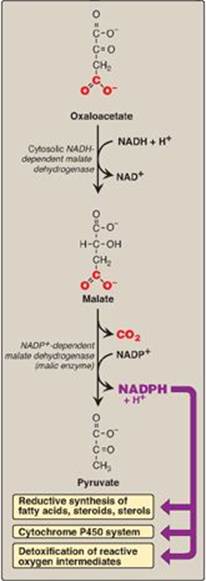
The major source of NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP⁺ or, in older notation, TPN, is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent. It is used by all forms of cellular life.
What is the role of NADPH in fatty acid synthesis?
Fatty acid synthesis utilizes two molecules of NADPH for each molecule of acetate incorporated into long-chain fatty acids. In liver, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (Fig. 1) probably furnish about half of the NADPH used in fatty acid synthesis, with the other half coming from malic enzyme.
Where does NADPH come from in the liver?
In liver, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (Fig. 1) probably furnish about half of the NADPH used in fatty acid synthesis, with the other half coming from malic enzyme.
What is the electron carrier needed for fatty acid synthesis?
What is the Electron carrier needed for fatty acid synthesis? NADPH What are the sources of NADPH for fatty acid synthesis? The pentose phosphate pathway (also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt) & Malic enzyme (which converts malate into pyruvate)
What is fatty acid synthesis?
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol and is carried out by a multienzyme complex called FAS (fatty acid synthase complex). Acetyl CoA is converted to malonyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase.
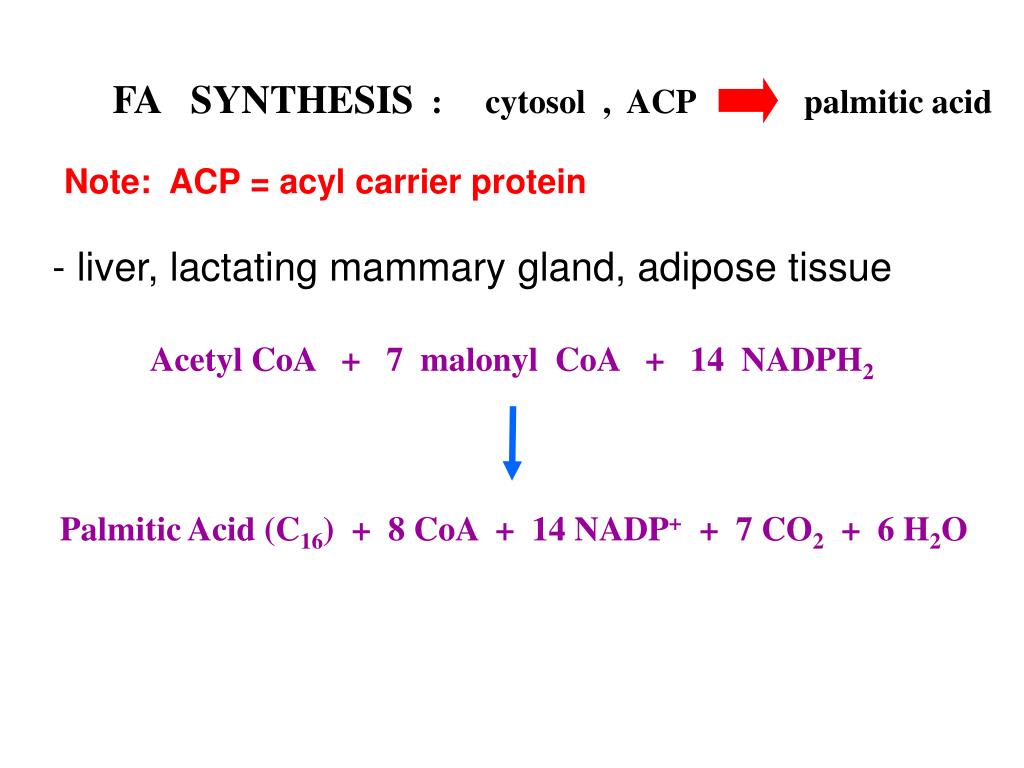
Does fatty acid synthesis generate NADPH?
Figure 4.15: Citrate shuttle reaction moves citrate from the mitochondria to the cytosol for fatty acid synthesis. The NADPH generated through this process is necessary for fatty acid synthesis. This is one of the primary pathways that produces NADPH, and the other is the oxidative portion of the pentose pathway.
What are the main inputs of the fatty acid synthesis?
The input to fatty acid synthesis is acetyl-CoA, a two carbon compound, which is carboxylated to three carbon compound malonyl-CoA. As with other carboxylation reactions, the enzyme prosthetic group is biotin.
Does fatty acid oxidation require NADPH?
We found that an essential function of fatty acid oxidation in cancer cells is to provide the reducing equivalent NADPH to maintain the antioxidant system against oxidative stress and thereby promote cell viability.
Does fatty acid synthesis require NADH?
This pathway utilizes desaturases to synthesize unsaturated fatty acids from full-length saturated fatty acid substrates. All desaturases require oxygen and ultimately consume NADH even though desaturation is an oxidative process.
Where does the NADPH used in the reductive steps of fatty acid biosynthesis originate?
The acetyl-CoA formed in the cytoplasm can then be used in reductive biosynthesis using NADPH as the reductant to form fatty acids, isoprenoids, and sterols. The NADPH for the reduction comes from the oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway and from the reaction catalyzed by malic enzyme.
What is the function of NADPH in fatty acid biosynthesis?
Fatty acid biosynthesis (and most biosynthetic reactions) requires NADPH to supply the reducing equivalents. Oxaloacetate is used to generate NADPH for biosynthesis in a two‐step sequence. The first step is the malate dehydrogenase reaction found in the TCA cycle.
What are the two sources of acetyl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis?
Acetyl-CoA is generated either by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate from glycolysis, which occurs in mitochondrial matrix, by oxidation of long-chain fatty acids, or by oxidative degradation of certain amino acids.
Does beta oxidation use NADPH?
NADPH-dependent beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids with double bonds extending from odd-numbered carbon atoms.
What are the 4 steps of fatty acid synthesis?
The cycle of transfer, elongation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction continues until palmitoyl‐ACP is made. Then the thioesterase activity of the FAS complex releases the 16‐carbon fatty acid palmitate from the FAS.
What are the three systems of fatty acid synthesis?
The systems are: 1. Mitochondrial System 2. Microsomal System for Chain Elongation 3. Extra Mitochondrial System for De NOVO Synthesis.
What stimulates fatty acid synthesis?
Abstract. Insulin stimulates fatty acid synthesis in white and brown fat cells as well as in liver and mammary tissue. Hormones that increase cellular cyclic AMP concentrations inhibit fatty acid synthesis, at least in white adipose tissue and liver.
What is the source of carbon in the biosynthesis of fatty acid?
In the biosynthesis, all of the carbon atoms of a fatty acid are derived from acetyl CoA, that transfers its acetyl group to the thiol group of an a protein-bound acyl carrier protein (ACP).
What does R stand for in chemistry?
R stands for a fatty acid with a varying length. During synthesis, the fatty acid as well as the malonate extension units are coupled to acyl carrier protein (ACP). ACP needs a prosthetic 4′-phosphopantetheine group in order to be functional as a carrier.
What enzyme is responsible for fatty acid biosynthesis?
Fatty acids are normally synthesized from acetyl-CoA, a process that requires ATP, biotin, Mg++, and Mn++. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in fatty acid biosynthesis, is inhibited by glucagon and epinephrine, and stimulated by insulin. Intermediates in fatty acid biosynthesis are attached to acyl carrier protein (ACP).
How are fatty acids derived?
Short-chain fatty acids are derived largely from bacterial fermentation such as that which occurs in the gut or rumen. Medium-chain fatty acids are characteristic of milk fat and are absorbed from the intestine directly into the portal blood, and subsequently metabolized largely by the liver. Fatty acids containing 14 or more carbons are absorbed from the intestine and transported to the periphery as chylomicrons. Very long chain fatty acids are largely found in neural tissue and used for myelin formation. Net fatty acid synthesis by humans is relatively small, but the de novo fatty acid biosynthetic pathway is essential for the production of malonyl-coenzyme A, a metabolite inhibitor of carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Consequently, substrate flux through the de novo lipogenic pathway plays a key role in determining if a fatty acid is partitioned to fatty acid oxidation or triglyceride assimilation.
What is malonyl-coa used for?
Malonyl-CoA serves as an activated donor of acetyl groups in fatty acid biosynthesis. Propionate (C3) may be used in place of acetate (C2) as a priming molecule for fatty acid biosynthesis in adipocytes and in the lactating mammary gland. Fatty acid elongation beyond palmitate takes place in mitochondria, or on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
How are fatty acids produced in bacteria?
This means that the FAS complex consists of a multienzyme complex in which every enzymatic reaction is performed by an individual protein. Fatty acid synthesis proceeds via cycles of four reactions, performed by four enzymes (Figure 4 ). Each cycle results in the elongation of the fatty acid with two carbon atoms. The cycles are repeated until the fatty acid reaches its final length. Each cycle consists of (i) condensation with malonate, (ii) keto-reduction, (iii) dehydration, and (iv) enoate-reduction. Condensation leads to the formation of a carbonyl group at carbon number three. This group is removed during the three subsequent steps of the elongation cycle. Keto-reduction yields a hydroxy group, dehydration leads to a double bond in the trans orientation, and enoate-reduction saturates this bond. In the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, the trans double bond that remains after dehydration is transformed into a cis double bond.
What are the steps of type II fatty acid biosynthesis?
Figure 8. Steps involved in type II fatty acid biosynthesis. The process involves (1) the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA (catalyzed by acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)) and then to malonyl-ACP (I) (catalyzed by FabD), (2) the condensation of malonyl-ACP with another molecule of acetyl-CoA (II) to form β-ketoacyl-ACP (III) (catalyzed by β-ketoacyl-ACP synthase III or FabH), (3) reduction of β-ketoacyl-ACP to β-hydroxyacyl-ACP (IV) by β-oxoacyl-ACP reductase (or FabG) and its dehydration by β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydratases (FabZ/A) to enoyl-ACP (V), and (4) reduction of V by enoyl-ACP reductase (FabI) to form butyryl-ACP (VI), which then reenters the FAS cycle (catalyzed by FabB/F), and gets elongated by two carbon atoms per cycle. Enoyl-ACP can also be a precursor for the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids through catalysis by FabA and FabB.
How many herbicides are used in fatty acid synthesis?
Fatty acid synthesis is a favored target as evident from the 58 herbicides acting in this way, some on acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and others at diverse sites altering very long chain fatty acid synthesis.
What is the name of the enzyme that converts acetyl to malonyl?
Acetyl CoA carboxylase : Transforms acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA with the use of biotin and bicarbonate as cofactors. Requires one ATP.
How is malonyl CoA transferred to FAS?
Malonyl CoA is transferred to FAS. Through a series of condensation, reduction, and dehydration reactions , the two carbons of malonyl CoA are added to the growing fatty acyl moiety on FAS. FAS are then recharged with another malonyl moiety, and the cycle continues.
How are fatty acids synthesized?
Fatty Acid Synthesis Pathway 1 Acetyl CoA is converted to malonyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase. 2 Malonyl CoA is transferred to FAS. 3 Through a series of condensation, reduction, and dehydration reactions, the two carbons of malonyl CoA are added to the growing fatty acyl moiety on FAS. 4 FAS are then recharged with another malonyl moiety, and the cycle continues. 5 Each turn of the cycle results in the addition of a two-carbon group to the fatty acid moiety as well as the use of one ATP, one acetyl CoA, and two NADPH. 6 When the cycle has completed seven turns, the 16-carbon fatty acid (palmitate) is released from FAS.
How many carbon groups are added to a fatty acid?
Each turn of the cycle results in the addition of a two-carbon group to the fatty acid moiety as well as the use of one ATP, one acetyl CoA, and two NADPH.
What is the process of synthesis of fatty acids?
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases.
Why are fatty acids important?
In addition to being the major component of membranes, fatty acids are important energy storage molecules , and fatty acyl derivatives possess a variety of physiological functions, including post-translational modification of numerous proteins.
Where does lipogenesis occur?
Lipogenesis, the synthesis of fatty acids and their esterification to glycerol to form triacylglycerols, which occurs mainly in the liver in humans , with dietary carbohydrate as the major source of carbon.