the first two parts of the cell theory, ...
